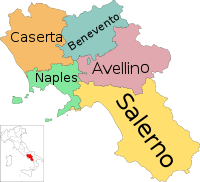
Irpinia
Irpinia (Latin Hirpinia) is a region of the Apennine Mountains around Avellino, a town in Campania, South Italy about 40 km east of Naples. In antiquity this was the territory of the Hirpini; its extent corresponds approximately to that of today’s province of Avellino.
Geography
The territory is largely mountainous, with an intricate network of hills and valleys and a predominantly limestone Karst topography. To the west, however, the rocks are mostly sandstone, and the land is lower. Irpinia is centred on the section of the Apennines which runs from the Sella di Ariano to the springs of the Sele River; the highest peak is Mount Avella (1,591 m). To the south are the Picentini Mountains, which include the highest peak of the region, Mount Terminio (1,783 m), and from which extends the Sorrentine peninsula. The region is bordered on the east by the Ofanto valley and the San Pietro lake, while to the north it merges with Sannio and Daunia.
History
The name "Irpinia" derives from the Oscan word "hirpus", which means wolf, and the wolf remains Irpinia's symbol to this day. Oscan tribes of the Sabines, under demographic pressure, migrated towards this area in the 6th century BC from what is now Umbria. The Hirpini occupied the region Sabato, Calore Irpino and Ofanto, becoming differentiated with time from the Samnites who settled the area from Molise and Matese. The main centres of the Hirpini were Malies or Maloenton (modern Benevento), Romulea (Bisaccia), Compsa (Conza), Aquilonia (Lacedonia), Aletrium (Calitri), and Abellinum (Avellino).
No certain date for the arrival of the Hiripini in the region can be given. They were already settled here at the time of the First Samnite War (342 BC). Their name is found in sources from 280 BC, when the Greek general Pyrrhus of Epirus made his expedition into Italy. A bronze medal reveals that they signed an alliance with the Samnites in 275 BC. Abellinum was conquered by the Romans in 252 BC. The Hirpini suffered internal divisions at the time of the Second Punic War. Caius Marius gave them Roman citizenship in 87 BC, but they were deprived of any privilege under the former's victor, Sulla (80 BC). In 22 BC Hirpinia became an imperial colony under the name Livia, which received substantial immigration from the Eastern Roman provinces at the time of emperor Alexander Severus (3rd century AD).
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, Irpinia came successively under Byzantine, Lombard, Hohenstaufen, Anjou, Aragonese and finally Spanish domination. As part of the Kingdom of Naples it was included in the Principato Ultra or Ulterior, the sole land-locked province of the kingdom. Feudalism was abolished in 1806, the same year in which Avellino was declared capital of the province.
Irpinia became part of the newly united Kingdom of Italy in 1861.
On November 23, 1980, the 6.9 Mw Irpinia earthquake affected the area with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme), killing 2,483–4,900, and injuring 7,700–8,934.
Traditional produce and tourist sites
Irpinia has a proud tradition of producing wines such as Fiano di Avellino, Greco di Tufo and Taurasi, all of which are classified as DOCG. Its cheeses, including scamorza and caciocavallo, have a high reputation. Irpinia’s salami (Subbursata and Sopressata) and sausages are popular, as are its chestnuts, its hazelnuts and the black truffles of Bagnoli Irpino.
Amenity highlights tourism are the ski resort Laceno, with the lake, the Terminio and some villages that are members of the most beautiful villages in Italy (Ex . Nusco), of note is the historic center of Gesualdo with the castle which was the home of the Prince of Musicians Carlo Gesualdo, Rocca San Felice, Calitri (particularly Castle Village ) and the medieval village of Castelvetere.
Among the religious sanctuary of Montevergine, Mercogliano, the Shrine of St. Gerard, in the municipality of Caposele and the Sanctuary of Carpignano in Grottaminarda, Shrine of Our Lady of Good Counsel in Frigento
Main comuni
Avellino, with a population of c. 57,000, is by far the largest municipality in the region. Others include:
- Atripalda (c. 11,000)
- Ariano Irpino (c. 23,000)
- Cervinara (c. 11,000)
- Fontanarosa (c. 3,500)
- Frigento (c. 4,000)
- Calitri (c. 5,000)
- Gesualdo (c. 4,000)
- Grottaminarda (c. 8,000)
- Lacedonia (c. 3,000)
- Lioni (c. 6,000)
- Mercogliano (c. 12,000)
- Mirabella Eclano (c. 8,000)
- Montella (c. 7,000)
- Montoro Inferiore (c. 9,000)
- Montoro Superiore (c. 8,000)
- Nusco (c. 4,000)
- Sant'Angelo dei Lombardi (c. 4,000)
- Solofra (c. 12,000)
- Serino (c. 7,000)
- Summonte (c. 1,500)
See also
References
- Gargano, Mauro (2005). Candida: in loco eminente et de bona aria. Naples: MCM.
External links
- Info and history of Irpinia (Italian)
- Associazione Irpinia Nostra (Italian)
- http://www.opinioneirpina.it Site that wants to show through forums, articles and opinion polls of the people Irpino. More: videos, a section devoted to immigrants and others.
- Irpinia portal (Italian)
- News from Irpinia (Italian)
- XD Magazine Irpinia (Italian)
- Lupi Emigrati (Italian) (English)