Jack the Ripper suspects
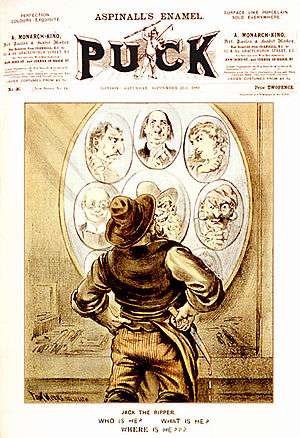
A series of murders that took place in the East End of London from August to November 1888 was blamed on an unidentified assailant who acquired the nickname Jack the Ripper. Since that time, the identity of the killer or killers has been hotly debated, and over one hundred Jack the Ripper suspects have been named.[1][2] Though many theories have been advanced, experts find none widely persuasive, and some can hardly be taken seriously at all.[3]
Contemporaneous police opinion
Metropolitan Police Service files show that their investigation into the serial killings encompassed eleven separate murders between 1888 and 1891, known in the police docket as the "Whitechapel murders".[4] Five of these—the murders of Mary Ann Nichols, Annie Chapman, Elizabeth Stride, Catherine Eddowes, and Mary Jane Kelly—are generally agreed to be the work of a single killer, known as "Jack the Ripper". They occurred between August and November 1888 within a few streets of each other, and are collectively called the "canonical five". The six other murders—those of Emma Elizabeth Smith, Martha Tabram, Rose Mylett, Alice McKenzie, Frances Coles, and an unidentified woman—have been linked with Jack the Ripper to varying degrees.
The swiftness of the attacks, and the manner of the mutilations performed on some of the bodies, which included disembowelment and removal of organs, led to speculation that the murderer had the skills of a physician or butcher.[5] However, others disagreed strongly, and thought the wounds too crude to be professional.[6] The alibis of local butchers and slaughterers were investigated, with the result that they were eliminated from the enquiry.[7] Over 2,000 people were interviewed, "upwards of 300" people were investigated, and 80 people were detained.[8]
During the course of their investigations of the murders, police regarded several men as strong suspects, though none was ever formally charged.
Montague John Druitt

Montague John Druitt (15 August 1857 – early December 1888) was a Dorset-born barrister who worked to supplement his income as an assistant schoolmaster in Blackheath, London, until his dismissal shortly before his suicide by drowning in 1888.[9] His decomposed body was found floating in the Thames near Chiswick on 31 December 1888. Some modern authors suggest that Druitt may have been dismissed because he was a homosexual and that this could have driven him to suicide.[10] However, both his mother and his grandmother suffered mental health problems,[11] and it is possible that he was dismissed because of an underlying hereditary psychiatric illness.[9] His death shortly after the last canonical murder (which took place on 9 November 1888) led Assistant Chief Constable Sir Melville Macnaghten to name him as a suspect in a memorandum of 23 February 1894. However, Macnaghten incorrectly described the 31-year-old barrister as a 41-year-old doctor.[12] On 1 September, the day after the first canonical murder, Druitt was in Dorset playing cricket, and most experts now believe that the killer was local to Whitechapel, whereas Druitt lived miles away on the other side of the Thames in Kent.[13] Inspector Frederick Abberline appeared to dismiss Druitt as a serious suspect on the basis that the only evidence against him was the coincidental timing of his suicide shortly after the last canonical murder.[14]
Seweryn Kłosowski

Seweryn Antonowicz Kłosowski (alias George Chapman—no relation to victim Annie Chapman) (14 December 1865 – 7 April 1903) was born in Congress Poland, but emigrated to the United Kingdom sometime between 1887 and 1888, shortly before the start of the Whitechapel murders. Between 1893 and 1894 he assumed the name of Chapman. He successively poisoned three of his wives and became known as "the borough poisoner". He was hanged for his crimes in 1903. At the time of the Ripper murders, he lived in Whitechapel, London, where he had been working as a barber under the name Ludwig Schloski.[15] According to H. L. Adam, who wrote a book on the poisonings in 1930, Chapman was Inspector Frederick Abberline's favoured suspect,[16] and the Pall Mall Gazette reported that Abberline suspected Chapman after his conviction.[17] However, others disagree that Chapman is a likely culprit, as he murdered his three wives with poison, and it is uncommon (though not unheard of) for a serial killer to make such a drastic change in their modus operandi.[18]
Aaron Kosminski
Aaron Kosminski (born Aron Mordke Kozminski; 11 September 1865 – 24 March 1919) was a Polish Jew who was admitted to Colney Hatch Lunatic Asylum in 1891.[19] "Kosminski" (without a forename) was named as a suspect by Sir Melville Macnaghten in his 1894 memorandum[20] and by former Chief Inspector Donald Swanson in handwritten comments in the margin of his copy of Assistant Commissioner Sir Robert Anderson's memoirs.[21] Anderson wrote that a Polish Jew had been identified as the Ripper but that no prosecution was possible because the witness was also Jewish and refused to testify against a fellow Jew.[22] Some authors are sceptical of this, while others use it in their theories.[23] In his memorandum, Macnaghten stated that no one was ever identified as the Ripper, which directly contradicts Anderson's recollection.[24] In 1987, author Martin Fido searched asylum records for any inmates called Kosminski, and found only one: Aaron Kosminski. Kosminski lived in Whitechapel;[25] however, he was largely harmless in the asylum. His insanity took the form of auditory hallucinations, a paranoid fear of being fed by other people, a refusal to wash or bathe, and "self-abuse".[26] In his book, The Cases That Haunt Us, former FBI profiler John Douglas states that a paranoid individual such as Kosminski would likely have openly boasted of the murders while incarcerated had he been the killer, but there is no record that he ever did so.[27] In 2014, DNA analysis attempted to link Kosminski with a shawl said to have belonged to victim Catherine Eddowes,[28][29] but experts – including Professor Sir Alec Jeffreys, the inventor of genetic fingerprinting – dismissed the claims as unreliable.[30]
Michael Ostrog

Michael Ostrog (c. 1833–in or after 1904) was a Russian-born professional con man and thief.[4] He used numerous aliases and assumed titles.[31] Among his many dubious claims was that he had once been a surgeon in the Russian Navy. He was mentioned as a suspect by Macnaghten, who joined the case in 1889, the year after the "canonical five" victims were killed. Researchers have failed to find evidence that he had committed crimes any more serious than fraud and theft.[32] Author Philip Sugden discovered prison records showing that Ostrog was jailed for petty offences in France during the Ripper murders.[33] Ostrog was last mentioned alive in 1904; the date of his death is unknown.[34]
John Pizer

John Pizer or Piser (c. 1850–1897) was a Polish Jew who worked as a bootmaker in Whitechapel. In the early days of the Whitechapel murders, many locals suspected that "Leather Apron" was the killer, which was picked up by the press, and Pizer was known as "Leather Apron". He had a prior conviction for a stabbing offence, and Police Sergeant William Thicke apparently believed that he had committed a string of minor assaults on prostitutes.[35] After the murders of Mary Ann Nichols and Annie Chapman in late August and early September 1888 respectively, Thicke arrested Pizer on 10 September, even though the investigating inspector reported that "there is no evidence whatsoever against him".[36] He was cleared of suspicion when it turned out that he had alibis for two of the murders. He was staying with relatives at the time of one of the canonical murders, and he was talking with a police officer while watching a spectacular fire on the London Docks at the time of another.[37] Pizer and Thicke had known each other for years,[38] and Pizer implied that his arrest was based on animosity rather than evidence.[35] Pizer successfully obtained monetary compensation from at least one newspaper that had named him as the murderer.[39] Thicke himself was accused of being the Ripper by H. T. Haslewood of Tottenham in a letter to the Home Office dated 10 September 1889; the presumably malicious accusation was dismissed as without foundation.[40]
James Thomas Sadler
James Thomas Sadler was a friend of Frances Coles, the last victim added to the Whitechapel murders police file. Coles was killed with a wound to the throat on 13 February 1891. Sadler was arrested, but there was little evidence against him. Though briefly considered by the police as a Ripper suspect, he was at sea at the time of the first four "canonical" murders, and was released without charge.[41] Sadler was named in Macnaghten's 1894 memorandum in connection with Coles' murder. Though Macnaghten thought Sadler "was a man of ungovernable temper and entirely addicted to drink, and the company of the lowest prostitutes", he thought any connection with the Ripper was unlikely.[42]
Francis Tumblety

Francis Tumblety (c. 1833–1903) earned a small fortune posing as an "Indian Herb" doctor throughout the United States and Canada, and was commonly perceived as a misogynist and a quack.[43] He was connected to the death of one of his patients,[44] but escaped prosecution.[45] In 1865, he was arrested for alleged complicity in the assassination of Abraham Lincoln, but no connection was found and he was released without being charged.[46] Tumblety was in England in 1888, and was arrested on 7 November, apparently for engaging in homosexuality, which was illegal at the time.[47] It was reported by some of his friends that he showed off a collection of "matrices" (wombs) from "every class of woman" at around this time.[48] Awaiting trial, he fled to France and then to the United States.[49] Already notorious in the States for his self-promotion and previous criminal charges, his arrest was reported as connected to the Ripper murders.[50] American reports that Scotland Yard tried to extradite him were not confirmed by the British press or the London police,[51] and the New York City Police said, "there is no proof of his complicity in the Whitechapel murders, and the crime for which he is under bond in London is not extraditable".[52] In 1913, Tumblety was mentioned as a Ripper suspect by Chief Inspector John Littlechild of the Metropolitan Police Service in a letter to journalist and author George R. Sims.[4][53]
Contemporaneous press and public opinion
The Whitechapel murders were featured heavily in the media, and attracted the attention of Victorian society at large. Journalists, letter writers, and amateur detectives all suggested names either in press or to the police. Most were not and could not be taken seriously.[54] For example, at the time of the murders, Richard Mansfield, a famous actor, starred in a theatrical version of Robert Louis Stevenson's book Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde. The subject matter of horrific murder in the London streets and Mansfield's convincing portrayal led letter writers to accuse him of being the Ripper.[55]
William Henry Bury

William Henry Bury (25 May 1859 – 24 April 1889) had recently moved to Dundee from the East End of London, when he strangled his wife Ellen Elliott, a former prostitute, on 4 February 1889. He inflicted extensive wounds to her abdomen after she was dead and packed the body into a trunk. On 10 February, Bury went to the local police and told them his wife had committed suicide. He was arrested, tried, found guilty of her murder, and hanged in Dundee. A link with the Ripper crimes was investigated by police, but Bury denied any connection, despite making a full confession to his wife's homicide. Nevertheless, the executioner, James Berry, promoted the idea that Bury was the Ripper.[56]
Thomas Neill Cream

Dr. Thomas Neill Cream (27 May 1850 – 15 November 1892) was a doctor secretly specialising in abortions. He was born in Glasgow, educated in London and Canada, and entered practice in Canada and later in Chicago, Illinois. In 1881 he was found guilty of the fatal poisoning of his mistress's husband.[57] He was imprisoned in the Illinois State Penitentiary in Joliet, Illinois, from November 1881 until his release on good behaviour on 31 July 1891. He moved to London, where he resumed killing and was soon arrested. He was hanged on 15 November 1892 at Newgate Prison. According to some sources, his last words were reported as being "I am Jack the...", interpreted to mean Jack the Ripper.[58] However, police officials who attended the execution made no mention of this alleged interrupted confession.[58] As he was still imprisoned at the time of the Ripper murders, most authorities consider it impossible for him to be the culprit. However, Donald Bell suggested that he could have bribed officials and left the prison before his official release,[59] and Sir Edward Marshall-Hall suspected that his prison term may have been served by a look-alike in his place.[60] Such notions are unlikely, and contradict evidence given by the Illinois authorities, newspapers of the time, Cream's solicitors, Cream's family and Cream himself.[61]
Thomas Hayne Cutbush
Thomas Hayne Cutbush (1865–1903) was a medical student sent to Lambeth Infirmary in 1891 suffering delusions thought to have been caused by syphilis.[62] After stabbing a woman in the backside and attempting to stab a second he was pronounced insane and committed to Broadmoor Hospital in 1891, where he remained until his death in 1903.[63] The Sun newspaper suggested in a series of articles in 1894 that Cutbush was the Ripper. There is no evidence that police took the idea seriously, and Melville Macnaghten's memorandum naming the three police suspects Druitt, Kosminski and Ostrog was written to refute the idea that Cutbush was the Ripper.[64] Cutbush was the suspect advanced in the 1993 book Jack the Myth by A. P. Wolf, who suggested that Macnaghten wrote his memo to protect Cutbush's uncle who was a fellow police officer,[65] and another recent writer, Peter Hodgson, considers that Cutbush is the most likely candidate.[66]
Frederick Bailey Deeming

Frederick Bailey Deeming (30 July 1842 – 23 May 1892) murdered his first wife and four children in Rainhill near St. Helens, Lancashire, in 1891. His crimes went undiscovered and later that year he emigrated to Australia with his second wife, whom he then also murdered. Her body was found buried under their house, and the subsequent investigation led to the discovery of the other bodies in England. He was arrested, sent to trial, and found guilty. He wrote in a book, and later boasted in jail that he was Jack the Ripper, but he was either imprisoned[67] or in South Africa[68] at the time of the Ripper murders. The police denied any connection between Deeming and the Ripper.[69] He was hanged in Melbourne.[70] According to Robert Napper, a former Scotland Yard detective, the British police did not consider him a suspect because of his two possible alibis but Napper believed Deeming was not in jail at the time, and there is some evidence that he was back in England.[71]
Carl Feigenbaum
Carl Ferdinand Feigenbaum (executed 27 April 1896) was a merchant seaman arrested in 1894 in New York City for cutting the throat of Mrs Juliana Hoffmann. After his execution, his lawyer, William Sanford Lawton, claimed that Feigenbaum had admitted to having a hatred of women and a desire to kill and mutilate them. Lawton further stated that he believed Feigenbaum was Jack the Ripper. Though covered by the press at the time, the idea was not pursued for more than a century. Using Lawton's accusation as a base, author Trevor Marriott, a former British murder squad detective, argued that Feigenbaum was responsible for the Ripper murders as well as other murders in the United States and Germany between 1891 and 1894.[72] According to Wolf Vanderlinden, some of the murders listed by Marriott did not actually occur; the newspapers often embellished or created Ripper-like stories to sell copy. Lawton's accusations were disputed by a partner in his legal firm, Hugh O. Pentecost, and there is no proof that Feigenbaum was in Whitechapel at the time of the murders.[73] Xanthé Mallett, a Scottish forensic anthropologist and criminologist who investigated the case in 2011, wrote there is considerable doubt that all of the Jack the Ripper murders were committed by the same person. She concludes that it is possible Feigenbaum committed one of the murders but not all.[74]
Robert Donston Stephenson
Robert Donston Stephenson (also known as Roslyn D'Onston) (20 April 1841 – 9 October 1916) was a journalist and writer interested in the occult and black magic. He admitted himself as a patient at the London Hospital in Whitechapel shortly before the murders started, and left shortly after they ceased. He authored a newspaper article, which claimed that black magic was the motive for the killings and alleged that the Ripper was a Frenchman.[75] Stephenson's strange manner and interest in the crimes resulted in an amateur detective reporting him to Scotland Yard on Christmas Eve, 1888.[76] Two days later Stephenson reported his own suspect, a Dr Morgan Davies of the London Hospital.[77] Subsequently he fell under the suspicion of newspaper editor William Thomas Stead.[78] In his books on the case, author and historian Melvin Harris argued that Stephenson was a leading suspect,[78] but the police do not appear to have treated either him or Dr Davies as serious suspects.[79] London Hospital night-shift rosters and practices indicate that Stephenson was not able to leave on the nights of the murders and hence could not have been Jack the Ripper.[80]
Proposed by later authors
Suspects proposed years after the murders include virtually anyone remotely connected to the case by contemporary documents, as well as many famous names, who were not considered in the police investigation at all. As everyone alive at the time is now dead, modern authors are free to accuse anyone they can, "without any need for any supporting historical evidence".[3] Most of their suggestions cannot be taken seriously,[3] and include English novelist George Gissing, British prime minister William Ewart Gladstone, and syphilitic artist Frank Miles.[81]
Joseph Barnett

Joseph Barnett (c. 1858–1927) was a former fish porter, and victim Mary Kelly's lover from 8 April 1887 to 30 October 1888, when they quarrelled and separated after he lost his job and she returned to prostitution to make a living. Inspector Abberline questioned him for four hours after Kelly's murder, and his clothes were examined for bloodstains, but he was then released without charge.[82] A century after the murders, author Bruce Paley proposed him as a suspect as Kelly's scorned or jealous lover, and suggested that he'd committed the other murders to scare Kelly off the streets and out of prostitution.[82] Other authors suggest he killed Kelly only, and mutilated the body to make it look like a Ripper murder, but Abberline's investigation appears to have exonerated him.[83] Other acquaintances of Kelly's put forward as her murderer include her landlord John McCarthy and her former boyfriend Joseph Fleming.[84]
Lewis Carroll

Lewis Carroll (pen name of Charles Lutwidge Dodgson) (27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898) was the author of Alice's Adventures in Wonderland and Through the Looking-Glass. He was named as a suspect based upon anagrams which author Richard Wallace devised for his book Jack the Ripper, Light-Hearted Friend. This claim is not taken seriously by scholars.[85]
David Cohen
David Cohen (1865–1889) was a Polish Jew whose incarceration at Colney Hatch Lunatic Asylum roughly coincided with the end of the murders. Described as violently antisocial, the poor East End local was suggested as a suspect by author and Ripperologist Martin Fido in his book The Crimes, Detection and Death of Jack the Ripper (1987). Fido claimed that the name "David Cohen" was used at the time to refer to a Jewish immigrant who either could not be positively identified or whose name was too difficult for police to spell, in the same fashion that "John Doe" is used in the United States today.[86] Fido identified Cohen with "Leather Apron" (see John Pizer above), and speculated that Cohen's true identity was Nathan Kaminsky, a bootmaker living in Whitechapel who had been treated at one time for syphilis and who could not be traced after mid-1888—the same time that Cohen appeared.[87] Fido believed that police officials confused the name Kaminsky with Kosminski, resulting in the wrong man coming under suspicion (see Aaron Kosminski above). Cohen exhibited violent, destructive tendencies while at the asylum, and had to be restrained. He died at the asylum in October 1889.[88] In his book The Cases That Haunt Us, former FBI criminal profiler John Douglas has asserted that behavioural clues gathered from the murders all point to a person "known to the police as David Cohen ... or someone very much like him".[89]
William Withey Gull

Sir William Withey Gull (31 December 1816 – 29 January 1890) was physician-in-ordinary to Queen Victoria. He was named as the Ripper as part of the evolution of the widely discredited Masonic/royal conspiracy theory outlined in such books as Jack the Ripper: The Final Solution. Coachman John Netley has been named as his accomplice. Thanks to the popularity of this theory among fiction writers and for its dramatic nature, Gull shows up as the Ripper in a number of books and films including the TV film Jack the Ripper (1988), Alan Moore and Eddie Campbell's graphic novel From Hell (1999), and its 2001 film adaptation, in which Ian Holm plays Gull. Conventional historians have never taken Gull seriously as a suspect due to sheer lack of evidence; in addition, he was in his seventies at the time of the murders and had recently suffered a stroke.[90]
George Hutchinson
George Hutchinson was an unemployed labourer. On 12 November 1888, he made a formal statement to the London police that in the early hours of 9 November 1888, Mary Jane Kelly approached him in the street and asked him for money. He stated that he had then followed her and another man of conspicuous appearance to her room, and had watched the room for about three-quarters of an hour without seeing either leave. He gave a very detailed description of the man, claiming he was "of Jewish appearance", despite the darkness of that night.[91] The accuracy of Hutchinson's statement was disputed among the senior police. Inspector Frederick Abberline, after interviewing Hutchinson, believed that Hutchinson's account was truthful.[92] However, Robert Anderson, head of the CID, later claimed that the only witness who got a good look at the killer was Jewish. Hutchinson was not a Jew, and thus not that witness.[93] Hutchinson's statement was made on the day that Mary Kelly's inquest was held, and he was not called to testify. Some modern scholars have suggested that Hutchinson was the Ripper himself, trying to confuse the police with a false description, but others suggest he may have just been an attention seeker who made up a story he hoped to sell to the press.[94]
James Kelly

James Kelly (20 April 1860 – 17 September 1929) was first identified as a suspect in Terence Sharkey's Jack the Ripper. 100 Years of Investigation (Ward Lock 1987) and documented in Prisoner 1167: The madman who was Jack the Ripper, by Jim Tully, in 1997.[95]
James Kelly murdered his wife in 1883 by stabbing her in the neck. Deemed insane, he was committed to the Broadmoor Asylum, from which he later escaped in early 1888, using a key he fashioned himself. After the last of the five canonical Ripper murders in London in November 1888, the police searched for Kelly at what had been his residence prior his wife's murder, but they were not able to locate him. In 1927, almost forty years after his escape, he unexpectedly turned himself in to officials at the Broadmoor Asylum. He died two years later, presumably of natural causes.
Retired NYPD cold-case detective Ed Norris examined the Jack the Ripper case for a Discovery Channel program called Jack the Ripper in America. In it, Norris claims that James Kelly was Jack the Ripper, and that he was also responsible for multiple murders in cities around the United States. Norris highlights a few features of the Kelly story to support his contention. He worked as a furniture upholsterer, a job that requires strong handiness with a large knife. His escape from Broadmoor before the first of the five canonical murders and eventual escape to America after the last meant Kelly was in or around London at the right time. He also claimed to have resided in the United States and left behind a journal that spoke of his strong disapproval of the immorality of prostitutes and of his having been on the "warpath" during his time as a fugitive. Norris further argues Kelly was in New York at the time of a Ripper-like murder of a prostitute named Carrie Brown as well as in a number of cities while each experienced, according to Norris, one or two brutal murders of prostitutes while Kelly was there. Norris reported Kelly's Broadmoor Asylum file from before his escape and his eventual return has never been opened since 1927 until Norris was given special permission for access to it, and that the file is the perfect profile match for Jack the Ripper.
Charles Allen Lechmere
Charles Allen Lechmere (1849–1920), also known as Charles Cross, was a meat cart driver for the Pickfords company, and is conventionally regarded as an innocent witness who discovered the body of Polly Nichols. Journalist Christer Holmgren believes that Lechmere was the Ripper. According to Holmgren, Lechmere lied to a policeman at the scene, telling him that he had been with the body for a few minutes, whereas researchers claimed that he must have been with her for about nine minutes, and gave a false name "Charles Cross" at the inquest; Cross was the surname of his stepfather. Lechmere's home address, visits to family, and route to work link him to the times and places of all the murder victims; he passed three streets roughly at the same time as Ripper murders happened there, and another happened on the street where his mother lived. His occupation as a meat cart driver would have allowed his blood-splattered appearance to escape suspicion.[96][97][98][99][100]
Jacob Levy
Jacob Levy (1856 – 29 July 1891) was born in Aldgate in 1856. He followed in his father’s trade as a butcher, and by 1888 he was living in Middlesex Street with his wife and children, which was right in the heart of Ripper territory (and close to where Catherine Eddowes was murdered). Levy contracted syphilis from a prostitute, making revenge a probable motive, and he was a butcher with the necessary skills to remove certain organs from the victims.[101]
James Maybrick

James Maybrick (24 October 1838 – 11 May 1889) was a Liverpool cotton merchant. His wife Florence was convicted of poisoning him with arsenic in a sensational, and possibly unjust, trial presided over by Sir James Fitzjames Stephen, the father of another modern suspect James Kenneth Stephen.[102] In her book, Jack the Ripper: The American Connection author Shirley Harrison asserted James Maybrick was both Jack the Ripper and the Servant Girl Annihilator of Austin, Texas. A diary purportedly by Maybrick, published in the 1990s by Michael Barrett, contains a confession to the Ripper murders. In 1995, Barrett confessed to writing the diary himself, and described the process of counterfeiting the diary in detail. He swore under oath that he and his wife, Anne, had forged it.[103] Anne Barrett, after their divorce, later denied forgery, and their story changed several times over the years. The diary was discredited by historians who pointed to factual errors in relation to some of the crimes,[104] and document experts pronounced the diary a fake; the handwriting does not match that of Maybrick's will,[105] and the ink contains a preservative not marketed until 1974.[106]
Alexander Pedachenko
Alexander Pedachenko (alleged dates 1857–1908) was named in the 1923 memoirs of William Le Queux, Things I Know about Kings, Celebrities and Crooks. Le Queux claimed to have seen a manuscript in French written by Rasputin stating that Jack the Ripper was an insane Russian doctor named Alexander Pedachenko, an agent of the Okhrana (the Secret Police of Imperial Russia), whose aim in committing the murders was to discredit Scotland Yard. He was supposedly assisted by two accomplices: "Levitski" and a tailoress called Winberg.[107] However, there is no hard evidence that Pedachenko ever existed, and many parts of the story as recounted by Le Queux fall apart when examined closely.[108] For example, one of the sources named in the manuscript was a London-based Russian journalist called Nideroest, who was known for inventing sensational stories. Reviewers of Le Queux's book were aware of Nideroest's background, and unabashedly referred to him as an "unscrupulous liar".[109] Pedachenko was promoted as a suspect by Donald McCormick, who may have developed the story by adding his own inventions.[110]
Walter Sickert
.jpg)
Walter Richard Sickert (31 May 1860 – 22 January 1942) was a German-born artist of British and Danish ancestry, who was first mentioned as a possible Ripper suspect in Donald McCormick's book The Identity of Jack the Ripper (1959).[111] He had a fascination with the Ripper murders, going so far as to stay in a room that was rumoured to have once had Jack the Ripper himself as a lodger, and depicted similar scenes in many of his paintings. Sickert subsequently appeared as a character in the royal/masonic conspiracy theory concocted by Joseph Gorman, who claimed to be Sickert's illegitimate son.[112] The theory was later developed by author Jean Overton Fuller, and by crime novelist Patricia Cornwell in her book Portrait of a Killer (2002). However, Sickert is not considered a serious suspect by most who study the case, and strong evidence shows he was in France at the time of most of the Ripper murders.[112][113][114]
Joseph Silver
South African historian Charles van Onselen claimed, in the book The Fox and the Flies: The World of Joseph Silver, Racketeer and Psychopath (2007), that Joseph Silver, also known as Joseph Lis, a Polish Jew, was Jack the Ripper.[115] Critics note, among other things, that van Onselen provides no evidence that Silver was ever in London during the time of the murders, and that the accusation is based entirely upon speculation. Van Onselen has responded by saying that the number of circumstances involved should make Silver a suspect.
James Kenneth Stephen

James Kenneth Stephen (25 February 1859 – 3 February 1892) was first suggested as a suspect in a biography of another Ripper suspect, Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale by Michael Harrison published in 1972. Harrison dismissed the idea that Albert Victor was the Ripper but instead suggested that Stephen, a poet and one of Albert Victor's tutors from Trinity College, Cambridge, was a more likely suspect. Harrison's suggestion was based on Stephen's misogynistic writings and on similarities between his handwriting and that of the "From Hell" letter, supposedly written by the Ripper. Harrison supposed that Stephen may have had sexual feelings for Albert Victor, and that Stephen's hatred of women arose from jealousy because Albert Victor preferred female company and did not reciprocate Stephen's feelings.[116] However, Harrison's analysis was rebutted by professional document examiners.[117] There is no proof that Stephen was ever in love with Albert Victor,[118] although he did starve himself to death very shortly after hearing of Albert Victor's death.[119][120]
Frank Spiering further developed the theory in his book Prince Jack (1978), which depicted Albert Victor as the murderer and Stephen as his lover. The book is widely dismissed as a sensational fiction based on previous theories rather than genuine historical research.[121] Spiering claimed to have discovered a copy of some private notes written by another suspect, Sir William Gull, in the library of the New York Academy of Medicine and that the notes included a confession by Albert Victor under a state of hypnosis. Spiering further suggested that Albert Victor died due to an overdose of morphine, administered to him on the order of Prime Minister Lord Salisbury and possibly Albert Victor's own father, Edward VII of the United Kingdom. The New York Academy of Medicine denies possessing the records Spiering mentioned,[122] and when Spiering was offered access to the Royal Archives, he retorted: "I don't want to see any files."[123]
Duke of Clarence and Avondale

Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale (8 January 1864 – 14 January 1892) was first mentioned in print as a potential suspect when Philippe Jullian's biography of Clarence's father, King Edward VII, was published in 1962. Jullian made a passing reference to rumours that Clarence might have been responsible for the murders. Though Jullian did not detail the dates or sources of the rumour, it is possible that the rumour derived indirectly from Dr. Thomas E. A. Stowell. In 1960, Stowell told the rumour to writer Colin Wilson, who in turn told Harold Nicolson, a biographer loosely credited as a source of "hitherto unpublished anecdotes" in Jullian's book. Nicolson could have communicated Stowell's theory to Jullian.[124][125] The theory was brought to major public attention in 1970 when an article by Stowell was published in The Criminologist that revealed his suspicion that Clarence had committed the murders after being driven mad by syphilis. The suggestion was widely dismissed, as Albert Victor had strong alibis for the murders, and it is unlikely that he suffered from syphilis.[126] Stowell later denied implying that Clarence was the Ripper[127] but efforts to investigate his claims further were hampered, as Stowell was elderly, and he died from natural causes just days after the publication of his article. The same week, Stowell's son reported that he had burned his father's papers, saying "I read just sufficient to make certain that there was nothing of importance."[128]
Subsequently, conspiracy theorists, such as Stephen Knight in Jack the Ripper: The Final Solution, have elaborated on the supposed involvement of Clarence in the murders. Rather than implicate Albert Victor directly, they claim that he secretly married and had a daughter with a Catholic shop assistant, and that Queen Victoria, British Prime Minister Lord Salisbury, his Freemason friends, and the Metropolitan Police conspired to murder anyone aware of Albert Victor's supposed child. Many facts contradict this theory and its originator, Joseph Gorman (also known as Joseph Sickert), later retracted the story and admitted to the press that it was a hoax.[129] Variations of the theory involve the physician Sir William Gull, the artist Walter Sickert, and the poet James Kenneth Stephen to greater or lesser degrees, and have been fictionalised in novels and films, such as Murder by Decree and From Hell.
Sir John Williams

Sir John Williams was obstetrician to Queen Victoria's daughter Princess Beatrice, and was accused of the Ripper crimes in the book, Uncle Jack (2005), written by one of the surgeon's descendants, Tony Williams, and Humphrey Price.[130] The authors claim that the victims knew the doctor personally, that they were killed and mutilated in an attempt to research the causes of infertility, and that a badly blunted surgical knife, which belonged to Williams, was the murder weapon.[131] Jennifer Pegg demonstrated in two articles that much of the research in the book was flawed; for example, the version of the notebook entry used to argue that Williams had met Ripper victim Mary Ann Nichols had been altered for print and did not match the original document, and the line as found in the original document was in handwriting that did not match the rest of the notebook.[132]
Williams' wife, Lizzie, was named as a possible suspect by author John Morris, who claims that she was unable to have children and, in an unhinged state, took revenge on those who could by killing them.[133][134]
Further theories
Other named suspects include Swiss butcher Jacob Isenschmid, German hairdresser Charles Ludwig, apothecary and mental patient Oswald Puckridge (1838–1900), insane medical student John Sanders (1862–1901), Swedish tramp Nikaner Benelius, and even social reformer Thomas Barnardo, who claimed he had met one of the victims (Elizabeth Stride) shortly before her murder.[135] Isenschmid and Ludwig were exonerated after another murder was committed while they were in custody.[136] There was no evidence against Barnardo, Benelius, Puckridge or Sanders.[137] According to Donald McCormick, other suspects included mountebank L. Forbes Winslow,[138] whose own suspect in the case was a religious maniac, G. Wentworth Bell Smith.[139] Most recently, morgue assistant Robert Mann was added to the long list of suspects.[140]
Named suspects who may be entirely fictional include "Dr Stanley",[141] cult leader Nicolai Vasiliev,[142] Norwegian sailor "Fogelma",[143] and Russian needlewoman Olga Tchkersoff.[144]
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle advanced theories involving a female murderer dubbed "Jill the Ripper". Supporters of this theory believe that the murderer worked, or posed, as a midwife, who could be seen with bloody clothes without attracting suspicion and would be more easily trusted by the victims than a man.[145] Women proposed as the Ripper include the convicted murderers Mary Pearcey[146] and Constance Kent,[147] and Theosophist Helena Blavatsky.[81] The 19 December 1893 edition of the Ohio Marion Daily Star reported that Lizzie Halliday, a mentally ill Irish immigrant suspected of leaving a string of dead husbands in her wake before being arrested in upper New York State for the murder of two women and her last husband, was likewise accused of the Whitechapel murders, of which she spoke "constantly". She denied any relation to them and there was no evidence to contradict her claim.[148]
Some Ripper authors, such as Patricia Cornwell, believe the killer sent letters to the police and press.[149] DNA analysis of the gum used on a postage stamp of one of these letters was "inconclusive" and "not forensically reliable".[150] The available material has been handled many times and is therefore too contaminated to provide any meaningful results.[151] Moreover, most authorities consider the letters hoaxes.[152] Nevertheless, a descendant of notorious American serial killer H. H. Holmes used these handwriting samples in an attempt to link Holmes to the Ripper case.[153]
Several theorists suggest that "Jack the Ripper" was actually more than one killer. Stephen Knight argued that the murders were a conspiracy involving multiple miscreants,[154] whereas others have proposed that each murder was committed by unconnected individuals acting independently of each other.[155] Author Frank Pearse, who purports to have access to a written confession, argues that the murders were performed by a man named John Pavitt Sawyer (who held multiple similarities, such as location and profession, to alternate suspect George Chapman), as part of an occult Freemason initiation.[156]
The police believed the Ripper was a local Whitechapel resident.[157] His apparent ability to disappear immediately after the killings suggests an intimate knowledge of the Whitechapel neighbourhood, including its back alleys and hiding places.[158] However, the population of Whitechapel was transient, impoverished and often used aliases. The lives of many of its residents were little recorded. The Ripper's true identity will almost certainly never be known.
Notes
- ↑ Whiteway, Ken (2004). "A Guide to the Literature of Jack the Ripper". Canadian Law Library Review vol.29 pp.219–229
- ↑ Eddleston, pp.195–244
- 1 2 3 Evans and Rumbelow, p. 261
- 1 2 3 "The Suspects". Metropolitan Police. Retrieved 1 October 2014.
- ↑ e.g. Dr Winslow, the examining pathologist, quoted in Haggard, Robert F. (1993). "Jack the Ripper As the Threat of Outcast London". Essays in History. Volume 35. Corcoran Department of History at the University of Virginia. Accessed 17 July 2008
- ↑ e.g. Letter from Thomas Bond to Robert Anderson, 10 November 1888, quoted in Rumbelow, pp.145–147; Dr Percy Clark, assistant to George Bagster Phillips interviewed in the East London Observer, 14 May 1910, quoted in Cook, Jack the Ripper, p. 187 and Evans and Rumbelow, p. 238
- ↑ Rumbelow, p.274; Inspector Donald Swanson's report to the Home Office, 19 October 1888, HO 144/221/A49301C, quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 206
- ↑ Inspector Donald Swanson's report to the Home Office, 19 October 1888, HO 144/221/A49301C, quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 205; Evans and Rumbelow, p. 113; Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, p. 125
- 1 2 Rumbelow, p.155
- ↑ Marriott, pp. 233–234
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 260
- ↑ Fido, p. 203; Marriott, pp. 231–234; Rumbelow, p. 157
- ↑ Marriott, p. 223
- ↑ Interview in the Pall Mall Gazette, 31 March 1903, quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 264
- ↑ Rumbelow, pp.188–193; Sugden, p. 441.
- ↑ Adam, Hargrave Lee (1930), The Trial of George Chapman, William Hodge, quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 281; Evans and Rumbelow, p. 229; Fido, p. 177; and Rumbelow, p.193
- ↑ Pall Mall Gazette, 24 March 1903 and 31 March 1903, quoted in Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 646–651
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 282; Cullen, p. 204; Evans and Rumbelow, p. 229; Marriott, p. 247; Rumbelow, p.195; Detective Inspector Edmund Reid quoted in Evans and Rumbelow, p. 237
- ↑ Colney Hatch Register of Admissions, quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 269
- ↑ Macnaghten's notes quoted by Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 584–587; Fido, pp. 147–148 and Rumbelow, p. 142
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 269; Evans and Rumbelow, p. 243; Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, p. 635; Rumbelow, p.179
- ↑ Quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 266; Evans and Rumbelow, p. 236; Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 626–633 and Fido, p. 169
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 276; Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 249–253; Rumbelow, p. 182
- ↑ Evans and Rumbelow, p. 255
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, pp. 269–270; Marriott, p. 238; Fido, p. 215
- ↑ Asylum case notes quoted by Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 270 and Fido, pp. 216, 228
- ↑ Douglas, John; Olshaker, Mark (2001). The Cases That Haunt Us. New York: Simon and Schuster. pp. 89.
- ↑ "Jack the Ripper unmasked by amateur sleuth as Aaron Kosminski". Mail Online. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
- ↑ "Jack the Ripper identified as Aaron Kosminski from 126 year old DNA from blood on the shawl of victim Catherine Eddowes". Daily KOS. Retrieved 9 September 2014.
- ↑ "Jack the Ripper: Scientist who claims to have identified notorious killer has 'made serious DNA error'", The Independent, 19 October 2014
- ↑ Sugden, p. 433
- ↑ Marriott, p. 250
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 277; Sugden, pp. xix
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 277; Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, p. 591
- 1 2 Marriott, p. 251
- ↑ Report by Inspector Joseph Helson, CID 'J' Division, in the Metropolitan Police archive, MEPO 3/140 ff. 235–8, quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 99 and Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, p. 24
- ↑ Rumbelow, p. 49
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, p. 48
- ↑ O'Connor, T. P. (1929). Memoirs of an Old Parliamentarian. London: Ernest Benn. Vol. 2, p. 257, quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 166 and Cook, Jack the Ripper, pp. 72–73
- ↑ Evans and Rumbelow, p. 213
- ↑ Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 218–222; Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 141
- ↑ Macnaghten's notes quoted in Rumbelow, p.143
- ↑ Rumbelow, p. 266; Whitehead and Rivett, p. 126
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 611–616; Rumbelow, p. 266; Whitehead and Rivett, p. 126
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, p. 126
- ↑ Roscoe, Theodore (1959) The Web of Conspiracy, Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall, Inc., pp. 301–302, 502.
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, p. 621
- ↑ Sugden, pp. xxv
- ↑ News dispatch in Ludington Record, 20 December 1888.
- ↑ "Something About Dr. Tumblety." The New York Times, 23 November 1888, quoted in Rumbelow, p. 266
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, p. 616
- ↑ Chief Inspector Byrnes quoted in Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 280
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 203
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 165; Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 105; Rumbelow, pp. 105–116
- ↑ Letter dated 5 October 1888 from "M.P." to City of London Police, Corporation of London Records Office, quoted in Evans and Rumbelow, p. 277 and Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 149; letter dated 4 October 1888 from Mrs S Luckett of 10 Somerford Grove to City of London Police, Corporation of London Records Office, quoted in Evans and Rumbelow, p. 283
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, pp. 207–208
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 209
- 1 2 Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 212; Rumbelow, p. 206
- ↑ Bell, Donald (1974), "Jack the Ripper – The Final Solution?", The Criminologist vol. 9, no. 33, quoted in Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 212 and Rumbelow, pp. 206–207
- ↑ Marjoribanks, Edward, The Life of Sir Edward Marshall Hall, quoted in Rumbelow, p. 208
- ↑ Rumbelow, pp. 206–208
- ↑ Rumbelow, pp. 141–142
- ↑ Moore, Wendy; Leach, Ben (8 November 2008). "Broadmoor files could unmask Jack the Ripper". London: The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 22 January 2010.
- ↑ Begg, Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, p. 284; Cook, pp. 198–199; Marriott, p.235; Rumbelow, pp.141–142; Whitehead and Rivett, pp. 105, 110
- ↑ Quoted in Whitehead and Rivett, p. 110
- ↑ Hodgson, Peter Jack the Ripper Through the Mists of Time
- ↑ Fido, p. 182; Rumbelow, p. 268
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 214
- ↑ Pall Mall Gazette, 8 April 1892, quoted in Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 577–578
- ↑ "Deeming at the Gallows; The Wife Murderer Hanged at Melbourne This Morning". The New York Times. 23 May 1892. p. 1.
- ↑ Prime Suspect, Jack The Ripper, Discovery channel, 2011, Narration by Dennis Cometti
- ↑ In the second edition of his book, Jack The Ripper: The 21st Century Investigation (John Blake Publishing, 2007) ISBN 978-1-84454-370-0
- ↑ Vanderlinden, Wolf (2008). "Carl Ferdinand Feigenbaum: An Old Suspect Resurfaces", in Ripper Notes: The Legend Continues, Inklings Press, pp. 4–24, ISBN 978-0-9789112-2-5
- ↑ Mallett, Xanthé (31 August 2011). "Is this the face of Jack the Ripper?". BBC News. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- ↑ Woods and Baddeley, pp. 179–181
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 608–609
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 606–608
- 1 2 Rumbelow, pp. 254–258; Woods and Baddeley, pp. 181–182
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell, p. 204
- ↑ Dimolianis, chapter 4
- 1 2 Whitehead and Rivett, p. 115
- 1 2 Rumbelow, p. 262; Whitehead and Rivett, pp. 122–123
- ↑ Rumbelow, p. 262
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, p. 123
- ↑ Woods and Baddeley, p. 61
- ↑ Fido quoted in Rumbelow, pp.180–181
- ↑ Fido, pp. 215–219
- ↑ Fido, p. 220
- ↑ Douglas, John; Olshaker, Mark (2001). The Cases That Haunt Us. New York: Simon and Schuster. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-0-7432-1239-7.
- ↑ Douglas, John; Olshaker, Mark (2001). The Cases That Haunt Us. New York: Simon and Schuster. pp. 72–4. ISBN 978-0-7432-1239-7.
- ↑ Cullen, p. 180; Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 190–192; Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 376–377; Fido, p. 96; Marriott, p. 263
- ↑ Inspector Abberline's report, 12 November 1888, Metropolitan police archives, MEPO 3/140 ff. 230–2, quoted in Begg,Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History, pp. 238–239 and Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 377–378
- ↑ Cook, Jack the Ripper, p. 176
- ↑ Marriott, p. 263
- ↑ Tully, Jim, Prisoner 1167: The madman who was Jack the Ripper .
- ↑ "Jack The Ripper: The Missing Evidence". Five.
- ↑ "Aberystwyth University – November". aber.ac.uk.
- ↑ http://www.casebook.org/dissertations/rip-charles-cross-was-jtr.html Ripper casebook
- ↑ Jack the Ripper was Whitechapel meat cart driver, claims criminologist
- ↑ EXCLUSIVE: Police overlooked Ripper 'hiding in plain sight'
- ↑ Roland, Paul The Crimes of Jack the Ripper: The Whitechapel Murders Re-Examined pp. 276-278
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, p. 124
- ↑ Affidavit of Michael Barrett, 5 January 1995, quoted in Marriott, pp.272–277
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, p. 125
- ↑ Marriott, p.272; Rumbelow, pp.252–253
- ↑ Rumbelow, p.251
- ↑ Le Queux, quoted in Rumbelow, p. 197 and Whitehead and Rivett, p. 103
- ↑ Begg, p. 309
- ↑ Quoted in Rumbelow, p.198
- ↑ Woods and Baddeley, p. 147
- ↑ Knight, p.250
- 1 2 Baron, Wendy (September 2004). "Sickert, Walter Richard (1860–1942)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Accessed 18 June 2008. (Subscription required)
- ↑ Ryder, Stephen P. "Patricia Cornwell and Walter Sickert: A Primer". Casebook: Jack the Ripper. Retrieved 10 March 2008.
- ↑ Sturgis, Matthew (3 November 2002). "Making a killing from the Ripper". The Sunday Times
- ↑ "Historian claims to identify Jack the Ripper". CTV Television Network. 2007-05-02. Retrieved 11 August 2007.
- ↑ Harrison, Michael (1972). Clarence: The life of H.R.H. the Duke of Clarence and Avondale (1864–1892). London and New York: W. H. Allen. ISBN 0-491-00722-1. pp.164–181
- ↑ Mann, Thomas J. (1975). World Association of Document Examiners Journal vol.2 no.1, quoted in Rumbelow, p.219
- ↑ Aronson, Theo (1994). Prince Eddy and the Homosexual Underworld. London: John Murray. ISBN 0-7195-5278-8. p.117
- ↑ Aronson, p.105
- ↑ McDonald, Deborah The Prince, His Tutor and the Ripper 2007 McFarland Press
- ↑ Meikle, p.177; Rumbelow, p.244 and Trow, p.153
- ↑ Letter from the New York Academy of Medicine, 13 January 1986, quoted in Rumbelow, p.244
- ↑ Spiering quoted in Rumbelow, p.244
- ↑ Evans, Stewart P. (October 2002). "On the Origins of the Royal Conspiracy Theory". Ripper Notes. Published online by Casebook: Jack the Ripper. Accessed 6 May 2008.
- ↑ Cook, Andrew (2006). Prince Eddy: The King Britain Never Had. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Tempus Publishing Ltd. ISBN 0-7524-3410-1. pp.8–9
- ↑ e.g. Rumbelow, pp.211–213
- ↑ Stowell, T. E. A. (9 November 1970). "Jack the Ripper". The Times p.9; Issue 58018; col.F
- ↑ PHS (14 November 1970). "The Times Diary: Ripper file destroyed". The Times p.12; Issue 58023; col.E
- ↑ The Sunday Times, 18 June 1978, quoted in Rumbelow, p.237
- ↑ Williams, Tony; Price, Humphrey (2005). Uncle Jack. London: Orion. ISBN 978-0-7528-6708-3
- ↑ Quoted in Whitehead and Rivett, pp. 128–129
- ↑ Pegg, Jennifer (October 2005). "Uncle Jack Under the Microscope". Ripper Notes issue #24. Inklings Press. ISBN 0-9759129-5-X.
* Pegg, Jennifer (January 2006). "'Shocked and Dismayed': An Update on the Uncle Jack Controversy". Ripper Notes issue #25, pp.54–61. Inklings Press. ISBN 0-9759129-6-8 - ↑ British author claims serial killer ‘Jack the Ripper' was a woman in new book (9 May 2012), Herald Sun.
- ↑ John Morris (2012). Jack the Ripper: The Hand of a Woman. Seren Books. ISBN 978-1-85411-566-9.
- ↑ Davenport-Hines, Richard (2004). "Jack the Ripper (fl. 1888)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. Subscription required for online version.
- ↑ Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 86–88
- ↑ Evans and Rumbelow, pp. 88, 80
- ↑ Cullen, p. 91
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, p. 109
- ↑ Trow, Mei J (2009). Jack the Ripper: Quest for a Killer. Pen & Sword Books. ISBN 978-1-84563-126-0
- ↑ Promoted by Leonard Matters in his book The Mystery of Jack the Ripper (1929), quoted in Meikle, pp. 74–75 and Whitehead and Rivett, p. 101
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, pp. 104–105
- ↑ Whitehead and Rivett, p. 111
- ↑ Promoted by E. T. Woodhall in his book Jack the Ripper: Or When London Walked in Terror (1937), quoted in Whitehead and Rivett, pp. 101–102
- ↑ Ackroyd, Peter, "Introduction", in Werner, p. 17
- ↑ Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, p. 577
- ↑ Meikle, p. 65
- ↑ Casebook: Jack the Ripper. Retrieved 31 July 2014
- ↑ Cornwell, Patricia (2002). Portrait of a Killer. G.P. Putnam's Sons. ISBN 0-399-14932-5
- ↑ Marks, Kathy (18 May 2006). "Was Jack the Ripper a Woman?" The Independent, retrieved 5 February 2009
- ↑ Meikle, p. 197; Rumbelow, p. 246
- ↑ See for example, Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 178–188
- ↑ McCormack, Simon (3 December 2012). "Was Jack The Ripper H.H. Holmes? Serial Killer's Relative Says He Has Proof". Huffington Post.
- ↑ Knight, Stephen (1976). Jack the Ripper: The Final Solution.
- ↑ e.g. Turnbull, Peter (1996). The Killer Who Never Was: A Re-appraisal of the Whitechapel Murders of 1888. ISBN 1-900540-00-2
- ↑ Pearse, Frank (2012). Hidden Suspect - The Whitechapel Murders. Egerton-Bear. ASIN B0077P43ZY.
- ↑ Robert Anderson's memoirs, quoted in Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 626–633
- ↑ A "Scotland Yard official" quoted in the Pall Mall Gazette, 8 April 1892, quoted in Evans and Skinner, The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook, pp. 577–578
References
- Begg, Paul (2003). Jack the Ripper: The Definitive History. London: Pearson Education. ISBN 0-582-50631-X
- Begg, Paul (2006). Jack the Ripper: The Facts. Robson Books Ltd. ISBN 1-86105-870-5
- Begg, Paul; Fido, Martin; Skinner, Keith (1996). The Jack the Ripper A-Z Headline Book Publishing. ISBN 0-7472-5522-9
- Cook, Andrew (2009). Jack the Ripper. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Amberley Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84868-327-3
- Cornwell, Patricia (2002). Portrait of a Killer. G.P. Putnam's Sons. ISBN 0-399-14932-5
- Cullen, Tom (1965). Autumn of Terror. London: The Bodley Head.
- Dimolianis, Spiro (2011). Jack The Ripper & Black Magic: Victorian Conspiracy Theories, Secret Societies & the Supernatural Mystique of the Whitechapel Murders. McFarland & Co. ISBN 978-0-7864-4547-9
- Eddleston, John J. (2002). Jack the Ripper: An Encyclopedia. London: Metro Books. ISBN 1-84358-046-2.
- Evans, Stewart P.; Rumbelow, Donald (2006). Jack the Ripper: Scotland Yard Investigates. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton Publishing. ISBN 0-7509-4228-2.
- Evans, Stewart P.; Skinner, Keith (2001). Jack the Ripper: Letters from Hell. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton Publishing. ISBN 0-7509-2549-3.
- Evans, Stewart P.; Skinner, Keith (2002). The Ultimate Jack the Ripper Sourcebook: An Illustrated Encyclopedia. Constable and Robinson. ISBN 1-84119-452-2
- Fido, Martin (1987). The Crimes, Detection and Death of Jack the Ripper. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-79136-2
- Jakuboski, Maxim; Braund, Nathan (2005). Jack the Ripper. Castle Books. ISBN 0-7858-1616-X
- Knight, Stephen (1976; rev. 1984; repr. 2000). Jack the Ripper: The Final Solution. London: Bounty Books. ISBN 0-7537-0369-6.
- Marriott, Trevor (2005). Jack the Ripper: The 21st Century Investigation. London: John Blake. ISBN 1-84454-103-7.
- Meikle, Denis (2002). Jack the Ripper: The Murders and the Movies. Richmond, Surrey: Reynolds and Hearn Ltd. ISBN 1-903111-32-3.
- Rumbelow, Donald (2004). The Complete Jack the Ripper: Fully Revised and Updated. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-017395-1.
- Stewart, William (1939). Jack The Ripper: A New Theory. Quality Press.
- Sugden, Philip (2002). The Complete History of Jack the Ripper. London: Robinson. ISBN 0-7867-0276-1.
- Trow, M. J. (1997). The Many Faces of Jack the Ripper. Chichester, West Sussex: Summersdale. ISBN 1-84024-016-4.
- Werner, Alex (editor) (2008). Jack the Ripper and the East End. London: Chatto & Windus. ISBN 978-0-7011-8247-2
- Whitehead, Mark; Rivett, Miriam (2006). Jack the Ripper. Harpenden, Hertfordshire: Pocket Essentials. ISBN 978-1-904048-69-5
- Woods, Paul; Baddeley, Gavin (2009). Saucy Jack: The Elusive Ripper. Hersham, Surrey: Ian Allan Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7110-3410-5