Menai Suspension Bridge
| Menai Bridge Pont Grog y Borth | |
|---|---|
|
The Menai Suspension Bridge from a viewpoint on the A5 near the Britannia Bridge | |
| Coordinates | 53°13′12.5″N 4°9′47.25″W / 53.220139°N 4.1631250°WCoordinates: 53°13′12.5″N 4°9′47.25″W / 53.220139°N 4.1631250°W |
| Carries |
|
| Crosses | Menai Straits |
| Locale | Anglesey, North Wales |
| Heritage status |
Grade 1 Candidate: World Heritage Site |
| Characteristics | |
| Design | Suspension bridge |
| Material |
Wrought Iron Stone |
| Total length | 417 metres (1,368 ft) |
| Width | 12 metres (39 ft) |
| Height | 30 metres (98 ft) |
| Longest span | 176 metres (577 ft) |
| Number of spans |
Main: One Arches: Eight |
| Piers in water | Five |
| Design life |
1893: wooden deck replaced in steel 1938/40: iron chains replaced in steel. |
| History | |
| Designer | Thomas Telford |
| Construction begin | 1819 |
| Opened | 30 January 1826 |
 Menai Bridge Location in Anglesey | |
The Menai Suspension Bridge (Welsh: Pont Grog y Borth) is a suspension bridge to carry road traffic between the island of Anglesey and the mainland of Wales. The bridge was designed by Thomas Telford and completed in 1826 and is a Grade I listed building.[1]
Construction
Before the bridge was completed in 1826, the island had no fixed connection to the mainland and all movements to and from Anglesey were by ferry across the fast flowing and dangerous waters of the Menai Strait. The main source of income on Anglesey was from the sale of cattle, and to move them to the markets of the mainland, including London, they had to be driven into the water and encouraged to swim across the Strait, a dangerous practice which often resulted in the loss of valuable animals.[2] With Holyhead as the closest point to, and thus one of the principal ports for ferries to Dublin, Engineer Thomas Telford was engaged to complete a survey of the route from London to Holyhead, and he proposed that a bridge should be built over the Menai Strait from a point near Bangor on the mainland to the village of Porthaethwy (which is now also known as Menai Bridge) on Anglesey.[2]
Because of the high banks and fast flowing waters of the Strait, it would have been difficult to build piers on the shifting sands of the sea-bed and, even if it could be done, they would have obstructed the navigation. Also, the bridge would have to be high enough to allow the passage of the tall ships of the day. In view of this, Telford proposed that a suspension bridge should be built and his recommendation was accepted by Parliament.[2]
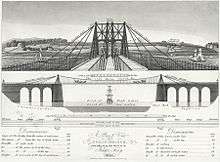
Construction of the bridge, to Telford's design, began in 1819 with the towers on either side of the strait. These were constructed from Penmon limestone and were hollow with internal cross-walls. Then came the sixteen huge chain cables, each made of 935 iron bars, that support the 176-metre (577 ft) span.[3] To avoid rusting between manufacture and use, the iron was soaked in linseed oil and later painted.[4] The chains each measured 522.3 metres (1,714 ft) and weighed 121 long tons (123 t; 136 short tons). Their suspending power was calculated at 2,016 long tons (2,048 t; 2,258 short tons).[2] The bridge was opened to much fanfare on 30 January 1826.[2]
Later history


The roadway was only 24 feet (7.3 m) wide and, without stiffening trusses, soon proved highly unstable in the wind. The deck of the Menai Bridge was strengthened in 1840 by W. A. Provis and, in 1893, the entire wooden surface was replaced with a steel deck designed by Sir Benjamin Baker.[5] Over the years, the 4 1⁄2-ton weight limit proved problematic for the increasing freight industry and in 1938 the original wrought iron[6] chains were replaced with steel ones without the need to close the bridge. In 1999 the bridge was closed for around a month to resurface the road and strengthen the structure, requiring all traffic to cross via the nearby Britannia Bridge.
On 28 February 2005 the bridge was promoted to UNESCO as a candidate World Heritage Site. On the same day one carriageway of the bridge was closed for six months restricting traffic to a single carriageway so that traffic travelled to the mainland in the morning and to Anglesey in the afternoon. The bridge was re-opened to traffic in both directions on 11 December 2005 after its first major re-painting in 65 years.
Surroundings
The Anglesey Coastal Path passes below the bridge. The bridge has a memorial to the Aberfan disaster victims on the Anglesey side.
Cultural references


The nearest settlement is the town of Menai Bridge. A representation of the Menai Bridge inside a border of railings and stanchions is featured on the reverse of British one-pound coins minted in 2005. The coin was designed by Edwins Ellis.
Quotation
- White Knight to Alice:
- "I heard him then, for I had just
- completed my design,
- To keep the Menai bridge from rust
- By boiling it in wine."
Famous Welsh englyn
- Uchelgaer uwch y weilgi – gyr y byd
- Ei gerbydau drosti,
- Chwithau, holl longau y lli,
- Ewch o dan ei chadwyni.
- —Dewi Wyn o Eifion[7] (David Owen) (1784–1841)
- High fortress above the sea – the world drives
- Its carriages across it;
- And you, all you ships of the sea,
- Pass beneath its chains.
See also
- Britannia Bridge, second bridge over the Menai Strait, opened in 1850
- List of bridges in Wales
- Swellies
References
Notes
- ↑ "Menai Suspension Bridge, Menai Bridge". British Listed Buildings. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Bartlett, W. H.; Harding, J.D.; Creswick, T. (2009). The Ports Harbours Watering Places (Reprint ed.). BiblioLife. ISBN 1-115-95868-2.
- ↑ Drewry, Charles Stewart (1832). A Memoir of Suspension Bridges: Comprising The History Of Their Origin And Progress. London: Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown, Green & Longman. pp. 46–66, and Plates. Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- ↑ Kovach, Warren (2010). "Menai Strait Bridges". Anglesey history. Retrieved 27 July 2010.
- ↑ "Menai Suspension Bridge". Asce.org. Retrieved 2014-05-19.
- ↑ The Saturday Magazine. Published by J. W. Parker: 212. 1835. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Llwybr y Llewod 8-13. BBC Lleol
Bibliography
- Jones, Reg Chambers (2011). Crossing the Menai: an illustrated history of the ferries and bridges of the Menai Strait. Wrexham: Bridge Books. ISBN 9781844940745.
- Norrie, Charles Matthew (1956) Bridging the Years – a short history of British Civil Engineering, Edward Arnold (Publishers) Ltd
- Richards, Robin (2004). Two Bridges over Menai (new revised ed.). Llanrwst: Gwasg Carreg Gwalch. ISBN 1845241304.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Menai Suspension Bridge. |
- Menai Bridge Website Menai Bridge Town Partnership Website with details on the news, council, events and businesses of Menai Bridge
- Menai Heritage A community project and museum celebrating the two bridges and the town of Menai Bridge