Lithic stage
| The Stone Age |
|---|
|
↑ before Homo (Pliocene) |
| ↓ Chalcolithic |
In the sequence of North American prehistoric cultural stages first proposed by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in 1958, the Lithic stage was the earliest period of human occupation in the Americas, occurring during the Late Pleistocene period, to time before 8,000 B.C. (before 10,000 years ago).[1] The term "lithic stage" refers to the cultures of the post-glacial hunters and collectors in South America.[2] The stage derived its name from the first appearance of Lithic flaked stone tools.[3] This stage was conceived of as embracing two major categories of stone technology: (1) unspecialized and largely unformulated core and flake industries, with percussion the dominant and perhaps only technique employed, and (2) industries exhibiting more advanced "blade" techniques of stoneworking, with specialized fluted or unfluted lanceolate points the most characteristic artifact types. Throughout South America, there are stone tool traditions of the lithic stage, such as the "fluted fishtail" that reflect localized adaptations to the diverse habitats of the continent.[4]
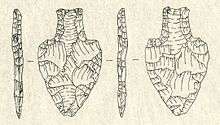
During the lithic stage people lived in rather small, mobile groups that survived on hunting, fishing, and plant gathering. The intensive and continual use of wild plants and animals eventually led to genetic changes to some of the species and ultimately to domestication by human groups. This lifestyle continued until around 5000 BC when people started to use domesticated plants and animals.[2]
One of the leading figures is Alex Krieger who has documented hundreds of sites that have yielded crude, percussion-flaked tools. The most convincing evidence for a lithic stage is based upon data recovered from sites in South America where such crude tools have been found and dated to more than 20,000 years ago.[5]
The time encompasses the Paleo-Indian period that subsequently is divided into more specific time terms such as Early Lithic stage or Early Paleo-Indians and Middle Paleo-Indians or Middle Lithic stage.[6] Examples include the Clovis culture and Folsom tradition groups.
The Lithic stage was followed by the Archaic stage.
- The Lithic stage
- The Archaic stage
- The Formative stage
- The Classic stage
- The Post-Classic stage
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Archaeology of the Americas. |
- Archaeology of the Americas
- Category:Archaeology of the Americas
- History of Mesoamerica (Paleo-Indian)
- History of the Americas
- Indigenous Amerindian genetics
- South American Indigenous people
- NCT (band)
References
- ↑ "Method and Theory in American Archaeology" (Digitised online by Questia Media). Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips. University of Chicago. 1958. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
- 1 2 Silberman, N.A.; Bauer, A.A. (2012). The Oxford Companion to Archaeology. OUP USA. pp. 2–151. ISBN 9780199735785. Retrieved 2015-02-26.
- ↑ Willey, Gordon R. (1989). "Gordon Willey". In Glyn Edmund Daniel; Christopher Chippindale. The Pastmasters: Eleven Modern Pioneers of Archaeology: V. Gordon Childe, Stuart Piggott, Charles Phillips, Christopher Hawkes, Seton Lloyd, Robert J. Braidwood, Gordon R. Willey, C.J. Becker, Sigfried J. De Laet, J. Desmond Clark, D.J. Mulvaney. New York: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05051-1. OCLC 19750309.
- ↑ "Method and Theory in American Archaeology - 1958, Page 79 by Gordon R. Willey, Philip Phillips. | Online Research Library: Questia". questia.com. Retrieved 2015-02-26.
- ↑ Walthall, J.A. (1990). Prehistoric Indians of the Southeast: Archaeology of Alabama and the Middle South. University of Alabama Press. p. 22. ISBN 9780817305529. Retrieved 2015-02-26.
- ↑ Gordon R. Willey and Philip Phillips (1957). Method and Theory in American Archaeology. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-89888-9.

.svg.png)
