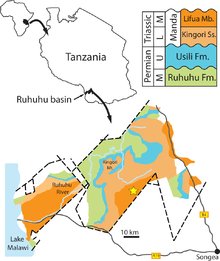
Manda Formation
The Manda Formation (also known as the Manda Beds) is a Middle Triassic geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Triassic, including some of the earliest archosaurs.[1]
History of study
One of the first to study rocks of the Manda Formation was British geologist G. M. Stockley. In 1932, Stockley explored the geology of the Ruhuhu Basin in Tanzania. He called a series of layers dating from the Late Carboniferous to the Middle Triassic the Songea Series and divided it into eight units labelled K1-K8. Stockley was also the first to describe fossils from these rocks, naming an older layer the "Lower Bone Bed" and a younger layer the "Upper Bone Bed".
In 1957, paleontologist Alan J. Charig described many more fossils from the bone beds in his Ph.D. thesis for the University of Cambridge.[2][3] Charig renamed the youngest of Stockley's units in 1963, calling unit K6 the Kawinga Formation, K7 the Kingori Sandstones, and K8 the Manda Formation. Fossils were identified in many strata, invalidating Stockley's division into two distinct bone beds. Since Charig's description, the Kawinga Formation has been renamed the Usili Formation, the Kingori Sandstones have become the Kingori Sandstone Member of the Manda Formation, and Charig's original Manda Formation has become a subunit of the formation called the Lifua Member.[1] Six formations and one informal unit are currently recognized in the Songea Group (Ruhuhu basin) rocks range in age from Pennsylvanian to Anisian, including the Idusi (K1), Mchuchuma (K2), Mbuyura (K3), Mhukuru (K4), Ruhuhu (K5), and Usili (K6) formations and the informal Manda Beds, which include the Kingori Sandstone (K7) and Lifua Member (K8).[4]
Paleobiota
Tetrapods
|
|
|
Color key
|
|
Notes
Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; crossed out taxa are discredited. |
Temnospondyls
Parareptiles
Archosauromorphs
| Taxon | Member | Material | Notes | Images |
| Asperoris mnyama | Lifua Member | NHMUK PV R36615, incomplete skull | A non-crurotarsan archosauriform of uncertain phylogenetic placement |  |
| "Stagonosuchus" tanganyikaensis[8] | Lifua Member | SAM 11754, right humerus | An indeterminate archosauromorph; possibly a rhynchosaur | |
| Stenaulorhynchus stockleyi | Lifua Member | | A rhynchosaur | |
| "Teleocrater rhadinus" | Lifua Member | NHMUK R6795, vertebrae, limb bones and other elements | An indeterminate archosauriform; a nomen nudum not yet formally described | |
| Unnamed[5] | Lifua Member | NHMUK PV R36619, incomplete skull and partial postcranial skeleton | A non-archosaurian archosauriform | |
|
Archosaurs
| Taxon | Member | Material | Notes | Images |
| Asilisaurus kongwe | Lifua Member | | A silesaurid dinosauriform |  |
| Hypselorhachis mirabilis | Lifua Member | NHMUK R16586, a complete dorsal vertebra | A sail-backed archosaur possibly belonging to the family Ctenosauriscidae | |
| "Mandasuchus tanyauchen" | Lifua Member | NHMUK R6792, partial mandible and postcranial skeletons | A "rauisuchian"; a nomen nudum not yet formally described | |
| Nundasuchus songeaensis[5][9] | Lifua Member | NMT RB48, partial skeleton and skull | An archosaur, possibly suchian | |
| Nyasasaurus parringtoni[10] | Lifua Member | NHMUK R6856, a right humerus, three partial presacral vertebrae and three sacral vertebrae. SAM-PK-K10654 is also potentially referable - see "Thecodontosaurus" alophos below. | A theropod or an ornithischian or the most advanced non-dinosaurian dinosauriform. Possibly the oldest dinosaur.[10] | |
| "Pallisteria angustimentum" | Lifua Member | NHMUK R36620, partial skull and some postcranial fragments | A "rauisuchian"; a nomen nudum first identified as a thecodont | |
| Parringtonia gracilis | Lifua Member | NHMUK R8646, a mandible, scapula, partial ischium, twelve vertebrae, and five osteoderms | An erpetosuchid | |
| Stagonosuchus nyassicus | Lifua Member | GPIT/RE/3831/1-21 and GPIT/RE/3832/1-15, two partial postcranial skeletons | A "rauisuchian" | |
| "Stenaulorhynchus" major[8] | Lifua Member | SAM S337, distal half of a left humerus | A subjective senior synonym of Stagonosuchus.[10] | |
| "Thecodontosaurus" alophos[10] | Lifua Member | SAM-PK-K10654, three neck vertebrae and two rear presacral vertebrae | A probable subjective senior synonym of Nyasasaurus, first identified as a sauropodomorph dinosaur.[10] | |
| Unnamed[11] | Lifua Member | Nearly complete skull and partial skeleton | A stem-aetosaur | |
|
Therapsids
Dicynodonts
Cynodonts
References
- 1 2 Butler, R. J.; Barrett, P. M.; Abel, R. L.; Gower, D. J. (2009). "A possible ctenosauriscid archosaur from the Middle Triassic Manda Beds of Tanzania". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 29 (4): 1022. doi:10.1671/039.029.0404.
- ↑ Charig, A. J. (1957). New Triassic archosaurs from Tanganyika, including Mandasuchus and Teleocrater: Dissertation Abstracts. Cambridge University.
- ↑ Nesbitt, S. J.; Butler, R. J. (2012). "Redescription of the archosaur Parringtonia gracilis from the Middle Triassic Manda beds of Tanzania, and the antiquity of Erpetosuchidae". Geological Magazine: 1. doi:10.1017/S0016756812000362.
- ↑ Sidor, C. A.; Angielczyk, K. D.; Weide †, D. M.; Smith, R. M. H.; Nesbitt, S. J.; Tsuji, L. A. (2010). "Tetrapod fauna of the lowermost Usili Formation (Songea Group, Ruhuhu Basin) of southern Tanzania, with a new burnetiid record". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (3): 696. doi:10.1080/02724631003758086.
- 1 2 3 Sidor, C. A.; Vilhena, D. A.; Angielczyk, K. D.; Huttenlocker, A. K.; Nesbitt, S. J.; Peecook, B. R.; Steyer, J. S.; Smith, R. M. H.; Tsuji, L. A. (2013). "Provincialization of terrestrial faunas following the end-Permian mass extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (20): 8129. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302323110.
- ↑ Sues, H.-D.; Fraser, N.C. (2010). "Early and early Middle Triassic in Gondwana". Triassic Life on Land: The Great Transition. New York: Columbia University Press. pp. 19–36. ISBN 9780231135221.
ISBN 0-231-13522-X
- ↑ Tsuji, L. A.; Sobral, G.; Müller, J. (2013). "Ruhuhuaria reiszi, a new procolophonoid reptile from the Triassic Ruhuhu Basin of Tanzania". Comptes Rendus Palevol. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2013.08.002.
- 1 2 Lautenschlager, S.; Desojo, J. B. (2011). "Reassessment of the Middle Triassic rauisuchian archosaurs Ticinosuchus ferox and Stagonosuchus nyassicus". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 85 (4): 357. doi:10.1007/s12542-011-0105-1.
- ↑ Nesbitt, Sterling J.; Sidor, Christian A.; Angielczyk, Kenneth D.; Smith, Roger M. H.; Tsuji, Linda A. (November 2014). "A new archosaur from the Manda beds (Anisian, Middle Triassic) of southern Tanzania and its implications for character state optimizations at Archosauria and Pseudosuchia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 34 (6): 1357–1382. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.859622.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Nesbitt, S. J.; Barrett, P. M.; Werning, S.; Sidor, C. A.; Charig, A. J. (2013). "The oldest dinosaur? A Middle Triassic dinosauriform from Tanzania". Biol. Lett. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2012.0949.
- ↑ Nesbitt, S.J.; Sidor, C.A.; Angielczyk, K.D.; Smith, R.M.; Parker, W. (2012). "Derivation of the aetosaur osteoderm carapace: evidence from a new, exceptionally preserved "stem aetosaur" from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) Manda Beds of southwestern Tanzania". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (Supp. 1): 149. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.10635175.