List of military equipment of Sweden
This is a list of the military equipment of Sweden, including the army, air force and navy.
Army
The Swedish army consists of 30,000 active troops along with 22,988 military reserves and 38,000 militias. Including storaged equipment still operational, the Swedish army possesses: 280 tanks, 212 tank destroyers, around 1,300 APCs, 860 IFVs, 11,300 utility vehicles, 220 mortars, and currently 4 (24 when all are delivered) 155 mm self-propelled artillery pieces. Sweden lacks conventional multiple rocket launchers, but instead relies on fast-moving vehicles equipped with guided anti-tank missiles. Long-range tactical missiles that could normally be launched from MRLs are instead assigned to the air force and navy. The Swedish military as a whole operates several hundred such missiles.
Utility vehicles: 11,308++
Armored personnel carriers: 1,267
Infantry fighting vehicles: 859
Tanks: 120 in active service (240 total including in storage)
Towed artillery pieces: 220+ (Mortars, all towed howitzers have been withdrawn from service)
Self-propelled artillery pieces: 4 in active service (24 when all delivered)
Small arms
| Name | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Pistol 88 | | Semi-automatic pistol | Glock 17 (pist 88) Glock 19 (pist 88B) | Unknown | Current standard-issue sidearm |
 CBJ-MS | | Submachine gun Personal defense weapon Assault weapon Light support weapon | - - - - | Unknown | Not yet in active service; will replace older submachine guns |
 H&K MP5 | | Submachine gun | Unknown | Unknown | Mainly used by police |
| Ak 4 | | Battle rifle | Ak 4 Ak 4B Ak 4OR | Unknown | Former standard-issue battle rifle Red dot sight; Current standard-issue for the Home Guard 4x24 telescopic sight |
| Ak 5 | | Assault rifle Designated marksman rifle Assault rifle Assault rifle Carbine Police combat rifle | FFV Ak 5 FFV Ak 5B Bofors Ak 5C Bofors Ak 5CF Bofors Ak 5D CGA5P | Unknown Unknown Unknown 40,000 Unknown Unknown | Standard-issue assault rifle 4x tritium sight Multiple modifications by Bofors Multiple modifications by Bofors Lightweight carbine version Semi-automatic version with improved accuracy |
Diemaco C8SFW | | Assault carbine | C8SFW | Unknown | [1] |
 Ag 90 | | Anti-materiel rifle | Ag 90A Ag 90B Ag 90C | Unknown | - - - |
| Psg 08 | | Sniper rifle | TRG-42 | Unknown | Current standard-issue sniper rifle |
| Psg 90 | | Sniper rifle | AW | Unknown | - |
| Förstärkningsvapen 870 | | Shotgun | Unknown | - | |
| HK21 | | General-purpose machine gun | Unknown | - | |
 Ksp 58 | | General-purpose machine gun | Unknown | - | |
 Ksp 90 | | Light machine gun | Ksp 90 Ksp 90B | Unknown | - |
 Ksp m/39 | | Medium machine gun | Unknown | - | |
 Ksp m/42 | | Medium machine gun | Ksp m/42 Ksp m/42B | Unknown | Phased out of service, replaced by the Ksp m/39 |
 Ksp m/94 | | Armament on Leopard tanks | Unknown | - | |
| Ksp 95 | | Armament on ex-East German Pbv401-series | Unknown | - | |
 Tksp 12,7 mm | | Heavy machine gun | Unknown | - | |
 Grsp 40 mm | | Automatic grenade launcher | Unknown | - | |
 Granattillsats 40 mm Ak | | Grenade launcher | Unknown | - | |
 Grg m/48 | | Multirole recoilless rifle | Unknown | Former standard-issue anti-tank weapon | |
 Pskott m/86 | | Anti-tank weapon | Unknown | Current standard-issue anti-tank weapon | |
| BILL 2 | | Anti-tank guided weapon | Unknown | - | |
 RB 57 | | Anti-tank missile launcher | Unknown | - | |
 RBS 55 | | Anti-tank guided weapon | Unknown | - | |
| RBS 56 | | Anti-tank guided weapon | Unknown | - | |
 RBS 70 | | Man-portable air defense system | Unknown | - | |
Utility vehicles
| Vehicle | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Ptgb 5 | | 4x4 utility vehicle | Unknown | - | |
 RG-32M Galten | | Mine-resistant 4x4 vehicle | 260 | Additional 120 on order | |
Terrängbil 11 | | 4x4 infantry truck 4x4 anti-tank vehicle 6x6communications vehicle 6x6 infantry truck 6x6 communications vehicle 6x6 ambulance 6x6 artillery spotter 6x6 armored personnel carrier MANPADS carrier | Tgb 11 Tgb 1111 Tgb 1112 Tgb 13 Tgb 1313 Tgb 1314 Tgb 1321 Tgb 21 Tgb 22 | Roughly 6,500 | - Equipped with the Pvpj 1110 90mm recoilless gun - - - - - - Equipped with the RBS 70 |
 Bv 202 | | All-terrain carrier | 5,000 produced | To be replaced by Bv 206 | |
 Bv 206 | All-terrain carrier Military ambulance Military firefighting apparatus Improved intelligence vehicle Mobile military radio transmitter | Bv 206 Bv 206A Bv 206F Bv 2064 Bv2068 | Totally 4,500+ |
Current main transport vehicle | |
| BvS 10 | | All-terrain carrier | 48 | Additional 127 on order | |
Armoured Personnel Carriers
| Name | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOWAG Piranha | | Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | Piranha IIIC | 33 | - |
 Patria AMV | | Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | 113 | - | |
 Patria Pasi | | Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | XA-180S XA-202S XA-203S | 200 in total | - |
 Bv 206 | | Tracked armoured personnel carrier | Bv 206S | 50 | |
 Pbv 302 | | Tracked armoured personnel carrier | 194[2] | To be replaced by CV90 | |
 Pbv 401 | | Tracked armoured personnel carrier | 460 | 147 in active service, 313 to be sold to Finland | |
 Pbv 4020 | | Tracked armoured personnel carrier Command vehicle Military ambulance | Pbv 4020 Stripbv 4021 Sjvpbv 4024 | 38 12 10 | 60 in total, may be phased out of service |
| M113 | | Tracked armoured personnel carrier | 1 | For evaluation purpose | |
Infantry Fighting Vehicles
| Vehicle | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Strf 90 | | Tracked infantry fighting vehicle | CV9040 CV9040A CV9040B CV9040C | 354[3] | Main infantry fighting vehicle |
Tanks
| Vehicle | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Ikv 91 | | Tank destroyer | Ikv 91 | 0[4] | |
.jpg) Strv 121 | | Main battle tank | Strv 121 | 12[5] | |
 Strv 122 | Main battle tank Armoured recovery vehicle Combat engineering vehicle | Strv 122 A/B Bgbv 120 Pionierpanzer 3 Kodiak | 120[6] Unknown 0 |
On order | |
Artillery and mortars
| Name | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 M/41D | | Heavy mortar | 600 | 120mm caliber mortar | |
.jpg) Haubits FH77 | | Towed howitzer | FH77 A FH77 B | 0[7] | To be replaced by Artillerisystem 08 |
| PvBv 2062 | | Mobile anti-tank gun | Unknown | Equipped with Pvpj 1110 90mm recoilless gun | |
| PvBv 2063 | | ATGM carrier | Unknown | Equipped with Rbs 55 or Rbs 56 | |
| Pvrbbv 551 | ATGM carrier | Unknown | May be phased out of service; equipped with Rbs 55[8] | ||
 Pvrbbv 452 | | ATGM carrier | Unknown | Equipped with Rbs 56 | |
| SSG120 | | Self-propelled mortar system | GRKPBV90120 | Unknown | - |
 Bkan 1 | | Self-propelled artillery | Bkan 1A Bkan 1C | 0 | Phased out of service in 2003; in storage |
 Panzerhaubitze 2000 | | Self-propelled artillery | PzH 2000 | 0 | Slightly modified, to be replaced by Artillerisystem 08 |
 Artillerisystem 08 | | Self-propelled artillery | FH77BW L52 | 4[9] | Next-generation artillery system |
 Bofors 40 mm | | Anti-aircraft autocannon | Bofors L/60 Bofors L/70 | Unknown | - |
 MIM-23 Hawk | | Surface-to-air missile | RBS 77 RBS 97 | 8 launchers | Unknown number of missiles, at least 24 |
 Lvrbpbv 4016 | | MANPADS carrier | 147 in service 313 may be sold to Finland | Equipped with RBS 70 | |
| Lvrbv 701 | MANPADS carrier | 49 | Equipped with RBS 70[10] | ||
Navy
Sweden possesses highly sophisticated stealth and radar technology. For example, during an exercise outside California, the HMS Gotland managed to penetrate the massive defensive measures of an entire American carrier group, "sinking" the USS Ronald Reagan among other ships. While the Gotland-class still hasn't been surpassed in terms of stealth, Sweden is already working on an improved diesel-electric submarine: the A26. The first out of two A26 submarines will be laid down at the end of 2012.
Corvettes
| Ship | Quantity | Names | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Stockholm class | 2 | K11 - HMS Stockholm K12 - HMS Malmö | | Equipped with stealth technology |
 Göteborg class | 4 | K21 - HMS Göteborg K22 - HMS Gävle K23 - HMS Kalmar K24 - HMS Sundsvall | | - |
 Visby class | 5 | K31 - HMS Visby K32 - HMS Helsingborg K33 - HMS Härnösand K34 - HMS Nyköping K35 - HMS Karlstad | | Equipped with advanced stealth technology |
Minesweepers
| Ship | Quantity | Names | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Styrsö class | 4 | M11 - HMS Styrsö M12 - HMS Spårö M13 - HMS Skaftö M14 - HMS Sturkö | | - |
_and_RSS_Bedok_(M105)_at_Changi_Naval_Base%2C_Singapore_-_20070527.jpg) Landsort class | 2 | M71 - HMS Landsort M72 - HMS Arholma | | Will be replaced by the Koster class |
.jpg) Koster class | 5 | M73 - HMS Koster M74 - HMS Kullen M75 - HMS Vinga M76 - HMS Ven M77 - HMS Ulvön | | Improved version of the Landsort class |
Patrol boats
| Ship | Quantity | Names | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Tapper class | 12 | 81 - HMS Tapper 82 - HMS Djärv 83 - HMS Dristig 84 - HMS Händig 85 - HMS Trygg 86 - HMS Modig 87 - HMS Hurtig 88 - HMS Rapp 89 - HMS Stolt 90 - HMS Ärlig 91 - HMS Munter 92 - HMS Orädd | | - |
 Jägaren class | 1 | V150 - HMS Jägaren | | - |
 Stridsbåt 90 | 147[11] | Unknown | | - |
 Stridsbåt 90 E | 5 | Unknown | | - |
| Stridsbåt 2010 | 1 | Unknown | | With 2x 120 mm mortars |
Submarines
| Submarine | Quantity | Names | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
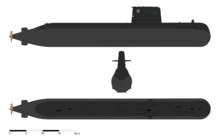 Gotland class | 3 | HMS Gotland HMS Halland HMS Uppland | | Equipped with unsurpassed stealth capacity |
Södermanland class | 2 | HMS Södermanland HMS Östergötland | | |
| A26 | 0 (2) | Unknown | | Was intended to enter service 2018-2019,[12] but was cancelled in February 2014 due to disagreements with ThyssenKrupp, the new owners of Kockums. A similar design might be built by Saab instead.[13] |
Auxiliary vessels
| Ship | Quantity | Name | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Belos | | Used as submarine rescue ship |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Arkösund | | Used as command vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Furusund | | Used as salvage vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Fårösund | | Used for mine warfare training |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Grundsund | | Used as command vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Orion | | Used as signals intelligence vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Pelikanen | | Used as torpedo salvage vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Pingvinen | | Used as torpedo salvage vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Sleipner | | Used as transport vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Trossö | | Used as command vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Urd | | Used as research vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Visborg | | Used as command vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Ägir | | Used as training vessel |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Carlskrona | | Used as command vessel and royal flagship |
Landing craft
| Ship | Quantity | Names | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
G class | 100 | Unknown | - | |
School ships
| Class | Quantity | Name | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A500 class | 5 | A501 - HMS Altair A502 - HMS Antares A503 - HMS Arcturus A504 - HMS Argo A505 - HMS Astrea | | - |
| M15 class | 3 | HSwMS M20 HSwMS M21 HSwMS M22 | | Used as a museum ship Possibly decommissioned Possibly decommissioned |
| Unknown | 2 | HMS Gladan HMS Falken | | Schooners used for naval training |
| Unknown | 1 | HMS Viksten | | Retired from military service, sold to Strömstads Gymnasium |
Coast Guard ships
The Swedish Coast Guard is a civilian government agency not directly linked to the Swedish navy. The Coast Guard possesses 22 surveillance craft, 12 environmental protection vessels, 2 multirole vessels, 5 hovercraft, 1 large barge and over 100 boats, totalling a force of more than 142 ships that can be deployed for military purposes, although lacking proper armament.
Air force
Due to recent cuts in defensive expenditures, about half of the JAS 39 Gripens will be taken out of active service and put into storage during 2012. As the threat from the Soviet Union is gone, there is no need to maintain a large air force since most possible enemies of Sweden lack the ability to shoot down a Gripen.
Nine JAS 39 Gripens was sent to protect Libyan civilians during the Libyan Civil War. No shots were fired by the aircraft, nor were they fired upon.
Between 2007 and 2008, a report from the Riksdag revealed what was called Flygsystem 2020 ("flight system 2020"), or FS 2020, a project to research and develop a fifth generation jet fighter with fully developed stealth capabilities by the year of 2020.
In 2012, it was announced that the Swedish government wishes to upgrade 70 Gripens to the NG/IN model by 2020, equipping them with a new engine, improved fuel capacity, higher payload and upgraded avionics.
Combat aircraft
The total number of combat aircraft and armed trainers in the Swedish air force is currently 217, and will in time be increased to 317-337.
| Aircraft | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 JAS 39A | Multirole fighter | 50 | Will be replaced by JAS 39E | |
 JAS 39B | Two-seat attack fighter | 13 | Will be replaced by JAS 39F | |
 JAS 39C | Multirole fighter | 60 | Current main combat aircraft | |
 JAS 39D | Two-seat multirole fighter | 11 | Primary two-seater version | |
 JAS 39 E/F | Multirole fighter | 0 (70) | Currently under construction | |
 Gripen Demo | Technology demonstrator | 1 | Prototype for development of the Gripen NG/IN | |
Sea Gripen | Carrier-based strike fighter | 0 | Currently under development; intended for the Indian air force | |
| FS 2020 | Stealth air superiority fighter | 0 | Currently under development[14] | |
 Dassault nEUROn | Stealth unmanned combat air vehicle | 0 | Currently under development | |
Saab J 32U Lansen | Fighter and attack aircraft | 2 | Used for training purposes | |
 Saab 105 | Trainer and light attack aircraft | 80 | Trainer, but can be equipped for ground attack missions | |
Non-combat aircraft
| Aircraft | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 C-130 | Heavy transport aircraft | 6 | Primary transport aircraft | |
.jpg) S 102B Korpen | Signals intelligence aircraft | 2 | Modified version of the Gulfstream IV, equipped for SIGINT purposes | |
.jpg) TP 102A | VIP transport | 1 | Royal Family transport | |
.jpg) TP 102C | VIP transport | 1 | Prime minister's transport | |
.jpg) TP 100 | VIP passenger aircraft | 8 | - | |
 S 100 | Airborne early warning and control | 2 | Previously 6 in service, sold to other countries | |
 UAV 02 Falken | Unmanned aerial vehicle | 48 | The smallest aircraft in the Swedish Royal Air Force, used for battlefield reconnaissance | |
UAV 03 Örnen | Unmanned aerial vehicle | 8 | - | |
 UAV 04 Svalan | Unmanned aerial vehicle | 3 | - | |
| UAV 05B Korpen | Unmanned aerial vehicle | 12 | Deployed by the SOG | |
Helicopters
| Aircraft | Origin | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
_10410_90_(8373587581).jpg) HKP 10 | MEDEVAC helicopter | 20 | Originally a utility helicopter, upgraded for MEDEVAC duties | |
_15025_25_(8392481059).jpg) HKP 15 | Utility helicopter | 20 | - | |
_161227_02_(8358593585).jpg) HKP 16 | Utility helicopter | 15 | - | |
_142045_45_(8363167092).jpg) HKP 14 | Utility helicopter | 3-5 | 18 (9 TTH, 9 NFH) to be delivered by 2018 | |
Weapons and munitions
| Name | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mauser BK-27 | | 27 mm revolver cannon | Unknown | Primary gun for JAS 39 | |
| Mark 82 | | 227 kg unguided bomb | BLU-111A/B BLU-111B BLU-126B Mark 62 Quickstrike mine | Unknown | Added thermal-protective coating Less sensentive explosive filler Lowered collateral damage for close support Naval mine version |
| GBU-12 Paveway II | | 227 kg laser-guided bomb | Unknown | - | |
| Bk.90 | | 600 kg cluster bomb | Unknown | Banned from service, but not withdrawn | |
| RBS-15 | | Air-to-surface/anti-ship missile | RBS-15F Mk2 | Unknown | - |
| METEOR | | Radar-guided air-to-air missile | 0 | Currently under development; will reach IOC in 2016 | |
| Rb.71 | | Semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile | British Aerospace Skyflash | Unknown | - |
| Rb.74 | | Heat-seeking air-to-air missile | AIM-9M Sidewinder | Unknown | - |
| Rb.75 | | Air-to-ground tactical missile | AGM-65B Maverick | 500 | - |
| Rb.98 | | Heat-seeking air-to-air missile | IRIS-T | 400 | Developed in collaboration between many EU countries, including Sweden |
| Rb.99 | | Active radar homing air-to-air missile | AIM-120B | Unknown | - |
See also
Sources and further reading
- Home page of the Swedish Armed Forces
- http://www.soldf.com/
- See article links for further information on specific equipment
References
- ↑ "Vapnen slutade fungera - mitt under eldstrid". Expressen. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 139.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 139.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 139.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 139.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 139.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 139.
- ↑ http://hem.passagen.se/pgroen/pvrbbv551.htm
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 134.
- ↑ http://hem.passagen.se/pgroen/pvrbbv551.htm
- ↑ The Military Balance 2014. p. 140.
- ↑ "Sverige ska satsa på nya ubåtar". SvD.se. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- ↑ Karlskrona TT. "FMV avbryter ubåtsförhandling". SvD.se. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- ↑ Limén, Helene. Rapport från Riksdagen 2007/08:RFR8. Försvarsutskottets ansvarsområde, 2007, p. 31.