Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse
| Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born |
23 August 1741 near Albi, France |
| Died |
1788? (aged c. 47) Unconfirmed Vanikoro, Solomon Islands |
| Allegiance |
|
| Service/branch |
|
| Years of service | 1756–1788 |
| Rank |
|
| Commands held |
Amazone, Astrée, Boussole |
| Battles/wars |
Seven Years' War Battle of Quiberon Bay American Revolutionary War Naval battle of Louisbourg |
| Awards | Chevalier de Saint-Louis |
Jean François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse (French: [ʒɑ̃ fʁɑ̃swa də ɡalop kɔ̃t də lapeʁuːz]; variant spelling of his name comte "de La Pérouse"; 23 August 1741 – 1788?) was a French Naval officer and explorer whose expedition vanished in Oceania.[1]
Early career

Jean-François de Galoup was born near Albi, France.[2] Lapérouse was the name of a family property that he added to his name.[3] He studied in a Jesuit college and entered the naval college in Brest when he was fifteen. In 1757 he was posted to the Célèbre and participated in a supply expedition to the fort of Louisbourg in New France. Lapérouse also took part in a second supply expedition in 1758 to Louisbourg, but as this was in the early years of the Seven Years' War, the fort was under siege and the expedition was forced to make a circuitous route around Newfoundland to avoid British patrols.
In 1759 Lapérouse was wounded in the Battle of Quiberon Bay, where he was serving aboard the Formidable. He was captured and briefly imprisoned before being paroled back to France; he was formally exchanged in December 1760.[4] He participated in a 1762 attempt by the French to gain control of Newfoundland, escaping with the fleet when the British arrived in force to drive them out.
Following the Franco-American alliance, Lapérouse fought against the Royal Navy off the American coast, and victoriously led the frigate Astree in the Naval battle of Louisbourg, 21 July 1781. He was promoted to the rank of commodore when he defeated the English frigate Ariel in the West Indies. He then escorted a convoy to the West Indies in December 1781, participated in the attack on St. Kitts in February 1782 and then fought in the defeat at the Battle of the Saintes against the squadron of Admiral Rodney. In August 1782 he made his name by capturing two English forts (Prince of Wales Fort and York Fort) on the coast of Hudson Bay, but allowed the survivors, including Governor Samuel Hearne of Prince of Wales Fort, to sail off to England in exchange for a promise to release French prisoners held in England. The next year his family finally consented to his marriage to Louise-Eléonore Broudou, a young creole of modest origins whom he had met on Ile de France (present-day Mauritius)[5] eight years earlier.[6]
Scientific expedition around the world

Objectives
Lapérouse was appointed in 1785 by Louis XVI and his Minister of the Marine, the Marquis de Castries, to lead an expedition around the world. Many countries were initiating voyages of scientific exploration.
Louis XVI and his court had been stimulated by a proposal from the Dutch-born merchant adventurer William Bolts, who had earlier tried unsuccessfully to interest Louis’s brother-in-law, the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II (brother of Queen Marie Antoinette), in a similar voyage. The French court adopted the concept (though not its author, Bolts), leading to the dispatch of the Lapérouse expedition. Charles Pierre Claret de Fleurieu, Director of Ports and Arsenals, stated in the draft memorandum on the expedition that he submitted to the King: "the utility which may result from a voyage of discovery ... has made me receptive to the views put to me by Mr. Bolts relative to this enterprise". But Fleurieu explained to the King: "I am not proposing at all, however, the plan for this voyage as it was conceived by Mr. Bolts".[7]
The expedition's aims were to complete the Pacific discoveries of James Cook (whom Lapérouse greatly admired), correct and complete maps of the area, establish trade contacts, open new maritime routes and enrich French science and scientific collections. His ships were the Astrolabe (under Fleuriot de Langle) and the Boussole,[8] both 500 tons. They were storeships reclassified as frigates for the occasion. Their objectives were geographic, scientific, ethnological, economic (looking for opportunities for whaling or fur trading), and political (the eventual establishment of French bases or colonial cooperation with their Spanish allies in the Philippines). They were to explore both the north and south Pacific, including the coasts of the Far East and of Australia, and send back reports through existing European outposts in the Pacific.
Preparations
As early as March 1785, Lapérouse proposed that Paul Monneron, who had been chosen as the expedition's chief engineer, go to London to find out about the anti-scurvy measures recommended by Cook and the exchange items used by Cook in his dealings with native peoples, and to buy scientific instruments of English manufacture.[9]
The best-known figure from Cook's missions, Joseph Banks,[10] intervened at the Royal Society to obtain for Monneron two inclining compasses that had belonged to Cook. Furnished with a list produced by Charles Pierre Claret de Fleurieu, Monneron also bought scientific instruments from some of the largest English firms, particularly Ramsden. He even surpassed Fleurieu's directives by acquiring two sextants of a new type.
Crew
Lapérouse was well liked by his men. Among his 114-man crew there were ten scientists: Joseph Lepaute Dagelet (1751–1788), an astronomer and mathematician;[11] Robert de Lamanon, a geologist; La Martinière, a botanist; a physicist; three naturalists; and three illustrators, Gaspard Duché de Vancy and an uncle and nephew named Prévost.[12] Another of the scientists was Jean-André Mongez. Even both chaplains were scientifically schooled.
One of the men who applied for the voyage was a 16-year-old Corsican named Napoléon Bonaparte.[13] Bonaparte, a second lieutenant from Paris's military academy at the time, made the preliminary list but he was ultimately not chosen for the voyage list and remained behind in France. At the time Bonaparte was interested in serving in the navy rather than army because of his proficiency in mathematics and artillery, both valued skills on warships.
Copying the work methods of Cook's scientists, the scientists on this voyage would base their calculations of longitude on precision watches and the distance between the moon and the sun followed by theodolite triangulations or bearings taken from the ship,[14] the same as those taken by Cook to produce his maps of the Pacific islands. As regards geography, Lapérouse decisively showed the rigour and safety of the methods proven by Cook. From his voyage, the resolution of the problem of longitude was evident and mapping attained a scientific precision. Impeded (as Cook had been) by the continual mists enveloping the northwestern coast of America, he did not succeed any better in producing complete maps, though he managed to fill in some of the gaps.
Chile and Hawaii

Lapérouse and his 220 men left Brest on 1 August 1785,[15] rounded Cape Horn, investigated the Spanish colonial government in the Captaincy General of Chile.[16] He arrived on 9 April 1786 at Easter Island [17] He then sailed to the Sandwich Islands, the present-day Hawaiian Islands,[18] where he became the first European to set foot on the island of Maui.
Alaska
Lapérouse sailed on to Alaska, where he landed near Mount St. Elias in late June 1786[19] and explored the environs. On 13 July 1786 a barge and two longboats, carrying 21 men, were lost in the heavy currents of the bay called Port des Français by Lapérouse, but now known as Lituya Bay.[20] The men visited with the Tlingit tribe.[21] (This encounter was dramatized briefly in episode 13 of Carl Sagan's Cosmos: A Personal Voyage.) Next, he headed south, exploring the northwest coast, including the outer islands of present-day British Columbia [22][23]
California
Lapérouse sailed during 10–30 August all the way south to the Spanish Las Californias Province, present-day California. He reportedly observed the only historical eruption of Mount Shasta on 7 September 1786, although this account is disputed.[24] He stopped at the Presidio of San Francisco long enough to create an outline map of the Bay Area, "Plan du Port du St. Francois," which was reproduced as Map 33 in L. Aubert's 1797 "Atlas du Voyage de la Perouse." He arrived in Monterey Bay and at the Presidio of Monterey on 14 September 1786.[25] He examined the Spanish settlements, ranchos, and missions. He made critical notes on the missionary treatment of the California indigenous peoples with the Indian Reductions at the Franciscan run missions. France and Spain were on friendly terms at this time. Lapérouse was the first non-Spanish visitor to California since Drake in 1579 , and the first to come to California after the founding of Spanish missions and presidios.
East Asia
Lapérouse again crossed the Pacific Ocean in 100 days, arriving at Macau, where he sold the furs acquired in Alaska, dividing the profits among his men.[26] The next year, on 9 April 1787,[27] after a visit to Manila, he set out for the northeast Asian coasts. He saw the island of Quelpart, present-day Cheju in South Korea, which had been visited by Europeans only once before when a group of Dutchmen shipwrecked there in 1635. He visited the Asian mainland coasts of Korea.
Japan and Russia
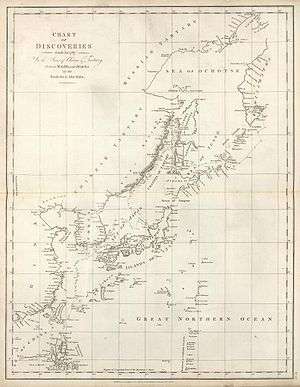
Lapérouse then sailed northward to Northeast Asia and Oku-Yeso Island, present day Sakhalin Island, Russia. The Ainu people, Oku-Yeso Island residents, drew him a map showing: their second domain of Yezo Island, present day Hokkaidō Island, Japan; and the coasts of Tartary, Russia on mainland Asia. Lapérouse wanted to sail north through the narrow Strait of Tartary between Oku-Yeso Island and mainland Asia but failed. Instead he turned south, and then sailed west through La Pérouse Strait, between Oku-Yeso Island (Sakhalin) and (Hokkaidō), where he met more Ainu in their third domain of the Kuril Islands, and explored.
Lapérouse then sailed north and reached Petropavlovsk on the Russian Kamchatka peninsula on 7 September 1787.[28] Here they rested from their trip, and enjoyed the hospitality of the Russians and Kamchatkans. In letters received from Paris, Lapérouse was ordered to investigate the settlement the British were establishing in New South Wales, Australia. Barthélemy de Lesseps, the French vice consul at Kronstadt, Russia, who had joined the expedition as an interpreter, disembarked in Petropavlovsk to bring the expedition's ships' logs, charts, and letters to France, which he reached after a year-long, epic journey across Siberia and Russia.[29]
South Pacific
Lapérouse next stopped in the Navigator Islands (Samoa), on 6 December 1787.[30] Just before he left, the Samoans attacked a group of his men, killing twelve of them, among whom were Lamanon and de Langle, commander of the Astrolabe. Twenty men were wounded.[31] The expedition drifted to Tonga, for resupply and help, and later recognized the île Plistard and Norfolk Island.
Australia
The expedition continued to Australia,[32] arriving off Botany Bay on 24 January 1788,[33] just as Captain Arthur Phillip was attempting to move the colony from there to Sydney Cove in Port Jackson.[34] The First Fleet was unable to leave until 26 January because of a tremendous gale, which also prevented Lapérouse's ships from entering Botany Bay.


The British received him courteously, and each captain, through their officers, offered the other any assistance and needed supplies.[33] Lapérouse was 6 weeks in the colony and this was his last recorded landfall. The French established an observatory, held Catholic masses, made geological observations, and established a garden.[35] Their chaplain from L'Astrolabe was buried there and is celebrated annually on the anniversary of his death. Although Phillip and Lapérouse did not meet, there were 11 visits recorded between the French and English.[36] Over the past 200 years commanders from the French Navy have regularly paid their respects at the Lapérouse Monument. Lapérouse Day, Bastille Day and the foundation of the Lapérouse Monument by Hyacinthe de Bougainville are celebrated every year.
Lapérouse took the opportunity to send his journals, some charts and also some letters back to Europe with a British naval ship from the First Fleet—the Alexander.[37] He also obtained wood and fresh water and, on 10 March,[33] left for New Caledonia, Santa Cruz, the Solomons, the Louisiades, and the western and southern coasts of Australia.
Lapérouse wrote that he expected to be back in France by June 1789. The documents that he dispatched with the Alexander from the in-progress expedition were returned to Paris, where they were published after his presumed death.[38] However, neither he nor any of his men were seen again.
Epilogue
HMS Pandora
Reportedly HMS Pandora missed a chance to rescue the survivors in May 1791. See the discussion below in The saga.
Rescue mission of D'Entrecasteaux
On 25 September 1791 Rear Admiral Bruni d'Entrecasteaux departed Brest in search of Lapérouse. His expedition followed Lapérouse's proposed path through the islands northwest of Australia while at the same time making scientific and geographic discoveries. The expedition consisted of two ships, Recherche and Esperance.[39]
In May 1793, he arrived at the island of Vanikoro, which is part of the Santa Cruz group of islands (now part of the Solomon Islands). D'Entrecasteaux thought he saw smoke signals from several elevated areas on the island, but was unable to investigate due to the dangerous reefs surrounding the island and had to leave. He died two months later. The botanist Jacques Labillardière, attached to the expedition, eventually returned to France and published his account, Relation du Voyage à la Recherche de la Pérouse, in 1800.[40]
During the French Revolution, Franco-British relations deteriorated and unfounded rumours spread in France blaming the British for the tragedy which had occurred in the vicinity of the new colony. Before the mystery was solved the revolutionary French government had published the records of the voyage as far as Kamchatka: Voyage De La Pérouse Autour du Monde, 1–4 (Paris, 1797). These volumes are still used for cartographic and scientific information about the Pacific. Three English translations were published during 1798–99.[41]
Discovery of the expedition

1826 expedition
It was not until 1826 that an Irish sea captain, Peter Dillon, found enough evidence to piece together the events of the tragedy. In Tikopia (one of the islands of Santa Cruz), he bought some swords that he had reason to believe had belonged to Lapérouse or his officers. He made enquiries, and found that they came from nearby Vanikoro, where two big ships had broken up years earlier. Dillon managed to obtain a ship in Bengal, and sailed for the coral atoll of Vanikoro where he found cannonballs, anchors and other evidence of the remains of ships in water between coral reefs.
He brought several of these artifacts back to Europe, as did Dumont d'Urville in 1828.[42] De Lesseps, the only member of the original expedition still alive at the time, identified them as all belonging to the Astrolabe. From the information Dillon received from the people on Vanikoro, a rough reconstruction could be made of the disaster that struck Lapérouse. Dillon's reconstruction was later confirmed by the discovery, and subsequent examination in 1964, of what was believed to be the shipwreck of the Boussole.[43]
2005 expedition
In May 2005, the shipwreck examined in 1964 was formally identified as that of the Boussole.[44] The 2005 expedition had embarked aboard the Jacques Cartier, a French naval vessel. The ship supported a multi-discipline scientific team assembled to investigate the "Mystery of Lapérouse".[45] The mission was called "Opération Vanikoro - Sur les traces des épaves de Lapérouse 2005".
2008 expedition
A further similar mission was mounted in 2008.[46][47][48]
The 2008 expedition showed the commitment of France, in conjunction with the New Caledonian 'Association Salomon', to seek further answers about Lapérouse's mysterious fate. It received the patronage of the President of France as well as the support and co-operation of the French Ministry of Defense, the Ministry of Higher Education and Research, and the Ministry of Culture and Communication.
Preparation for this, the eighth expedition sent to Vanikoro, took 24 months. It brought together more technological resources than previously and involved two ships, 52 crew members and almost 30 scientists and researchers. On 16 September 2008, two French Navy boats set out for Vanikoro from Nouméa (New Caledonia) and arrived on 15 October, thus recreating a section of the final voyage of discovery undertaken more than 200 years earlier by Lapérouse.[49][50][51][52]
The saga
Both ships had been wrecked on Vanikoro's reefs, the Boussole first. The Astrolabe was unloaded and taken apart. A group of men, probably the survivors of the Boussole, was massacred by the local inhabitants.[53] According to the islanders, some surviving sailors built a two-masted craft from the wreckage of the Astrolabe and left in a westward direction about nine months later; but what happened to them is unknown. Also, two men, one a "chief" and the other his servant, had remained behind, but had left Vanikoro a few years before Dillon arrived.[54]
Sven Wahlroos, in his 1989 book, Mutiny and Romance in the South Seas, suggests that there was a narrowly missed chance to rescue one or more of the survivors in 1791.[55]
In November 1790, Captain Edward Edwards—in command of HMS Pandora—had sailed from England with orders to comb the Pacific for the mutineers of HMS Bounty. In March of the following year, the Pandora arrived at Tahiti and picked up 14 Bounty men who had stayed on that island. Although some of the 14 had not joined the mutiny, all were imprisoned and shackled in a cramped "cage" built on the deck, which the men grimly nicknamed "Pandora's Box". The Pandora then left Tahiti in search of the Bounty and the leader of the mutiny, Fletcher Christian.
Captain Edwards' search for the remaining mutineers ultimately proved fruitless. However, when passing Vanikoro on 13 August 1791, smoke signals were observed rising from the island. Edwards, single-minded in his search for the Bounty and convinced that mutineers fearful of discovery would not be advertising their whereabouts, ignored the smoke signals and sailed on.
Wahlroos argues that the smoke signals were almost certainly a distress message sent by survivors of the Lapérouse expedition, which later evidence indicated were still alive on Vanikoro at that time—three years after the Boussole and Astrolabe had foundered. Wahlroos is "virtually certain" that Captain Edwards, whom he characterizes as one of England's most "ruthless," "inhuman," "callous" and "incompetent" naval captains, missed his chance to become "one of the heroes of maritime history" by solving the mystery of the lost Lapérouse expedition.[55]
Legacy

Places later named in honour of Lapérouse include:
- Mount La Perouse (3231 m) and La Perouse Glacier, Fairweather Range, Alaska
- Mount La Pérouse (1127 m) on the Queen Charlotte Islands of British Columbia
- La Pérouse Reef off the west coast of the Queen Charlotte Islands of British Columbia
- La Perouse Bank, Off the West Coast of Vancouver Island / West of Ucluelet/Tofino. This is the site of Environment Canada weather buoy 46026, at location 48.83N 126.00W
- La Perouse Strait between Hokkaidō and Sakhalin
- Mount La Perouse (1157 m) and the La Perouse Range, Tasmania, Australia
- La Perouse Pinnacle (37 m), in the French Frigate Shoals, Hawaii
- La Perouse (mountain) (3078 m), in New Zealand's Southern Alps
- La Perouse Glacier, Westland, New Zealand
- La Perouse Bay, site of his landing on Maui
- La Pérouse (crater), on the Moon
- La Perouse, a suburb of Sydney, Australia, on the northern headland of Botany Bay
Several ships have also been named after him:
- The Lapérouse class are hydrographic survey ships of the French Navy. Three ships are currently active in the French Navy. One further ship of the class has been transferred to Patrol service duties (action de l'Etat en mer (AEM)).
- The Lapérouse A791 is a current serving ship of the Hydrographic and Oceanographic Service of the French Navy (Bâtiment hydrographique de deuxième classe (BH) - Service Hydrographique et Océanographique de la Marine-SHOM) and is based at Brest, DCN Lorient. The ship was laid down on 11 June 1985, launched on 15 November 1985 and entered service in the Marine nationale as Lapérouse A791 on 20 April 1988.[56][57][58]
- Lapérouse, 1877–1898, served as a defensive cruiser in the French Navy. The Lapérouse was built at Brest, with work commencing in 1875, launched in 1877 and was subsequently wrecked in 1898 in the East Indies. The unarmoured cruisers of the Lapérouse class were wooden hulled ships with iron beams. These ships had plough bows with a forecastle, a displacement of 2363 tons, a speed of 15 knots and had a complement of 264 sailors. Armament was fifteen 5.5-inch (140 mm) M1870M guns later replaced in Primauget with Quick Firing Conversions. Each ship also had eight 1 pounder revolvers.[59][60] Several other ships
Lapérouse in literature and film
The fate of Lapérouse, his ships and his men is the subject of a chapter from Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea by Jules Verne. Lapérouse was also mentioned in an episode ("The Quest") of the series Northern Exposure where the character Joel (Rob Morrow) finds an old chart of the French explorer that will lead to a legendary "jewelled city of the North" (New York).[61]
The novel "Landfalls" by Naomi J. Williams explores the Lapérouse expedition in depth.[62]
See also
- Age of Discovery
- Age of enlightenment
- Explorers
- History of the French Navy
- Lapérouse A791
- List of current French Navy ships
- Micronesian megapode
- Zo d'Axa (Alphonse Gallaud de la Pérouse, anarchist and the EnDehors)
Notes
- Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse-Naval officer; b. 23 August 1741 in the parish of Saint-Julien in Albi, France, son of Victor-Joseph de Galaup and Marguerite de Rességuier, Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online, University of Toronto. (2000)
- Lapérouse, University of Sydney (1868-1839) University of Sydney Library, 1997, Sydney Australia, Scott Ernest. From the print edition published by Angus and Robertson, Sydney 1912.
- The Lost Voyage of Lapérouse (Vancouver Maritime Museum, 1986). Allen, Edward Webber.
- The Vanishing Frenchman: The Mysterious Disappearance of Lapérouse (Rutland, Vermont: C.D. Tuttle, Co., 1959)" and "Inglis, Robin.
- The Lost Voyage of Lapérouse, Inglis, Robin. (Vancouver Maritime Museum, 1986)
- Mount Shasta Annotated Bibliography Chapter 4 Early Exploration: Lapérouse Expedition, 1786.
- Dunmore, J. (ed.) The Journal of Jean-François de Galaup de la Pérouse 1785–1788. Published by the Hakluyt Society. Volume 1; 1994, ISBN 0-904180-38-7. Volume 2; 1995, ISBN 0-904180-39-5.
- Reader's Digest, Great Mysteries of the Past. Published by Reader's Digest in 1991. Section "They Vanished Without a Trace". Article "Destination: Great South Sea". Pages 12–17.
- "2e Cahier du Conseil national des parcs et jardins - Le voyage des plantes - Les jardins, acteurs culturels de la biodiversité" (PDF) (in French). culture.gouv.fr. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
References
- ↑ Novaresio, Paolo (1996). The Explorers. Stewart, Tabori & Chang, NY ISBN 1-55670-495-X. p. 180. "Lapérouse was born in 1741."
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996, p. 180. "Lapérouse was born at Albi."
- ↑ John Dunmore. "French Explorers of the Pacific". Volume One: Eighteenth Century. Oxford Press: 1965, p255.
- ↑ Dunmore, John. Where fate beckons: the life of Jean-François de la Pérouse. pp. 26-32
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 181 "married a young Creole girl ... met ... at Mauritius"
- ↑ Pritchard, James (Spring 2009). "Review of Where Fate Beckons: The Life of Jean-Francois de La Pérouse, by John Dunmore" (PDF). Journal of Historical Biography. 5: 123–127.
- ↑ Robert J. King, "William Bolts and the Austrian Origins of the Lapérouse Expedition", Terrae Incognitae, vol.40, 2008, pp.1-28.
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 181 "Lapérouse ships, the Astrolabe and the Boussoule"
- ↑ The French Navy archives contain an interesting series of letters sent by Monneron to Lapérouse and de Castries during his mission to England. Presenting himself as an agent accredited by a Spanish lord, Monneron talked to junior officers who had known Cook. He met John Webb, the artist on the Resolution and painter of a justly famous painting of Cook as well as several drawings of north-west America. Besides his research findings, Webb passed on several other pieces of useful information: how to behave towards the native peoples, English prices for necessities for the voyage (showing him there was no financial advantage in buying exchange items in England rather than France), and above all, advice on anti-scurvy measures, particularly malt, of which Monneron dispatched several barrels to Paris, and how to cook anticorbutic preparations with ships' rations.
- ↑ Extract from Lapérouse's journal: I here must witness my recognition of Sir Joseph Banks, who, having realised that Monsieur de Monneron could not find an inclining compass in London, wished to lend us those that had served the famous captain Cook. I received these instruments with a sentiment of religious respect for the memory of this great man.
- ↑ Robert J. King, "Joseph Lepaute Dagelet and his pendulum experiments at Botany Bay, 1788", Map Matters, Issue 28, April 2016, pp.2-8.
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 184 "the mathematician and astronomer Dagelet, the botanist La Martiniére and the geologist Lamanon. Then there were the geographers, the physicists, the physicians, and the illustrators like Duché de Vancy and the two Prévosts (uncle and nephew)."
- ↑ Robert W. Kirk, "Paradise Past: The Transformation of the South Pacific, 1520-1929", McFarland & Company, Inc., 2012, p.206.
- ↑ De Langle's means of taking bearings was exactly that used by Cook.
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 181 "The expedition ... left the port of Brest on the 1st of August, 1785"
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 186 "stopping on the coast of Chile"
- ↑ Jean-François de Galaup, count de Lapérouse Jean-François de Galaup, count de Lapérouse. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 20 September 2006.
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 186 "Lapérouse headed for Easter Island ... left the island two days after his arrival ... after a brief stop in the Hawaiian Islands"
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 186 "Towards mid-June ... the coast of Alaska, dominated by ... Mount Saint Elias"
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 186–187 "entered a deep inlet that was baptised French Port (now Lituya Bay) ... On the 13th of July, 1786 .. Only one of the three boats that landed returned ...engulfed by a particularly violent ebb tide. ... Around twenty men perished"
- ↑ "Pérouse, Jean-Francois de la". abcbookworld.com.
- ↑ Little, Gary. "Lapérouse: 1786 Chart of the B.C. Coast". garylittle.ca.
- ↑ "Alaska's Digital Archives". Vilda Alaska-materials from libraries, museums and archives throughout the State of Alaska USA, including From Atlas du Voyage de la Perouse, No. 17. "1e Feuille." Drawn by Herault, engraved by Bouclet. Published in [Paris] by [L'Impimerie de la Republic] in [1797].
- ↑ "Early Exploration: Lapérouse Expedition, 1786, (Lapérouse, contrary to legend, did not see Mount Shasta in eruption in 1786)". siskiyous.edy. Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2007.
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 187 "Monterey ... was reached on the 14th of September"
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 187 "After 100 days of sailing ... reached the port of Macao. ... trying to trade the furs they had acquired in North America"
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 187, 191 "On the 9th of April, 1787, ... set sail for Japan."
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 191 "On the 7th of September, the expedition reached the coast of Kamchatka. The Russian authorities at Petropavlosk"
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 191 "to send a young officer across Siberia and Russia to France with the ships' logs and the valuable charts."
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 191 "On the 6th of December, ... the explorers dropped anchor off a Samoan island."
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 191 "The squad ... was attacked as they were returning to their boats, and 12 men were killed, including De Langle, Lamanon and another officer. Another 20 were seriously wounded."
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 192 "After having reached Tonga, he headed toward Australia"
- 1 2 3 David Hill, 1788: The Brutal Truth of the First Fleet
- ↑ King, Robert J (December 1999). "What brought Lapérouse to Botany Bay?". 85, pt.2. Journal of the Royal Australian Historical Society: 140–147.
- ↑
- ↑ Protos, A.(2000) The Road to Botany Bay. Randwick & District Historical Society Inc.
- ↑ http://laperousemuseum.org/french-firsts/first-mail/
- ↑ Laperouse museum last documents
- ↑ "The fate of La Perouse". Discover Collections. State Library of NSW. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- ↑ Duyker, Edward (September 2002). "In search of Lapérouse". NLA news Volume XII Number 12. National Library of Australia.
- ↑ "La Pérouse, Jean-François de Galaup (1741–1788)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Retrieved 14 February 2013.
- ↑ Novaresio, 1996. p. 192 "Dumont d'Urville locate the remains of a wreck on the reef around the coral atoll of Vanikoro ... The material recovered ... belonged to the Astrolabe."
- ↑ "After Vanikoro-In Search of the Lapérouse Expedition (Lapérouse Museum)". Albi, France: laperouse-france.fr.
- ↑ "La Perouse wreck identified in Solomon Is". abc.net.au.
- ↑ Wéry, Claudine (8 April 2005). "One of France's greatest maritime mysteries is slowly yielding up its secrets". Guardian Weekly.
- ↑ "Le mystère Lapérouse - Vanikoro 2008 - Report de la mission" (in French). lemysterelaperouse.blogspot.com. 2 May 2008. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "Expédition Lapérouse 2008" (in French). operationlaperouse2008.fr. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ Discombe (1919-2007), Vale Reece. "Pacific Manuscripts Bureau Newsletter". rspas.anu.edu.au. p. 10. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "Lapérouse operation 2008". eramet.fr. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "Expéditon Lapérouse 2008". operationlaperouse 2008. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ On 8 September, Mr. Patrick Buffet took part in the press conference organised at the Press Club de France to launch Operation Lapérouse 2008, which was attended by Admiral Jean-Louis Battet "Launch of "Lapérouse 2008" Operation". Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "Le mystère Lapérouse, enquête dans le Pacifique sud" (in French). Musée de la Marine - Paris.
- ↑ Australian Shipwrecks - vol1 1622–1850, Charles Bateson, AH and AW Reed, Sydney, 1972, ISBN 0-589-07112-2, p24
- ↑ Peter Dillon, Narrative and Successful Result of a Voyage in the South Seas, Performed by Order of the Government of British India, to Ascertain the Actual Fate of Lapérouse's Expedition, in 2 volumes, London 1829.
- 1 2 Wahlroos, Sven, "Mutiny and Romance in the South Seas", Salem House Publishers, c/o Harper & Row, New York, NY, 1989
- ↑ "Homepage" (in French). Service Hydrographique et Océanographique de la Marine. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "?" (PDF) (in French). defense.gouv.fr. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "?" (in French). defense.gouv.fr. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "Armorique - March 1862". battleships-cruisers.co.uk. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ "Lapérouse". worldnavalships.com. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ Dianne Frovlov and Andrew Schneider, (CBS) airdate: Monday 8 February 1995-Transcript by TwizTV.com. "Northern Exposure, 6X14 - "The Quest"".
- ↑ Williams, Naomi J., "Landfalls", Farrar, Straus and Giroux, New York, 2015, http://naomijwilliams.com/landfalls/
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Jean-François de La Pérouse. |
External links
- Archive.org The Commonwealth of Australia, Australian Federal Handbook 84th meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science, held in Australia. August 1914.
- Siskiyous.edu, English language bibliography with extensive references to Lapérouse both in translations to English and the citation of original French document sources spanning many decades.
- André Engels, Jean-François de Galoup, Comte de Lapérouse
- John Robson, La Perouse, Eighteenth Century French Sailor and leader of a Voyage into the Pacific
- see Lapérouse genealogy on samlap Geneanet
- Wéry, Claudine (8 April 2005). "'What news of Lapérouse?'". The Guardian.
 "Lapérouse, Jean-François de Galaup, Comte de". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
"Lapérouse, Jean-François de Galaup, Comte de". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911. "Lapérouse, Jean François de Galaup". Appletons' Cyclopædia of American Biography. 1892.
"Lapérouse, Jean François de Galaup". Appletons' Cyclopædia of American Biography. 1892.- Biography at the Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online
- La Pérouse in Port-des-Français (Alaska) and La Pérouse baptismal certificate (in French)
- http://naomijwilliams.com/landfalls/
Archives
- Invoice for stores consumed on the Amazone, signed by La Pérouse, and portraits of La Pérouse. 1779-1828. 0.06 cubic feet ( 1 oversize folder). At the University of Washington Libraries, Special Collections.