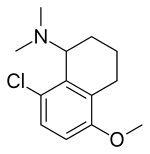
Lometraline
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | None |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | N,N-dimethyl-8-chloro-5-methoxy-1-aminotetralin |
| CAS Number |
39951-65-0 34552-78-8 (hydrochloride) |
| PubChem (CID) | 34789 |
| ChemSpider | 32014 |
| UNII | V78B234QEY |
| KEGG | D02669 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2111119 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18ClNO |
| Molar mass | 239.741 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Lometraline (INN; codenamed CP-14,368) is a drug which is an aminotetralin derivative.[1] A structural modification of the investigative neuroleptic pinoxepin, lometraline was originally patented by Pfizer as an antipsychotic, tranquilizer, and antiparkinsonian agent (likely as an anticholinergic).[2][3] However, it was instead later studied as a potential antidepressant and/or anxiolytic agent, but clinical studies revealed no psychoactivity at the doses used and further investigation was suspended.[1][4][5] However, further experimental modifications of the chemical structure of lometraline directly resulted in the discovery of tametraline, a potent inhibitor of the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, which in turn led to the discovery of the now widely popular antidepressant sertraline, which, remarkably, acts contrarily as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).[6]
See also
Other Reinhard Sarges Pfizer compounds:
- gliamilide
- sertraline
- sorbinil
- tametraline
References
- 1 2 Park S, Gershon S, Angrist B, Floyd A (February 1972). "Evaluation of an aminotetraline, CP 14.368, as an antidepressant". Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental. 14 (2): 65–70. PMID 4401233.
- ↑ Ellen Drake; W.B. Saunders Company (27 January 1994). Saunders pharmaceutical word book, 1994. W.B. Saunders Co. ISBN 978-0-7216-5254-2. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ United States. Patent Office (1972). Official gazette of the United States Patent Office: Patents. The Office. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ Francis Gilbert McMahon (1974). Psychopharmacological agents. Futura Pub. Co. ISBN 978-0-87993-052-3. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ Bayerische Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg. Arbeitskreis für Schlafforschung (1973). The Nature of sleep. Die Natur des Schlafes. La nature du sommeil: International symposium, Würzburg, 23-26.9.1971. G. Fischer. ISBN 978-3-437-10295-0. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ↑ B. Kenneth Koe, Charles A. Harbert, Reinhard Sarges, Albert Weissman, Willard M. Welch (2006). "Discovery of sertraline (Zoloft®)". Retrieved 2012-04-27.