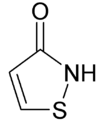
Isothiazolinone
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2-Thiazol-3-one | |||
| Other names
Isothiazolin-3-one; 3(2H)-Isothiazolone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 1003-07-2 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 87509 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.225.492 | ||
| MeSH | C001490 | ||
| PubChem | 96917 | ||
| UNII | E57JT172V7 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H3NOS | |||
| Molar mass | 101.127 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Isothiazolinone is a heterocyclic chemical compound. Derivatives of isothiazolinone are used as biocides, including:
- Methylisothiazolinone (MIT, MI)
- Chloromethylisothiazolinone (CMIT, CMI, MCI)
- Benzisothiazolinone (BIT)
- Octylisothiazolinone (OIT, OI)
- Dichlorooctylisothiazolinone (DCOIT, DCOI)
- Butylbenzisothiazolinone (BBIT)
Applications
Isothiazolinones are antimicrobials used to control bacteria, fungi, and algae in cooling water systems, fuel storage tanks, pulp and paper mill water systems, oil extraction systems, wood preservation and antifouling agents. They are frequently used in personal care products such as shampoos and other hair care products, as well as certain paint formulations. Often, combinations of MIT and CMIT (known as Kathon CG) or MIT and BIT are used.
Biological implications
Together with their wanted function, controlling or killing microorganisms, isothiazolinones also have undesirable effects: They have a high aquatic toxicity and some derivatives can cause hypersensitivity by direct contact or via the air.
See also
- Methylisothiazolinone#Other isothiazolinones
- Mercaptobenzothiazole, also a common allergen