Military history of Romania
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Romania |
 |
|
Post-Revolution |
|
|

The military history of Romania deals with conflicts spreading over a period of about 2500 years across the territory of modern Romania, the Balkan Peninsula and Eastern Europe and the role of the Romanian military in conflicts and peacekeeping worldwide.
During antiquity, the territory of modern Romania was the scene of sporadic wars between the native Dacian tribes and various invaders (Persians, Macedonians, Celts or Romans). Ultimately, the Kingdom of Dacia was conquered by the Roman Empire in 106 and large parts of its territory became a Roman province. As the Roman Empire declined, Dacia was abandoned because of pressure from the Free Dacians and Goths.
For 1000 years, numerous migrating peoples including the Goths, Huns, Gepids, Avars, Slavs, Bulgars, Magyars, Cumans and Mongols overran the territory of modern Romania. In the 13th century, a number of small Romanian states emerged and evolved into the medieval principalities of Moldavia, Wallachia and Transylvania.
During the Late Middle Ages, all three provinces had to deal with the danger posed by the growing power of the Ottoman Turks. John Hunyadi, Voivode of Transylvania and regent of Hungary managed to halt the Turkish advance into Central Europe and secured a major victory at the Battle of Belgrade in 1456. Stephen the Great of Moldavia, Mircea the Elder and Vlad the Impaler of Wallachia also successfully fought off the Turks and distracted them from the strategically more important objectives in the Mediterranean and the Balkans. However, by the middle of the 16th century, the three principalities had become Ottoman vassals. Michael the Brave of Wallachia managed to unite his realm with Transylvania and Moldavia and gain independence for a short time in 1600.[1]
The early modern period was characterised by continuous warfare between the Habsburg Empire, Ottoman Empire, Poland (until the 18th century) and Russia for the control of the Danubian principalities and Transylvania. The defeat of the Ottomans at the Battle of Vienna in 1683 marked the beginning of their decline in the region.
The 19th century saw the formation of the modern Romanian state through the unification of Moldavia and Wallachia. Independence from the Ottoman Empire was secured after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878 and Romania became a kingdom in 1881. The participation on the Allied (Entente) side during World War I triggered the unification of the remaining Romanian inhabited territories with the kingdom, thus forming Greater Romania.
Romania reached its zenith during the inter-war period. After World War II, it was reduced to its modern borders and fell in the Soviet sphere of influence. The revolution of 1989 ended Communism and the geopolitical mutations in the region after the collapse of the Soviet Union paved the way for European integration, economically, politically, and militarily. Today, the Romanian army participates in peacekeeping missions with its NATO allies in Afghanistan, Bosnia, Kosovo and elsewhere.
Themes in Romanian military history
The national unity objective
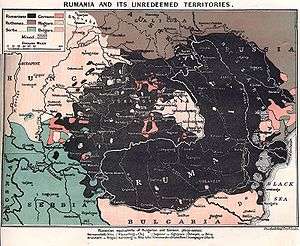
The primary objective of the Romanian leadership in the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century was to join all the territories inhabited by Romanians in a single state and to maintain its unity. The Romanian strategic thinking was driven by this need especially during the two World Wars. Today, Romania and the Republic of Moldova are comprising most of the regions where Romanians formed the majority of the population before World War II.
Important military rivalries resulted from the clash of Romania's national interests with the interests of neighbouring countries in the past.
- Romanian-Hungarian rivalry for the control of Transylvania. It started at the end of World War I when Transylavania was awarded to Romania through the Treaty of Trianon. Transylvania had an absolute Romanian majority in 1918, but had been for extensive periods of time under Hungarian rule. In 1940, Northern Transylvania was given to Hungary at the Second Vienna Award only to be ceded back to Romania in 1945. After 1989, relations between the two countries flourished, especially after both Romania and Hungary entered NATO and the European Union. Hungary renounced all territorial claims to Transylvania in a 1995 bilateral treaty.
- Romanian-Bulgarian rivalry was triggered by the Romanian annexation of Southern Dobruja (Cadrilater). Southern Dobruja was populated mainly by ethnic Bulgarians and Turks and was taken by Romania after the Romanian invasion of Bulgaria during the Second Balkan War. In World War I, Bulgaria regained Southern Dobruja and gained a part of Northern Dobruja at the Treaty of Bucharest (and eventually the whole of Northern Dobruja after a secret protocol with the other Central Powers in September 1918), but it was forced to give the territory back to Romania in 1919 through the Treaty of Neuilly. With the advent of World War II, Bulgaria regained the region in the September 1940 Axis-sponsored Treaty of Craiova. Since then relations between both countries normalised.
- Romanian-Russian (Soviet) rivalry erupted because of the Russian occupation of Eastern Moldavia (Bessarabia), a territory which had been part of the Principality of Moldavia, and, according to the Romanian view, had a Romanian majority. In the chaos that ensued after the October Revolution, Bessarabia seceded from Russia and joined Romania. The Soviets never accepted the loss and a small border war took place along the Dniestr River in 1920. In 1924, they sponsored the Tatarbunary Uprising in Southern Bessarabia. In 1940, Romania was pressured into evacuating Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina, which were consequently occupied by Soviet troops. While Romania already had an authoritarian government closely aligned with Nazi Germany, the event prompted the country to openly join the Axis powers and contribute extensively with troops and material to Operation Barbarossa and the subsequent fighting against the USSR. The Paris Peace Treaty of 1947 reaffirmed the 1940 Soviet annexations. Today, most of Bessarabia with some portions of Transnistria form the Republic of Moldova, successor to the Moldavian SSR, while Northern Bukovina and parts of Bessarabia (the Budjak and Hotin regions) are in Ukraine.
The regional balance of power
In the modern period, Romania has sought to neutralise the growing power of its neighbours in order to prevent any of them from overshadowing its influence. During the Second Balkan War, Romania allied itself with Serbia, Greece and Turkey in order to check Bulgaria, which the allies saw as too powerful after the complete victory over Turkey in the First Balkan War. In 1919, the Hungarian Soviet Republic allied with Soviet Russia posed a major threat to the conservative regimes in the region. Romania started an offensive that ended with the conquest of Budapest and the overthrow of the Communist government. In the inter-war period, the Little Entente was envisioned as an alliance between Romania, Czechoslovakia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes to counter Bulgarian and Hungarian irredentism.
Dacians and Romans
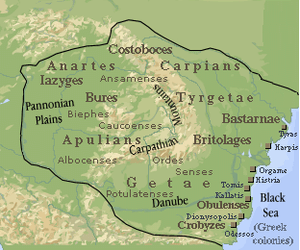
The Dacians (Lat. Daci, Gr. Dákai), and the probably closely related tribes of the Getae, were part of the greater Thracian family of peoples. Ancient authors describe the two tribes as inhabiting the territories of present-day Romania, eastern Hungary, south-western Ukraine and northern Bulgaria.
In (335 BC), Alexander the Great engaged the Thracians in order to secure the northern boundary of the Macedonian kingdom. He crossed the Danube and made a short incursion on the Getae living north of the river.
Lysimachus, one of the successors of Alexander, who ruled over Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedonia tried to conquer territories north of the Danube, but was defeated and taken prisoner by the Getae king Dromichaetes. However, Dromichaetes set him free on amicable terms.
Burebista, one of the greatest kings of Dacia ruled between 82 BC and 44 BC and unified the Thracian population from Hercynia (today's Moravia) in the west, to the Southern Bug River in the east, and from the northern Carpathians to Dionysopolis. Burebista sided with the inhabitants of the Greek cities on the Western coast of the Black Sea when they were occupied by Varro Lucullus, the proconsul of the province of Macedonia during the Second Mithridatic War (74 BC–72 BC). The Getae defeated the Roman army of Gaius Antonius Hybrida near Histria and continued their incursions in the region, taking the Celtic settlement of Aliobrix (Cartal, Ukraine), Tyras and Odessos and destroying Olbia. In 48 BC, the Dacian king sided with Pompey during his struggle against Julius Caesar in the Roman civil war but failed to supply him with troops in time for the Battle of Pharsalus.
Dacian Wars
- See also: Domitian's Dacian War and Trajan's Dacian Wars
Faced with the growing military presence of the Roman Empire in the region, Decebalus (reigned 87-106), son of king Duras, reorganized the army and in 85 AD the Dacians began minor raiding in the heavily fortified Roman province of Moesia, located south of the Danube. In 86, a more vigorous attack south into Moesia, prompted emperor Domitian to intervene with fresh legions and supplies. Domitian planned an attack into Dacia the next year to stop Dacian marauding.
A strong offensive was carried in 87 when five or six legions commanded by general Cornelius Fuscus crossed the Danube and continued northwards to the Dacian capital of Sarmizegetusa. They encountered the Dacian army at Tapae, where the Romans were ambushed, suffering a major defeat. Almost all of the soldiers from Legio V Alaudae were killed and the Dacians captured their flags and war machines. Cornelius Fuscus himself was killed in battle. After this victory, Decebalus replaced Duras as king of Dacia.
The Roman offensive continued the following year, with general Tettius Iulianus now in command. The Roman army entered Dacia following the same route as Cornelius Fuscus the previous year. The battle took place mainly in the same area, at Tapae, this time the outcome being a Roman victory. Because of the difficult road to Sarmizegetusa and the defeats suffered by Domitian in Pannonia, the Roman offensive was halted and Decebalus sued for peace.

According to the peace of 89, Decebalus became a client king of Rome receiving money, craftsmen and war machines from the Roman Empire, to defend the empire's borders. Instead of using the money as Rome intended, Decebalus decided to build new citadels in the mountains and to reinforce the already existing ones. This was the main reason for the following Roman attack under emperor Trajan.

In 101 Trajan (reigned 98-117), after gaining the approval of the Roman Senate, began advancing on Dacia. A stone bridge later known as Trajan's bridge was constructed over the Danube to assist the legionaries' advance. The Roman offensive was spearheaded by two legionary columns, marching right to the heart of Dacia, burning towns and villages in the process. In the winter of 101-102, the Dacians led massive assaults on the legions stantioned in Moesia, but were defeated by Trajan in the Battle of Adamclisi. In 102 the Roman armies converged for a final assault and defeated the Dacian army at the third Battle of Tapae. After the battle, Decebalus chose to surrender. The war concluded with a Roman victory but the Dacians planned to organize further resistance.
Trajan invaded again in 105, this time with the intention of transforming Dacia into a Roman province. After several skirmishes, an assault against the capital Sarmisegetusa took place in 106 with the participation of the legions II Adiutrix, IV Flavia Felix and a cavalry detachment (vexillatio) from Legio VI Ferrata. The Romans destroyed the water pipes to the capital and the city fell. Decebalus fled, but committed suicide rather than face capture. Nevertheless, the war went on and the last battle with the Dacian army took place at Porolissum.
At the end of the war the Romans organized the province of Dacia on large parts of the former Dacian kingdom. The Roman rule would last from 106 until 271 (or 275 according to some sources).
Roman Dacia
- See also: Roman Dacia and Daco-Roman
.svg.png)
The province of Dacia was administered by a Roman governor of praetorian rank. Legio XIII Gemina (stationed at Apulum, modern Alba Iulia), Legio V Macedonica (stationed at Potaissa, modern Turda) and numerous auxiliaries had their fixed quarters in the province. For protection against the attacks of the "free Dacians" (Dacians that lived outside Roman rule), Carpians and other neighbouring tribes, the Romans built forts and delimited the Roman held territory with a limes. Three great military roads were constructed, linking the chief towns of the province.

Dacians were recruited into the Roman Army, and were employed in the construction and guarding of Hadrian's Wall in Britannia, or elsewhere in the Roman Empire. Several Cohors Primae Dacorum ("First cohort of Dacians") and Alae Dacorum fighting in the ranks of legions were stationed in Britannia at Deva (Chester), Vindolanda (on the Stanegate) and Banna (Birdoswald).
In the third century, the attacks on Roman Dacia conducted by the Free Dacians and Goths intensified. Emperor Aurelian (270-275), confronted with the secession of Gaul and Hispania from the empire, the advance of the Sassanids in Asia and the devastations that the Carpians and the Goths had done to Moesia and Illyria, abandoned the province and withdrew the troops and administration, fixing the Roman frontier on the Danube. A new Dacia Aureliana was reorganised south of the Danube, with its capital at Serdica (modern Sofia). At the beginning of the next century, Romans had tried to retake control of the north of the Danube: in Constantine the Great's campaign from 332, 100000 Goths were killed in battles on north of the Danube.[2][3][4] For a very short time, near 328, there were plans regain administration of the north of the Danube, a stone bridge was erected between Sucidava and Oescus. Still after 334AD Constantine the Great campaign, 300.000 Sarmatians were evacuated from the north of the Danube, and the Roman limes were once again reestablished on Danube[3][5][6][7]
Early Middle ages
During the Early Middle Ages, the Northern Balkan Peninsula became a conduit for invading tribes who targeted richer lands further west and south. Information about the military operations conducted in this period is very scarce.
The territory of modern Romania was part of the Hun Empire, but after its disintegration different parts were under successive control of the Gepids, Avars, Slavs, Bulgars and Pechenegs. Most of these invaders did not permanently occupy the territory, as their organization was of typical nomadic confederacies. From them, only the Slavs settled in large numbers beginning with the 7th century.
The Byzantine Empire held the region between the Danube and the Black Sea (modern Dobruja) from time to time (such as during Justinian's reign in the 6th century) or again under some emperors of the Macedonian and Komnenian dynasties, being part of the Byzantine Paristrion thema (province) between in the period 971-976 and between 1001 and 1185, although it was a border that was hard to maintain due to the constant invasions from the north. Dobrudja was part of the Bulgarian Empire during its whole period of existence. The area around the Danube Delta was the site of battle of Ongal in 680 which led to the formation of Bulgaria in 681.[8] Since the formation of the country the Bulgarians controlled the Wallachian Plain and Bessarabia to the north of the Danube, bordering the Avars to the north-west.[9] The Bulgarians under Khan Krum destroyed the crumbling Avar Khanate in 803 and moved the border along the river Tisza,[10] thus including Transylvania and parts of Pannonia in the Bulgarian state. In a military conflict with the Franks between 827-829 the Bulgarians secured their border with the Frankish Empire.
At the end of the 10th century, Dobruja was the theatre of operations between the Kievan Rus army led by Prince Sviatoslav I, the Bulgarian army and the Byzantine army led by emperor John Tzimiskes. Sviatoslav controlled large parts of the First Bulgarian Empire and established his capital at Pereyaslavets (near modern Nufăru) on the Danube. The Byzantines, led by John Tzimiskes were on the offensive after they defeated the united Russo-Bulgarian forces in the Battle of Arcadiopolis. Pereyaslavets was captured and Sviatoslav was forced to flee westwards to the fortress of Dorostolon (Durostorum). Emperor John proceeded to lay siege to Dorostolon, which resisted for sixty five days until Sviatoslav agreed to sign a peace treaty with the Byzantine Empire, whereby he renounced his claims on Bulgaria and the city of Chersonesos in Crimea. Sviatoslav was allowed to evacuate his army to Kiev.
The Magyars settled the Pannonian Plain and subdued Transylvania from Bulgaria in the 10th and 11th centuries, while the Cumans occupied the Lower Danube region in the 11th century.
High and Late Middle Ages
Transylvania and the Mongol Invasion of 1241
From the 11th century until 1541 Transylvania was an autonomous part of Hungary and was ruled by a Voivode. As it formed the eastern border of Hungary, great emphasis was put on its defenses. By the 12th century the Székelys were established in eastern Transylvania as border guards, while the Saxons were colonised to guard the southern and northeastern frontier. Early in the 13th century, king Andrew II of Hungary called on the Teutonic Knights to protect the Burzenland from the Cumans. After the Order began expanding their territory outside Transylvania and acted independently, Andrew expelled it in 1225.
In 1241 Transylvania suffered greatly during the Mongol invasion of Europe. The overall invasion was planned and carried out by Subutai, under the nominal command of Batu Khan. The attack on Transylvania was commanded by Güyük Khan, the future great khan of the Mongols.
Güyük invaded Transylvania in three columns through the Tihuţa and Oituz Passes and the Timiş-Cerna Gap, while Subutai attacked through the fortified Verecke Pass towards central Hungary. Güyük sacked Sibiu, Cisnadie, Alba Iulia, Bistriţa, Cluj-Napoca, Oradea as well as the Hungarian king's silver mine at Rodna. This prevented the Transylvanian nobility from aiding King Béla IV in the crucial Battle of Mohi. A separate Mongol force destroyed the Cumans near the Siret River and annihilated the Cuman Catholic Bishopric of Milcov. Estimates of population decline in Transylvania owing to the Mongol invasion range from 15-20% to 50%.
Wallachia and Moldavia

The lands east and south of the Carpathians fell under Mongol occupation after 1241, until the Principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia emerged in the 14th century as Hungarian vassals.
In 1330 Basarab I, the voivode of Wallachia, managed to ambush and defeat a 30,000-strong Hungarian army led by King Charles I Robert in the Battle of Posada, eliminating Hungarian interference in Wallachia.
In the same period, Moldavia freed itself from Hungarian control, although the Hungarians made some attempts to regain the principality. During the later 14th century and the first half of the 15th century, Moldavia was under Polish suzerainty and the Moldavians supplied Poland with troops during the campaigns against the Teutonic Order in Prussia. Moldavian light cavalry detachments participated in the Battle of Grunwald and the Siege of Marienburg on the Polish-Lithuanian side.
Anti-Ottoman Wars
The Ottoman Empire became a major military power in the later 14th century, when they conquered Anatolia, most of the Balkans and were threatening Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire.
Conflict firstly erupted between the Ottomans led by Beyazid I and the Wallachians led by Mircea the Elder after the voivode openly supported the Christian peoples south of the Danube who were fighting the Turks. There was also a contest for the control of Dobruja, which had been independent for most of the 14th century, but fell under Ottoman rule in 1388. In 1389 Mircea took control of the province and held it with some interruptions until 1418.
In 1394 Beyazid I crossed the Danube, leading a strong army with the purpose of overthrowing Mircea and replacing him with an Ottoman vassal. The Wallachians adopted scorched earth and guerrilla tactics by starving the Ottomans and mounting small scale attacks. The two armies finally clashed in the indecisive Battle of Rovine. Beyazid failed to put Vlad the Usurper on the Wallachian throne and in 1396 Mircea was again commanding his army during the Battle of Nicopolis. At Nicopolis, the Wallachian force of 10.000 men formed the left wing of the crusader army and, having witnessed the disastrous attacks made by the western knights and the surrender of Sigismund, escaped the massacre that followed.
The defeat and capture of sultan Beyazid I by Timur Lenk (Tamerlane) in the Battle of Ankara in 1402 started a period of anarchy in the Ottoman Empire and Mircea took part in the struggles for the Ottoman throne supporting various pretenders. Towards the end of his reign, Mircea signed a treaty with the Ottomans whereby he accepted paying tribute and gave up his claims on Dobruja.

Wallachia fell into anarchy following Mircea’s death in 1418. After 1420 control of the principality changed hands until Alexander I Aldea, an Ottoman vassal was instaled. King Sigismund of Hungary arranged for Aldea’s overthrow and replacement with his own vassal, Vlad II Dracul.
A series of anti-Ottoman offensives were carried by the voivode of Transylvania John Hunyadi, a hungarian Nobleman. Hunyadi’s forces soundly defeated the Turks in 1441 and 1442. A smaller crusading force commanded by Hunyadi, consisting of Hungarians, Wallachians under Vlad Dracul, Serbs, and a large contingent of German and French knights crossed the Danube into Serbia, defeated two Ottoman armies, captured Niš, crossed the Balkan Mountains in winter, and advanced as far as Sofia. The Turkish sultan Murad II, faced with revolts in Albania and the Peloponnese, negotiated with the crusaders, signing a ten-year truce at Edirne in 1444 that recognized Serbian independence and formally released Wallachia from Ottoman vassalage.

In 1444 Pope Eugenius urged the crusade’s renewal, and Hunyadi marched eastward along the southern bank of the Danube, through northern Bulgaria, toward the Black Sea. The crusaders arrived at Varna in November 1444 only to discover that Murad II had assembled a powerful army to meet them. In the ensuing Battle of Varna, king Wladislaw of Poland and Hungary was killed and the crusader army was completely destroyed. Hunyadi escaped with a small portion of his troops and became governour of Hungary.
In 1447 the Turks campaigned in Albania against Skanderbeg’s rebels, but operations were cut short by news of a new crusader invasion led by Hunyadi. The crusaders, joined by troops sent by Skanderbeg and Voivode Vladislav II (1447–56), Hunyadi’s Wallachian vassal met the Ottoman army in October 1448 at Kosovo Polje but were defeated.
Hunyadi’s greatest victory was at the Battle of Belgrade where, in 1456, his much smaller army defeated Sultan Mehmet II, the conquereor of Constantinople, and secured Hungary’s southern border. However, Hunyadi died of plague in his camp shortly after the battle. His son, Matthias Corvinus would become king of Hungary in 1458.

Wallachia, led by Vlad III the Impaler (1456–1462, born in Sighişoara, three-time voivode) stopped paying tribute to the Ottomans in 1459 and in the winter of 1461 to 1462 Vlad crossed the Danube and devastated Northern Bulgaria and Dobruja, leaving over 20,000 dead. In response, Sultan Mehmed II raised an army of around 60,000 troops and 30,000 irregulars and headed towards Wallachia in the spring of 1462. With his army of 20,000–30,000 men Vlad was unable to stop the Turks from entering Wallachia and occupying the capital Târgovişte (June 4, 1462), so he resorted to organizing small attacks and ambushes on the Turks. The most important of these attacks took place on the night of June 16–17, when Vlad and some of his men allegedly entered the main Turkish camp (wearing Ottoman disguises) and attempted to assassinate Mehmed. The Turks eventually installed Vlad’s brother, Radu the Handsome, as the new voivode; he gathered support from the nobility and chased Vlad to Transylvania, and by August 1462 he had struck a deal with the Hungarian Crown.
Moldavia located in the extreme northeast, beyond Wallachia, was spared from problems with the Ottomans until 1420, when Mehmed I first raided Moldavia after suppressing a rebellion. During the 1450s and 1440s the principality was wracked by civil wars, of which Sultan Murad II took advantage. As the state weakened, voivode Peter Aron (1455–57) accepted Ottoman suzerainty and agreed to pay tribute, but, given Moldavia’s distance from Ottoman borders, his acts were merely symbolic.
Stephen the Great initially used the Ottoman vassalage inherited from his father as a tool against Hungary, Moldavia’s traditional enemy. He participated in Mehmed II’s invasion of Wallachia against his cousin Vlad the Impaler in 1462 because, at the time, Vlad was a Hungarian ally. An exceptional military commander and organizer, Stephen captured the Danube commercial city of Chilia from Wallachia in 1465 and defeated a Hungarian invasion of his state in 1467 at the Battle of Baia. As his successes both on the battlefield and in imposing his authority within Moldavia grew, Stephen ceased paying the annual tribute to the Ottomans, and his relationship with Mehmed II deteriorated. He invaded Wallachia in 1474 and ousted its prince, who was Mehmed’s vassal. In response, Mehmed demanded that Stefan resume his tribute payments and turn over the city of Chilia as well. Stefan refused and soundly repulsed Mehmed’s subsequent punitive invasion of Moldavia in early 1475 near Vaslui.
Stephen realized that Mehmed would seek to avenge the defeat, so he sought Hungarian aid by becoming the vassal of Matthias Corvinus. Mehmed personally led an invasion of Moldavia in 1476, and his forces plundered the country up to Suceava, Stephen’s capital, winning the Battle of Valea Alba on the way. However, all of Stephen's fortresses held fast, and a lack of provisions and an outbreak of cholera among the Ottoman troops forced Mehmed to retire, and Stefan went on the counteroffensive. With Hungarian help, he pushed forth into Wallachia in 1476, reinstalled Vlad the Impaler on the Wallachian throne, and spent the next nine years fighting a heroic border war with the Ottomans. Stefan’s efforts were the primary reason that the two Romanian Principalities maintained their independence and did not suffer the fate of the other Ottoman vassal states south of the Danube. During the last years of his rule, Stephen defeated a Polish invasion at Codrii Cosminului in 1497 and, by the time of his death, Moldavia was de facto independent.
Kingdom of Romania
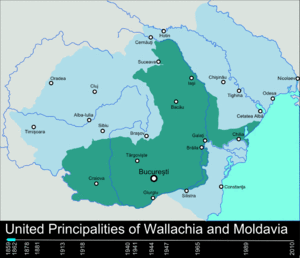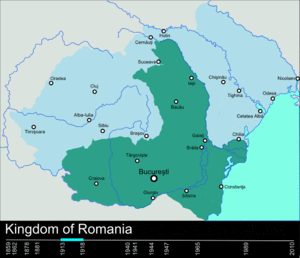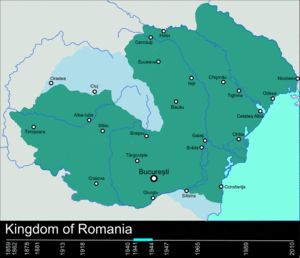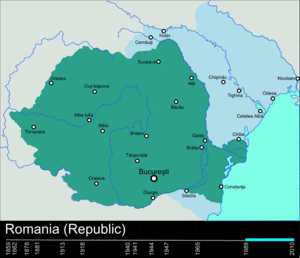
World War I and inter-war period
World War II
See also
References
Footnotes
- ↑ Stoica, Vasile (1919). The Roumanian Question: The Roumanians and their Lands. Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh Printing Company. p. 18.
- ↑ Origo Constantini 6.32 mentions the actions
- 1 2 Eusebius Vita Constantini IV.6
- ↑ Charles Manson Odahl Constantine and the Christiane Empire chapter X
- ↑ Barnes Victories of Constantine page 150-154
- ↑ Grant Constantine the Great pages 61-68
- ↑ Charles Manson Odahl Constantine and the Christian Empire Chapter X
- ↑ Runciman, S. A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. Book I, pp. 26-27
- ↑ Runciman, S. A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. Book I, pp. 27-28
- ↑ Runciman, S. A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. Book II, pp. 50-51
Sources
- UNRV History - Dacia
- Ancient Worlds
- Country Studies - Romania
- Breviarium historiae Romanae by Eutropius
External links
| Wikisource has original works written by or about: Military history of Romania |
- Dromichaites, philological and linguistical aspects (Romanian) at Sorin Olteanu's LTDM Project (soltdm.com)