Megalonyx
| Megalonyx Temporal range: late Miocene to Pleistocene, 10.3–0.011 Ma | |
|---|---|
| | |
| M. wheatleyi skeleton. | |
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Superorder: | Xenarthra |
| Order: | Pilosa |
| Family: | Megalonychidae Gervais, 1855 |
| Subfamily: | Megalonychinae |
| Genus: | †Megalonyx Harlan, 1825 |
| Species | |
| |
Megalonyx (Greek, "large claw") is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Megalonychidae endemic to North America from the Hemphillian of the Late Miocene through to the Rancholabrean of the Pleistocene, living from ~10.3 Mya—11,000 years ago, existing for approximately 10.289 million years. Type species, M. jeffersonii, measured about 3 m (9.8 ft) and weighed up to 1,000 kilograms.[1]
Description
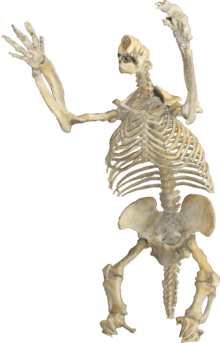
Megalonyx was a large, heavily built animal about 3 m (9.8 ft) long. Its maximum weight is estimated at 1,000 kg (2,205 lb).[1] This is medium-sized among the giant ground sloths. Like other ground sloths it had a blunt snout, massive jaw, and large peg-like teeth. The hind limbs were plantigrade (flat-footed) and this, along with its stout tail, allowed it to rear up into a semi-erect position to feed on tree leaves. The forelimbs had three highly developed claws that were probably used to strip leaves and tear off branches.
Paleobiology
Ongoing excavations at Tarkio Valley in southwest Iowa may reveal something of the familial life of Megalonyx. An adult was found in direct association with two juveniles of different ages, suggesting that adults cared for young of different generations.[2][3]
Habitat
Megalonyx ranged over much of North and Central America.[4] Their remains have been found as far north as Alaska[5] and the Yukon.[6]
M. jeffersonii was apparently the most wide ranging giant ground sloth. Fossils are known from many Pleistocene sites in the United States, including most of the states east of the Rocky Mountains as well as along the west coast. It was the only ground sloth to range as far north as the present-day Yukon[7] and Alaska.[8]
In the fall of 2010, the first specimen ever found in Colorado was discovered at the Ziegler Reservoir site near Snowmass Village (In the Rocky Mountains at an elevation of 8,874 feet).[9] The Firelands ground sloth fossil dated between 11,727 and 11,424 B.C. represents the earliest known hunting activity by Ohioan paleoindians.[10]
Taxonomy and evolution
The generic name Megalonyx was proposed by future U.S. President Thomas Jefferson in 1797, based on fossil specimens of what later came to be called Megalonyx jeffersonii that he had received from western Virginia. His presentation to the American Philosophical Society that year is often credited as the beginning of vertebrate paleontology in North America. However, Jefferson's name has no validity in zoological nomenclature, and Megalonyx was first formally named by Richard Harlan in 1825.[11]
Megalonyx evolved from ancestors that island-hopped across the Central American Seaway from South America, where ground sloths arose, prior to formation of the Panamanian land bridge. Its appearance in North America thus predates the bulk of the faunal exchange between North and South America. Its immediate predecessor was Pliometanastes and its closest living relatives are the two-toed sloths (Choloepus).
M. jeffersoni lived from the Illinoian Stage during the Middle Pleistocene (150,000 years BP) through to the Rancholabrean of the Late Pleistocene (11,000 BP[12]). It belongs to the genus Megalonyx, a name proposed by Thomas Jefferson, future president of the United States, in 1797. (Jefferson's surname was appended to the animal as the specific epithet in 1822 by the French zoologist Anselme Gaëtan Desmarest.) M. jeffersoni was probably descended from M. wheatleyi, which was in turn was probably derived from M. leptostomus.
M. leptostomus was named by Cope (1893). This species lived from Florida to Texas, north to Kansas and Nebraska, and west to New Mexico, Nevada, Oregon, and Washington. It is about half the size of M. jeffersoni.
Discovery and history
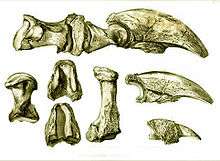
In 1796, Colonel John Stuart sent Thomas Jefferson, then Vice President of the United States, some fossil bones: a femur fragment, ulna, radius, and foot bones including three large claws. The discoveries were made in a cave in Greenbrier County, Virginia (present-day West Virginia). Jefferson then presented a paper on "Certain Bones" to the American Philosophical Society in Philadelphia on 10 March 1797. In the paper he theorized that the bones represented the remains of a lion which he named Megalonyx ("giant claw").[13] Jefferson's paper took as a premise the idea that the creature was still extant. Contrary to the scientific consensus merging at the time that extinction had played an important role in natural history, Jefferson believed in a "completeness of nature" whose inherent balance did not allow species to go extinct naturally. He asked Lewis and Clark, as they planned their famous expedition in 1804–1806, to keep an eye out for living specimens of "Megalonyx", as this would support his case. His idea made no headway among scientists and, of course, was later shown to be incorrect.[14]
As a result of presenting his paper, Jefferson is often credited with initiating the science of vertebrate paleontology in the United States. In 1799 Dr. Caspar Wistar correctly identified the remains as those of a giant ground sloth. In 1822 Wistar proposed naming the species Megalonyx jeffersonii in honor of the former statesman.[15][16] Desmarest then published it as such.
Recent research confirms that the sloth bones were discovered in Haynes Cave in Monroe County. For many decades in the twentieth century the reported origin of Jefferson's "Certain Bones" was Organ Cave in what is now Greenbrier County, West Virginia. This story was popularized in the 1920s by a local man, Andrew Price of Marlinton.[17] The story came under scrutiny when in 1993 two fragments of a Megalonyx scapula were found in Haynes Cave in neighboring Monroe County. Smithsonian paleontologist Frederick Grady presented evidence in 1995 confirming [18] Haynes Cave as the original source of Jefferson's fossil. Jefferson reported that the bones had been found by saltpeter workers. He gave the cave owner’s name as Frederic Crower. Correspondence between Jefferson and Colonel Stuart, who sent him the bones, indicates that the cave was located about five miles from Stuart’s home and that it contained saltpeter vats. , An investigation of property ownership records revealed 'Frederic Crower' to be an apparent misspelling of the name Frederic Gromer. Organ Cave was never owned by Gromer, but Haynes Cave was. Two letters written by Tristram Patton, the subsequent owner of Haynes Cave, indicate that this cave was located in Monroe County near Second Creek. Monroe County had originally been part of Greenbrier County; it became a separate county shortly after the discovery of the bones. In his own letters Patton described the cave and indicated that more fossil bones remained inside.[19]
M. jeffersonii is still the most commonly identified species of Megalonyx. It was designated the state fossil of West Virginia in 2008.
- SeaTac, Washington, est. age ~12,600—12,760 years[20]
- Wild Horse Butte aka UO 2396, Owyhee County, Idaho, est. age ~2.7—2.1 Mya.
- Buckeye Creek (UCMP V-93067), Douglas County, Nevada, est. age ~4.4—4.5 Mya.
- Taunton site, Adams County, Washington, est. age ~3.4—3.3 Mya.
- Kuchta Sand Pit, Yankton County, South Dakota, est. age ~2.9—2.1 Mya.
- Meade's Quarries 4 and 5, Crosby County, Texas, est. age ~3.7—1.5 Mya.
- Haile 7C, Alachua County, Florida, est. age ~1.6—1.5 Mya.
- Kissimmee River, Okeechobee County, Florida, est. age ~2.3 Mya.
- Nebraska, est. age ~10.3—4.9 Mya.
(incomplete listing)
References
Citations
- 1 2 http://library.sandiegozoo.org/factsheets/_extinct/sloth_extinct/extinct_sloth.htm
- ↑ Semken and Brenzel, http://slothcentral.com/?page_id=2
- ↑ Semken; Brenzel (2007). "One Sloth Becomes Three". Newsletter of the Iowa Archeological Society. 57: 1.
- ↑ "Megalonyx". Paleobiology Database. Retrieved 2011-07-16.
- ↑ Stock, C. (1942-05-29). "A ground sloth in Alaska". Science. AAAS. 95 (2474): 552–553. doi:10.1126/science.95.2474.552. PMID 17790868.
- ↑ McDonald, H. G.; Harington, C. R.; De Iuliis, G. (September 2000). "The Ground Sloth Megalonyx from Pleistocene Deposits of the Old Crow Basin, Yukon, Canada" (PDF). Arctic. Calgary, Alberta: The Arctic Institute of North America. 53 (3): 213–220. doi:10.14430/arctic852. Retrieved 2008-08-16. External link in
|publisher=(help) - ↑ McDonald, H. G.; Harington, C. R.; De Iuliis, G. (September 2000). "The Ground Sloth Megalonyx from Pleistocene Deposits of the Old Crow Basin, Yukon, Canada" (PDF). Arctic. Calgary, Alberta: The Arctic Institute of North America. 53 (3): 213–220. doi:10.14430/arctic852. Retrieved 2008-08-16. External link in
|publisher=(help) - ↑ Stock, C. (1942-05-29). "A ground sloth in Alaska". Science. AAAS. 95 (2474): 552–553. doi:10.1126/science.95.2474.552. PMID 17790868.
- ↑ "Snowmass tally: 10 mastodons, 4 mammoths, one "once-in-a-lifetime" find". The Denver Post. November 18, 2010.
- ↑ "Research reveals first evidence of hunting by prehistoric Ohioans". Cleveland Museum of Natural History. Feb 2012. Retrieved 12 Apr 2012.
- ↑ McKenna, M.C.; Bell, S.K. (1997). Classification of Mammals: Above the Species Level. Columbia University Press. p. 100. ISBN 0-231-11013-8.
- ↑ Fiedal, Stuart (2009). "Sudden Deaths: The Chronology of Terminal Pleistocene Megafaunal Extinction". In Haynes, Gary. American Megafaunal Extinctions at the End of the Pleistocene. Springer. pp. 21–37. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-8793-6_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-8792-9.
- ↑ Jefferson, Thomas, "A Memoir on the Discovery of Certain Bones of a Quadruped of the Clawed Kind in the Western Parts of Virginia", Read before the American Philosophical Society, March 10, 1797.
- ↑ Rowland, Steve, "The Fossil Record", Published lecture notes for "The Fossil Record" course at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, August 2010
- ↑ Jefferson, Thomas (1799). "A Memoir on the Discovery of Certain Bones of a Quadruped of the Clawed Kind in the Western Parts of Virginia". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. 4: 246–260. doi:10.2307/1005103. JSTOR 1005103.
- ↑ Wistar, Caspar (1799), “A Description of the Bones Deposited, by the President, in the Museum of the Society, and Represented in the Annexed Plates", Transactions, pp. 526-531, plates.
- ↑ Humphreys, Blanche (1928), History of Organ Cave Community (Greenbrier County, West Virginia); Agricultural Extension Division.
- ↑ Grady, Fred (1995), "The Search for the Cave from which Thomas Jefferson Described the Bones of the Megalonyx" [Abstract], In: "Selected Abstracts from the 1995 National Speleological Society National Convention in Blacksburg, Virginia"; In: Journal of Cave and Karst Studies, April 1997, pg 57.
- ↑ Grady (1995), Op. cit.
- ↑ Williams, David B. (2010). Construction at Sea-Tac Airport unearths an extinct giant sloth on February 14, 1961. HistoryLink.org.
Other sources
- Cope, ED. (1871) Preliminary report on the vertebrata discovered in the Port Kennedy Bone Cave. American Philosophical Society, 12:73-102.
- Cope, ED. (1893) A preliminary report on the vertebrate paleontology of the Llano Estacado. 4th Annual Report on the Geological Survey of Texas: 136pp.
- Hirschfeld, SE. and SD. Webb (1968) Plio-Pleistocene megalonychid sloths of North America. Bulletin of the Florida State Museum Biological Sciences, 12(5):213-296.