Rio de Janeiro Metro
|
| |||
|
| |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Native name | MetrôRio | ||
| Owner | Rio Trilhos (State of Rio de Janeiro) | ||
| Locale | Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 3 (Lines 1, 2 & 4)[1][2][3] | ||
| Number of stations | 41[1][3] | ||
| Daily ridership | 625 205 (2014)[4] | ||
| Annual ridership | 228.2 million (2014)[4] | ||
| Website | Metrô Rio | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | March 5, 1979[5] | ||
| Operator(s) | Concessão Metroviária do Rio de Janeiro S.A. (Invepar) | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 58 km (36 mi)[1][3] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in) | ||
| |||
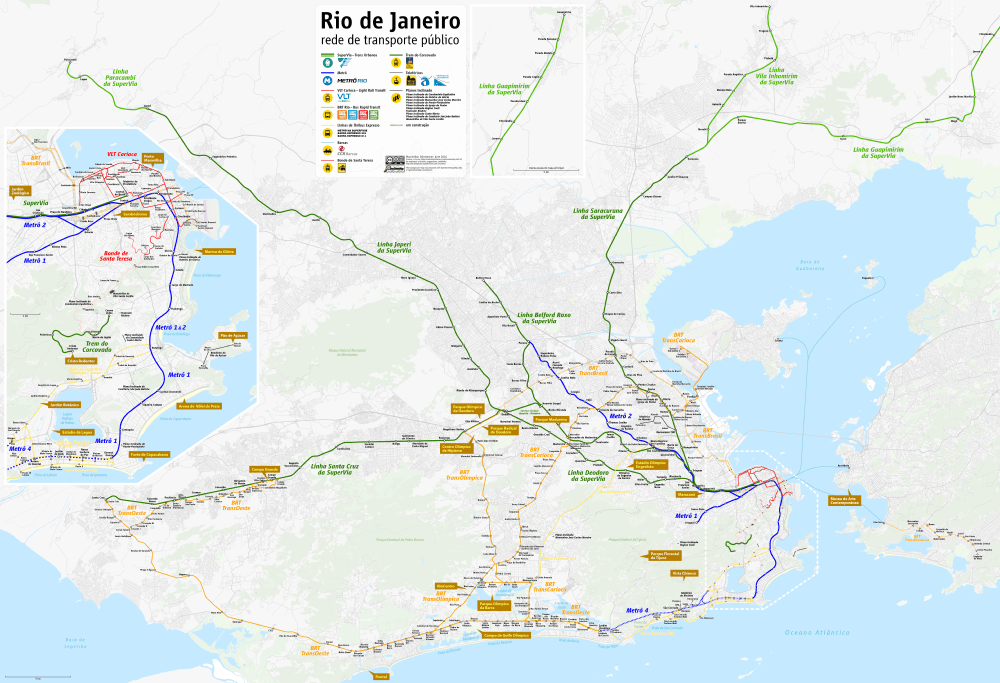
The Rio de Janeiro Metro (Portuguese: MetrôRio IPA: [meˌtɾo ˈʁi.u], commonly referred to as just the Metrô [Meˈtɾo]) in Rio, is a mass-transit underground railway network that serves the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The Metrô was inaugurated on March 5, 1979, with five stations operating on one line.[5] The system now covers a total of 58 kilometres (36 mi),[3] serving 41 stations,[1][3] divided into three lines: Line 1 (16 kilometres (9.9 mi)),[2] Line 2 (30.2 kilometres (18.8 mi)),[2] which together travel over a shared stretch of line that covers 10 stations[6] and an approximate distance of 5 kilometers, and Line 4 (16 kilometres (9.9 mi)).[3]
Line 1 (orange line) serves downtown Rio, tourist areas in the South Zone, and several neighbourhoods in the North Zone. It is a semicircular line, and is fully underground. It runs from Uruguai Station to Ipanema/General Osório Station. Line 2 (green line) serves working-class residential neighborhoods extending toward the north. It is a northwest-to-southeast line, and almost completely above-ground (mostly at grade and partly elevated). This line started as a light rail, but due to increasing numbers of commuters, it gradually changed to rapid transit or metro. Because of its origin as light rail, it is at grade except for Estácio Station (the former connection station between lines 1 and 2), which is underground and Cidade Nova Station, which is elevated, and Line 4 (yellow line), connecting Barra da Tijuca/Jardim Oceânico Station in the West Zone to Ipanema/General Osório Station on Line 1. Metrô Rio has the second highest passenger volume of the metro systems in Brazil, after the São Paulo Metro.
The Government of the State of Rio de Janeiro remains responsible for the expansion of the metro network, through Rio Trilhos. In late December 2007, the lease was renewed until 2038[7] and Metrô Rio assumed responsibility for the construction of Cidade Nova Station , which serves as a link between Line 2 and Line 1 ending the need to transfer stations, with the purchase of 114 cars, and construction of Uruguai Station, extending Line 1 further north.
The extension works of Line 2, called Line 1A, which ended the need for a transfer at Estácio Station and allowed the direct connection from Pavuna Station to Botafogo were started by Metrô Rio on November 13, 2008 and the tracks were completed in December 2009. With the extension, the 250 thousand passengers that circulate daily on Line 2 do not need to change trains any more in order to get to the South Zone. The interconnection of the two metro lines will reduce, by up to 13 minutes, the journey time from Pavuna station to the city's downtown, the destination of 83% of Line 2's passengers.[8]
History

Rio de Janeiro is the second largest city in Brazil and the most popular tourist attraction in the country. After 1950, the number of motor vehicles on the roads increased dramatically. Rio de Janeiro lies in a hilly region, between the mountains and the Atlantic Ocean. The landscape of the city is extremely uneven, making travelling by car or bus a very time-consuming task through the narrow streets, which were ideal for trams but not for the increasing traffic of motor vehicles. By the early 1960s, traffic jams, pollution, and smog had become a serious problem in the city. To overcome these problems, local transport authorities decided to greatly reduce the tram network and switch over to a metro network.
On December 14, 1968, the Companhia do Metropolitano do Rio de Janeiro (Metro Company of Rio de Janeiro in English) was created by State Law number 1736.[9] In March 1975, with Law–Decree number 25, the company effectively came into existence. On June 23, 1970, construction work started in Jardim da Glória. From 1971 to 1974, owing to a lack of resources, construction work stopped and was only resumed a year later. The Rio de Janeiro Metro began operating in March 1979, during the administration of governor Chagas Freitas. In the beginning, there were only five stations: Praça Onze, Central, Presidente Vargas, Cinelândia Station, and Glória Station, operating from 9:00 AM to 3:00 PM.
In the first 10 days, the system transported more than half a million people, averaging sixty thousand passengers per day. At that time, the subway worked with only four trains of four cars each, with an average interval of eight minutes. In December of the same year, the operating schedule was extended until 11:00 PM, including Saturdays. In 1980, the metro system began to be expanded with the opening of Uruguaiana Station and Estácio stations. The two new stations caused larger passenger demand, compelling an increase in the number of trains from four to six.
The Carioca station in Downtown Rio de Janeiro, the busiest station with more than eighty thousand passengers a day, was finished in January 1981. By the end of the same year, the stations Catete Station, Morro Azul (now called Flamengo Station), and Botafogo Station were completed. In November 1981, Line 2 (or Linha 2 in Portuguese) started operating with only two stations: São Cristóvão and Maracanã Station (which serves the Maracanã football stadium). In December, completing the southern section of the first Line 1, Largo do Machado Station began service. In 1982, the complementary inaugurations of the northern section of Line 1 started, with the beginning of operations of the Afonso Pena, São Francisco Xavier and Saens Peña stations.
To allow the completion of the second line to Irajá, in 1983, the trains on this line began operating from 6:00 AM to 2:00 PM. After a month, this schedule was extended until 8 PM, and a free bus service was established, integrating the Estácio, São Cristóvão, and Maracanã stations. After the conclusion of the works, the Pre-Metro and Maria da Graça, Del Castilho, Inhaúma Station and Irajá Station stations were opened. In 1984 the commercial operation of the second line began with five trains on workdays with a five-and-a-half-minute interval during the week.
Following the expansion, the Triagem station was inaugurated in July 1988, the year of the creation of the subway/train integration ticket. In 1991, the Engenho da Rainha station was inaugurated. From 1991 to 1996, two stations were opened, Thomaz Coelho and Vicente de Carvalho. In this period, the time interval of the nine stations of the second line was reduced to six minutes. In July 1998, Cardeal Arcoverde Station, in the traditional neighbourhood of Copacabana, was inaugurated. Five more stations became operational in the following two months: Irajá Station, Colégio Station, Coelho Neto, Engenheiro Rubens Paiva, Acari/Fazenda Botafogo and Pavuna Station.
In 1997, the Carnival Operation (Operação de Carnaval in Portuguese) began with continuous service during the Rio Carnival festivity days. In December of that year the system was privatised and the management and operation of the company passed into the hands of the Consortium Opportrans with a concession of 20 years, leaving the responsibility for expansion of the network in the hands of the state government of Rio de Janeiro through the company Rio Trilhos. The Rio Reveillón is highlighted by the performance of Opportrans that since 1999 has conducted a Special Operation to ensure a party for all. Tickets illustrated scheduled appointments to avoid overcrowding and provide the best service.
In 2003 Siqueira Campos Station in Copacabana was inaugurated. Cantagalo Station beyond Siqueira Campos was due to be completed in March 2006 but owing to financial problems the opening date was postponed to December 15.[10] This was again postponed and the final opening took place in February 2007. At the same time construction began on the subway extension to General Osório station in Ipanema. This was opened in December 2009.
In late December 2007, Metro Rio renewed the concession, then defined as for another 20 years, to 2038.
Line 1A from Pavuna to Botafogo opened in December 2009 with a connection between São Cristóvão and Central. Passenger traffic at Estácio is reduced and the elimination of the need to transfer between Lines 1 and 2 saves up to 13 minutes of journey time. A new station on the new section, Cidade Nova, was opened in November 2010;[11] the station is on Avenida Presidente Vargas and serves the City Hall.
In June 2010, the construction of Line 4 began, linking Ipanema to Barra da Tijuca, where most 2016 Olympic Games events will occur.
System
| Metrô Rio |
|---|
Legend |
Rolling stock
The cars are of monoblock construction in stainless steel. Passenger train composition can vary between four and six cars. Driving cars can accommodate a maximum of 351 passengers (40 seated), while non-driving cars accommodate a maximum of 378 passengers (48 seated). Thus, in six-car configurations the maximum number of passengers that can be transported is 2,214.
Line 1 is served by exclusively old types of rolling stock, which are full metro. Since Line 2 was formerly a light rail line, there are some old types of stock that have been converted from light rail to metro stock. New B type stock is full metro stock. This line is also served by old A type stock, built by La Brugeoise et Nivelles and Cobrasma.
Inside each coach, seat arrangement is both parallel and perpendicular to the windows. When the left side has parallel seats, the right side has perpendicular seats, and vice versa. Each vertical seat has a handle for easier standing. There are vertical stanchions from ceiling to floor for standing passengers, one set in front of the horizontal seats, another set at the middle of the coach. Both A and B type trains are air-conditioned.
Line 1A uses EMUs built by CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles Co. Ltd. The 6-car trains were designed in 18 months and all 19 sets are currently operating in passenger service. The trains entered revenue service 23 months after contract award.
Lines
- Line 1 (Orange): Uruguai, Saens Peña, São Francisco Xavier, Afonso Pena, Estácio, Praça Onze, Central, Presidente Vargas, Uruguaiana, Carioca, Cinelândia, Glória, Catete, Largo do Machado, Flamengo, Botafogo, Cardeal Arcoverde, Siqueira Campos, Cantagalo, General Osório.
All stations are underground. Cinelândia and Central stations have island platforms. Carioca, Saens Peña, Botafogo and General Osório stations have both side and island platforms, although Saens Peña consists of two island platforms and three tracks. The northernmost of the three tracks appears to be disused and planned for use after the Line 1 extension. Saens Peña is a very busy station, with train turnarounds made very quickly. All other stations have side platforms, up and down tracks are divided by a low wall at stations with side platforms. Siqueira Campos, Carioca, Central, Uruguaiana are Cardeal Arcoverde have a large mezzanine floor between surface and underground tracks.
Central, which is a major interchange point between the Metro, local and longer-distance bus lines, and the SuperVia train network, is the busiest station on the network. Cardeal Arcoverde is the most beautiful station; platform area has been dynamited out of the base of São João Mountain and retains a cavelike structure. General Osório has some painting in the hallways to remember prehistoric attempts at communication.
Uruguai Station opened in March 2014, becoming the new terminal station of Line 1 in the North Side of Rio de Janeiro.[12]
- Line 2 (Green): Pavuna, Engenheiro Rubens Paiva, Acari/Fazenda Botafogo Station, Coelho Neto, Colégio, Irajá, Vicente de Carvalho, Thomaz Coelho, Engenho da Rainha, Inhaúma, Nova América/Del Castilho, Maria da Graça, Triagem, Maracanã, São Cristóvão, Cidade Nova, Estácio (closed on working days).
- Line 1A: São Cristóvão, Cidade Nova, Central, Presidente Vargas, Uruguaiana, Carioca, Cinelândia, Glória, Catete, Largo do Machado, Flamengo, Botafogo.
Line 1A is actually an extension of Line 2 to Botafogo station. Line 2 is elevated from Irajá to Colégio. Many of the stations have island platforms, although Pavuna has both side and island platforms. Underground from Central to Botafogo.
Owing to its origin as light rail, it is fully above-ground (except Estácio station, which is underground). Most stations like Irajá and others, have an island platform, whereas some stations like Triagem have side platforms. Maracanã station is directly linked by an overbridge to the Maracanã Stadium across the street.
Connections
- Line 1 is fully underground with Cardeal Arcoverde being the deepest station. This station is under São João mountain. Non-free interchange with the Santa Teresa Tram is possible at Carioca (indefinitely suspended in 2011) and with the SuperVia trains at Central. Interchange to Line 2 is possible at all stations between Botafogo and Central on weekdays.[6] There is interchange with Line 2 at Estácio on weekends and holidays. Interchange to bus is possible at Cardeal Arcoverde, Botafogo, Largo do Machado, Estácio, São Francisco Xavier and Sáenz Peña.
- Line 2 is fully above-ground, except stations on Line 1A. It is elevated from Irajá to Colégio and the rest is at grade, except Cidade Nova and Triagem, which are elevated. Interchange with the train is possible at Triagem, Pavuna, São Cristóvão and Central. Interchange to line 1 is possible at Line 1A stations on weekdays, and at Estácio on weekends and holidays. Bus interchange is possible at Nova América/Del Castilho, Coelho Neto and Pavuna.
Fare structure

- Single Journey (Unitário in Portuguese): This is the most popular option. When a commuter buys a ticket from the counter, they then can travel by metro from any station to any station of any line. Once the commuter leaves the station, they need another ticket for another trip. There is a flat single fare (Unitário) R$ 4.10[13] regardless of distance.
- Single Journey with bus extension (Metrô na Superfície in Portuguese): Metro Rio operates a bus service from some of its stations, which acts as an extension of the metro service. No additional fee is charged for this service; however, when buying the ticket the traveller must ask for a Metrô na Superfície card. Cards can be bought directly on the Metrô na Superfície bus.
- Single Journey with express bus service: not to be confused with the bus extension, this fare allows a passenger to travel on the subway and on select bus services (Cosme Velho and Urca are served by express buses), also run by the metro company. The fare costs R$4.35 as of April 2014, and the ticket can be purchased on the subway or when boarding select buses.
- Prepaid Card (Cartão Pré-pago): a prepaid card, valid on the metro and on the buses run by the metro company (not valid on regular city buses) can be bought at any metro station. The card is free of charge, however a minimum prepayment of R$10 is required.
Tickets (a disposable contactless card) are purchased from a cashier in a booth. Prepaid tickets can be topped up at the vending booths, or at automated ticket recharging machines at select stations. Cards cannot be bought at the machines, and no change is given. Cash is the only accepted means of payment on any of the sales channels.
The Barra Expresso included a single ticket pass and the fare for a bus trip to Barra da Tijuca, a neighborhood located in the West Side of Rio. The fare is R$4.35 as of April 2014. This integration ended when Line 4 was opened to the public.
Modernization

The investment of R$1.15 billion contemplates also the purchase of 19 additional compositions: there will be 114 new cars[14] with a technology that allows the passengers to circulate inside the train. The first of the new compositions arrives in December 2010 and the others will start operating gradually until December 2011. All of them will ride in Line 2 and will have a dimensioned air conditioning system to bear the sun and heat's direct incidence, as most part of the line is in the surface. With the increase of 63% of the fleet, the concessionaire will also standardize the compositions of Lines 1 and 2: all 49 trains will have six cars.
The control, signalization, ventilation and energy systems will be also expanded and modernized. The energy supply for the metro's operation will be reinforced with two new proper sub-stations, at Uruguaiana and Largo do Machado Stations, and with the remodeling of São Cristóvão and Central sub-stations. On the other hand, the signalization will be automated in the two lines. Metrô Rio will enhance the ventilation at the stations and will modernize all equipment of the Control and Operations Center, from where the complete daily operation is monitored. These actions, combined with the extension of Line 2, will allow Metrô Rio to transport more than 1.1 million passengers/day.
Expansion

The construction of Pavuna-Botafogo Direct Connection is also part of an investment package of R$1.15 billion undertaken by Metrô Rio,[14] as part of the renewal of the concession contract with the Government of the State of Rio de Janeiro in December 2007. Titled 21st Century Metro, the project, which also includes the expansion of Line 1 and other enhancements, will allow the subway capacity to more than double, from 600,000 passengers/day to more than 1.1 million passengers/day. The extension of Line 1 started in 2012, with the recovery works of 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) of via from Tijuca's tail, which goes from Saens Peña square to the corner of Rua Conde the Bonfim with Rua Uruguai, where Uruguai Station will be built. It was forecast that the expansion of Line 1 will be completed in 2014, the year of 2014 FIFA World Cup in Brazil, and the last station of the expansion, Uruguai Station, opened in March 2014, becoming the new north/west terminal station of Line 1.[12]
Line 4 (yellow line) was completed on July 30, 2016, connecting Barra da Tijuca neighbourhood in the West Zone, passing under São Conrado and Rocinha, to Ipanema/General Osório Station. All stations are underground, but when arriving in Barra da Tijuca, trains exit a tunnel, pass briefly by an elevated bridge and go underground again.[3][15]
See also
- List of Rio de Janeiro metro stations
- Rio de Janeiro Suburban Train
- Rio de Janeiro Light Rail
- Santa Teresa Tram in Rio
- List of Latin American rail transit systems by ridership
- List of metro systems
References
- 1 2 3 4 "METRÔ RIO - Concessão Metroviára Do Rio De Janeiro S/A" [METRÔ RIO - Concession Metroviára Of Rio De Janeiro S/A] (pdf) (in Portuguese). MetrôRio. December 31, 2013. Retrieved 2014-06-14.
- 1 2 3 "EXTENSÕES DAS LINHAS EM KILÔMETROS" [LENGTH OF THE LINES IN KILOMETERS] (in Portuguese). MetrôRio. Archived from the original on 2013-10-16. Retrieved 2013-09-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Temer participa de inauguração da Linha 4 do Metrô no Rio" [President Temer takes part in inauguration of Rio's metro's line four] (url) (in Portuguese). G1 Portal. 30 July 2016. Retrieved 2016-07-30.
- 1 2 http://www.metrorio.com.br/Content/Upload/ArqConteudo/Demonstracoes_Financeiras_2014.pdf
- 1 2 "History - How it all began". MetrôRio. Retrieved 2014-06-14.
- 1 2 "Maps". MetrôRio. Retrieved 2014-06-14.
- ↑ "MetrôRio". Invepar. Retrieved 2014-08-28.
- ↑ "Linha 2" (blog) (in Portuguese). Metrô do Rio (não oficial).
- ↑ "Decreto-lei 35/75 | Decreto-lei nº 35, de 15 de Março de 1975" [Decree-Law 35/75 | Legislative Decree No. 35 of March 15, 1975] (in Portuguese). JusBrasil. Retrieved 2014-08-29.
- ↑ Thomé, Juliet (August 6, 2006). "Estação Cantagalo do metrô será inaugurada em dezembro" [Cantagalo metro station will be opened in December]. SRZD (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2014-08-29.
- ↑ "Metrô Rio inaugura a estação Cidade Nova" [Metro Rio inaugurates Cidade Nova station]. R7 (in Portuguese). November 1, 2010. Retrieved 2014-08-29.
- 1 2 Hearst, Chesney (March 17, 2014). "New Tijuca Metro Station Opened in Rio: Daily - Rio de Janeiro's Zona Norte neighborhood of Tijuca has a new subway (metro) station; the Estação Uruguai.". The Rio Times. Retrieved 2014-08-27.
- ↑ "Fares and Payments". MetrôRio. Retrieved 2016-05-07.
- 1 2 "History - A new time has come". MetrôRio. Retrieved 2014-08-28.
- ↑ "O que é o projeto" [What is the project] (in Portuguese). Metrô Linha 4. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rio de Janeiro Metro. |
- Metrô Rio – official website (Portuguese) & (English)
- Rio de Janeiro Metro at NYCSubway.org (English)
- Cantagalo Station information (Portuguese)
- Rio Trilhos (Portuguese)
- Rio de Janeiro metro map (English)