Lower Peninsula of Michigan
| Lower Peninsula of Michigan | |
| Michigan | |
| Nickname: The Mitten | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | Michigan |
| Length | 277 mi (446 km), north to south |
| Width | 195 mi (314 km), east to west |
| Area | 40,162 sq mi (104,019 km2) |
| Population | 9,584,261 (2015 est.) |
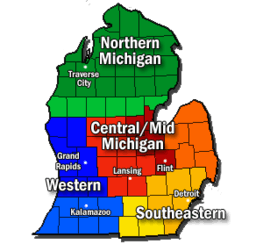 Regions and major cities of the Lower Peninsula | |
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan is the southern of the two major landmasses of the U.S. state of Michigan, the other being the Upper Peninsula. It is surrounded by water on all sides except its southern border, which it shares with Indiana and Ohio. Although the Upper Peninsula is commonly referred to as "the U.P." it is fairly uncommon for the Lower Peninsula to be called "the L.P."
Because of its recognizable shape, the Lower Peninsula is nicknamed "the mitten", with the eastern region identified as "The Thumb". This has led to several folkloric creation myths for the area, one being that it is a hand print of Paul Bunyan, a giant lumberjack and popular European-American folk character in Michigan. When asked where they live, Lower Peninsula residents may hold up their right palm and point to a spot on it to indicate the location.[1] The peninsula is sometimes divided into the Northern Lower Peninsula—which is more sparsely populated and largely forested—and the Southern Lower Peninsula—which is largely urban or farmland.
The Lower Peninsula dominates Michigan politics, and maps of it without the Upper Peninsula are sometimes presented as "Michigan", which contribute to resentment by "Yoopers" (residents of "the U.P").[2][3] Yoopers jokingly refer to residents of the Lower Peninsula as "flat-landers" (referring to the region's less rugged terrain) or "trolls" (because, living south of the Mackinac Bridge, they "live under the bridge").[4]
Geography
The Lower Peninsula is bounded on the south by the states of Indiana and Ohio. It is bounded by the west by Lake Michigan and on the northeast by Lake Huron, which connect at the Straits of Mackinac. In the southeast, the waterway of the St. Clair River, Lake St. Clair, Detroit River, and Lake Erie separate it from the province of Ontario, Canada.
At its widest points, the Lower Peninsula is 277 miles (446 km) long from north to south and 195 miles (314 km) from east to west. It contains nearly two-thirds of Michigan's total land area. The surface of the peninsula is generally level, broken by conical hills and glacial moraines usually not more than a few hundred feet tall. The western coast features extensive sandy beaches and dunes. It is divided by a low water divide running north and south. The larger portion of the state is on the west of this and gradually slopes toward Lake Michigan. The highest point in the Lower Peninsula is not definitely established but is either Briar Hill at 1,705 feet (520 m), or one of several points nearby in the vicinity of Cadillac. The lowest point is the surface of Lake Erie at 571 feet (174 m).
Flora and fauna
The American Bird Conservancy and the National Audubon Society have designated several locations as internationally Important Bird Areas.[5]
Geology
The Lower Peninsula is dominated by a geological basin known as the Michigan Basin. That feature is represented by a nearly circular pattern of geologic sedimentary strata in the area with a nearly uniform structural dip toward the center of the peninsula. The basin is centered in Gladwin County where the Precambrian basement rocks are 16,000 feet (4,900 m) deep. Around the margins, such as under Mackinaw City, Michigan, the Precambrian surface is around 4,000 feet (1,200 m) down. This 4,000-foot (1,200 m) contour on the bedrock clips the northern part of the lower peninsula and continues under Lake Michigan along the west. It crosses the southern counties of Michigan and continues on to the north beneath Lake Huron.
Transportation
Major airports
- Alpena County Regional Airport (APN) (Alpena)
- Bishop International Airport (FNT) (Flint)
- Capital Region International Airport (LAN) (Lansing)
- Cherry Capital Airport (TVC) (Traverse City)
- Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW) (Romulus)
- Gerald R. Ford International Airport (GRR) (Grand Rapids)
- Kalamazoo/Battle Creek International Airport (AZO) (Kalamazoo)
- MBS International Airport (MBS) (Saginaw)
- Pellston Regional Airport (PLN) (Pellston)
Highways
Primary Interstate Highways have two digits on their shields; auxiliary Interstate Highways have three digits. Interstate Highways include:
U.S. Highways include:
The Great Lakes Circle Tour is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River.[6]
Regions
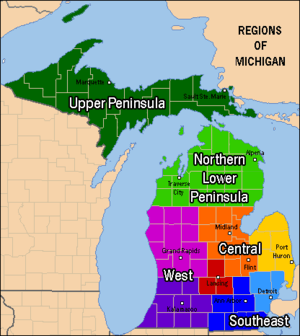
Michigan's Lower Peninsula can be divided into four main regions based on geological, soil, and vegetation differences; amount of urban areas or rural areas; minority populations; and agriculture. The four principal regions listed below can further be separated into sub-regions and overlapping areas.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Keilman, John (December 9, 2011). "Hand-to-hand combat". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved August 22, 2014.
- ↑ "Update: U.P. Added to White House Medicaid Map". Cadillac, MI: WWTV-TV. Retrieved 2016-10-05.
- ↑ "The Upper Peninsula Is Not Optional". theupperpeninsulaisnotoptional.tumblr.com. Retrieved 2016-10-05.
- ↑ Parrish, P. J. (2007). "Somebody's Daughter". A Thousand Bones. Simon and Schuster. p. 22. ISBN 1-4165-2587-4. Retrieved August 26, 2008.
A troll was what people from Michigan's Upper Peninsula called anyone who lived 'below the bridge,' the five-mile-long span that connected the Upper and Lower peninsulas.
- ↑ "Michigan's IBAs are online". Michigan Important Bird Areas (IBA) Program. February 28, 2010. Retrieved August 22, 2014.
- ↑ "Great Lakes Circle Tour". Great Lakes Information Network. August 22, 2014. Retrieved August 22, 2014.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Lower Peninsula. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lower Peninsula of Michigan. |
- Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University, Bibliography on Michigan (arranged by counties and regions)
- Michigan Geology -- Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University
- Michigan Department of Natural Resources website, harbors, hunting, resources and more
- Info Michigan, detailed information on 630 cities
- List of Museums, other attractions compiled by state government
- Michigan's Official Economic Development and Travel Site
- "Historic Light Station Information and Photography: Michigan". United States Coast Guard Historian's Office.
- Map of Michigan Lighthouse in PDF Format
- Northern Michigan Live Streaming Webcam
- Terry Pepper on lighthouses of the Western Great Lakes
Coordinates: 43°40′N 84°44′W / 43.66°N 84.73°W