Monocline
A monocline (or, rarely, a monoform) is a step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a zone of steeper dip within an otherwise horizontal or gently-dipping sequence.
Formation

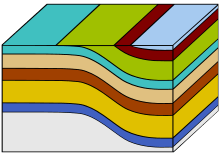
Possible modes of formation of monoclines
Monoclines may be formed in several different ways (see diagram)
- By differential compaction over an underlying structure, particularly a large fault at the edge of a basin due to the greater compactibility of the basin fill, the amplitude of the fold will die out gradually upwards.[1]
- By mild reactivation of an earlier extensional fault during a phase of inversion causing folding in the overlying sequence.[2]
- As a form of fault propagation fold during upward propagation of an extensional fault in basement into an overlying cover sequence.[3]
- As a form of fault propagation fold during upward propagation of a reverse fault in basement into an overlying cover sequence.[4]
Examples
- Waterpocket Fold in Capitol Reef National Park, Utah
- Grandview-Phantom Monocline in Grand Canyon, Arizona
- Lapstone monocline in the Blue Mountains (Australia)
- Purbeck Monocline on the Isle of Purbeck, Dorset, England
See also
References
- ↑ Skuce, A.G. (1996). "Forward modelling of compaction above normal faults: an example from the Sirte Basin, Libya". In Buchanan,P.G. and Nieuwland,D.A. Modern Developments in Structural Interpretation, Validation and Modelling (PDF). Special Publications. 99. London: Geological Society. pp. 135–146. ISBN 978-1-897799-43-7.
- ↑ Chadwick, R.A. (1993). "Aspects of basin inversion in southern Britain". Journal of the Geological Society. 150: 311–322. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.150.2.0311.
- ↑ Willsey, S.P.; Umhoefer,P.J. and Hilley,G.E. (2002). "Early evolution of an extensional monocline by a propagating normal fault: 3D analysis from combined field study and numerical modeling" (PDF). Journal of Structural Geology. 24: 651–669. Bibcode:2002JSG....24..651W. doi:10.1016/S0191-8141(01)00120-1. Cite uses deprecated parameter
|coauthors=(help) - ↑ Finch, E.; Hardy,S. and Gawthorpe,R. (2003). "Discrete element modelling of contractional fault-propagation folding above rigid basement fault blocks". Journal of Structural Geology. 25: 515–528. Bibcode:2003JSG....25..515F. doi:10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00053-6. Cite uses deprecated parameter
|coauthors=(help)
External links
http://bio-geo-terms.blogspot.com/2006_12_01_bio-geo-terms_archive.html
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/17/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.