Ion channel family
| Ion channel (eukaryotic) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
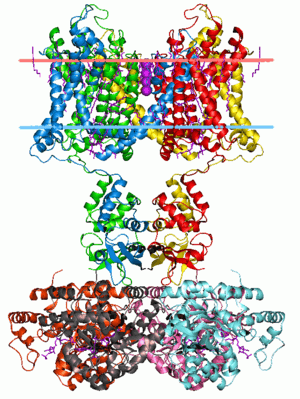
Potassium channel Kv1.2 (with beta2 auxiliary subunits), structure in a membrane-like environment. Calculated hydrocarbon boundaries of the lipid bilayer are indicated by red and blue dots. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Ion_trans | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00520 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005821 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1bl8 | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1bl8 | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.A.1 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 8 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 2a79 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Ion channel (bacterial) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
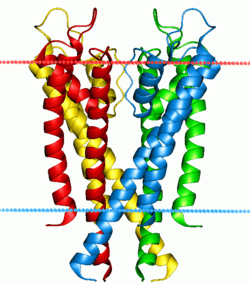
Potassium channel KcsA. Calculated hydrocarbon boundaries of the lipid bilayer are indicated by red and blue dots. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Ion_trans_2 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07885 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR013099 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1bl8 | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1bl8 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1r3j | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Transmembrane cation channel superfamily was defined in InterPro and Pfam as the family of tetrameric ion channels. These include the sodium, potassium,[1] calcium, ryanodine receptor, HCN, CNG, CatSper, and TRP channels. This large group of ion channels apparently includes families 1.A.1, 1.A.2, 1.A.3, and 1.A.4 of the TCDB transporter classification.
They are described as minimally having two transmembrane helices flanking a loop which determines the ion selectivity of the channel pore. Many eukaryotic channels have four additional transmembrane helices (TM) (Pfam PF00520), related to or vestigial of voltage gating. The proteins with only two transmembrane helices (Pfam PF07885) are most commonly found in bacteria. This also includes the 2-TM Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Pfam PF01007) found primarily in eukaryotes. There are commonly additional regulatory domains which serve to regulate ion conduction and channel gating. The pores may also be homotetramers or hetrotetramers; where hetrotetramers may be encoded as distinct genes or as multiple pore domains within a single polypepetide. Interestingly, the HVCN1 and Putative tyrosine-protein phosphatase proteins do not contain an expected ion conduction pore domain, but rather have homology only to the voltage sensor domain of voltage gated ion channels.
Human channels with 6 TM helices
Cation
Transient receptor potential channel
Canonical TRP Channels
Melastatin TRP Channels
Vanilloid TRP Channels
Mucolipin TRP Channels
Ankyrin TRP Channels
TRPP
- PKD1L3;
Calcium
Voltage-dependent calcium channel
Cation channels of sperm
Ryanodine receptor
Potassium
Voltage-gated potassium channels
Delayed rectifier
- Kvα1.x - Shaker-related: Kv1.1 (KCNA1), Kv1.2 (KCNA2), Kv1.3 (KCNA3), Kv1.5 (KCNA5), Kv1.6 (KCNA6), Kv1.7 (KCNA7), Kv1.8 (KCNA10)
- Kvα2.x - Shab-related: Kv2.1 (KCNB1), Kv2.2 (KCNB2)
- Kvα3.x - Shaw-related: Kv3.1 (KCNC1), Kv3.2 (KCNC2)
- Kvα7.x: Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) - KvLQT1, Kv7.2 (KCNQ2), Kv7.3 (KCNQ3), Kv7.4 (KCNQ4), Kv7.5 (KCNQ5)
- Kvα10.x: Kv10.1 (KCNH1)
A-type potassium channel
- Kvα1.x - Shaker-related: Kv1.4 (KCNA4)
- Kvα3.x - Shaw-related: Kv3.3 (KCNC3), Kv3.4 (KCNC4)
- Kvα4.x - Shal-related: Kv4.1 (KCND1), Kv4.2 (KCND2), Kv4.3 (KCND3)
Outward-rectifying
- Kvα10.x: Kv10.2 (KCNH5)
Inwardly-rectifying
- Kvα11.x - ether-a-go-go potassium channels: Kv11.1 (KCNH2) - hERG, Kv11.2 (KCNH6), Kv11.3 (KCNH7)
Slowly activating
Modifier/silencer
- Kvα5.x: Kv5.1 (KCNF1)
- Kvα6.x: Kv6.1 (KCNG1), Kv6.2 (KCNG2), Kv6.3 (KCNG3), Kv6.4 (KCNG4)
- Kvα8.x: Kv8.1 (KCNV1), Kv8.2 (KCNV2)
- Kvα9.x: Kv9.1 (KCNS1), Kv9.2 (KCNS2), Kv9.3 (KCNS3)
Calcium-activated potassium channel
BK channel
SK channel
- KCa2.x: KCa2.1 (KCNN1) - SK1, KCa2.2 (KCNN2) - SK2, KCa2.3 (KCNN3) - SK3
- KCa3.x: KCa3.1 (KCNN4) - SK4
- KCa4.x: KCa4.1 (KCNT1) - SLACK, KCa4.2 (KCNT2) - SLICK
IK channel
Other subfamilies
Sodium
- NALCN
- SCN1A; SCN2A; SCN2A2; SCN3A; SCN4A; SCN5A; SCN7A; SCN8A; SCN9A; SCN10A; SCN11A
- SLC9A10; SLC9A11
Cyclic nucleotide-gated
Proton
Related Proteins
- TPTE, part of the larger Voltage sensitive phosphatase family
Human channels with 2 TM helices in each subunit
Potassium
Tandem pore domain potassium channel
- KCNK1; KCNK2; KCNK3; KCNK4; KCNK5; KCNK6; KCNK7; KCNK9; KCNK10; KCNK12; KCNK13; KCNK15; KCNK16; KCNK17; KCNK18
Non-human Channels
Two-pore channels
Pore-only Potassium Channels
Ligand Gated Potassium Channel
- GluR0[2]
Voltage-gated Potassium Channels
- KvAP[3]
Prokaryotic KCa Channels
Voltage and Cyclic Nucleotide Gated Potassium Channel
- MlotiK1[16]
Sodium Channels
Non-Selective Channels
- NaK[22]
Prokaryotic Inward-rectifier potassium channels
- KirBac[23]
Engineered Channels
References
- ↑ Choe S (February 2002). "Potassium channel structures". Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3 (2): 115–21. doi:10.1038/nrn727. PMID 11836519.
- ↑ Chen, GQ; Cui, C; Mayer, ML; Gouaux, E (16 December 1999). "Functional characterization of a potassium-selective prokaryotic glutamate receptor.". Nature. 402 (6763): 817–21. doi:10.1038/45568. PMID 10617203.
- ↑ Jiang, Y; Lee, A; Chen, J; Ruta, V; Cadene, M; Chait, BT; MacKinnon, R (1 May 2003). "X-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel.". Nature. 423 (6935): 33–41. doi:10.1038/nature01580. PMID 12721618.
- ↑ Milkman R (Apr 1994). "An Escherichia coli homologue of eukaryotic potassium channel proteins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 91 (9): 3510–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.9.3510. PMC 43609
 . PMID 8170937.
. PMID 8170937. - ↑ Jiang Y, Pico A, Cadene M, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (Mar 2001). "Structure of the RCK domain from the E. coli K+ channel and demonstration of its presence in the human BK channel". Neuron. 29 (3): 593–601. doi:10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00236-7. PMID 11301020.
- ↑ Jiang Y, Lee A, Chen J, Cadene M, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (May 2002). "Crystal structure and mechanism of a calcium-gated potassium channel". Nature. 417 (6888): 515–22. Bibcode:2002Natur.417..515J. doi:10.1038/417515a. PMID 12037559.
- ↑ Smith FJ, Pau VP, Cingolani G, Rothberg BS (2013). "Structural basis of allosteric interactions among Ca2+-binding sites in a K+ channel RCK domain". Nature Communications. 4: 2621. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4E2621S. doi:10.1038/ncomms3621. PMID 24126388.
- ↑ Ye S, Li Y, Chen L, Jiang Y (Sep 2006). "Crystal structures of a ligand-free MthK gating ring: insights into the ligand gating mechanism of K+ channels". Cell. 126 (6): 1161–73. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.029. PMID 16990139.
- ↑ Dvir H, Valera E, Choe S (Aug 2010). "Structure of the MthK RCK in complex with cadmium". Journal of Structural Biology. 171 (2): 231–7. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2010.03.020. PMC 2956275
 . PMID 20371380.
. PMID 20371380. - ↑ Smith FJ, Pau VP, Cingolani G, Rothberg BS (Dec 2012). "Crystal structure of a Ba(2+)-bound gating ring reveals elementary steps in RCK domain activation". Structure. 20 (12): 2038–47. doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.09.014. PMC 3518701
 . PMID 23085076.
. PMID 23085076. - ↑ Cao Y, Jin X, Huang H, Derebe MG, Levin EJ, Kabaleeswaran V, et al. (Mar 2011). "Crystal structure of a potassium ion transporter, TrkH". Nature. 471 (7338): 336–40. Bibcode:2011Natur.471..336C. doi:10.1038/nature09731. PMC 3077569
 . PMID 21317882.
. PMID 21317882. - ↑ Cao Y, Pan Y, Huang H, Jin X, Levin EJ, Kloss B, et al. (Apr 2013). "Gating of the TrkH ion channel by its associated RCK protein TrkA". Nature. 496 (7445): 317–22. Bibcode:2013Natur.496..317C. doi:10.1038/nature12056. PMC 3726529
 . PMID 23598339.
. PMID 23598339. - ↑ Vieira-Pires RS, Szollosi A, Morais-Cabral JH (Apr 2013). "The structure of the KtrAB potassium transporter". Nature. 496 (7445): 323–8. Bibcode:2013Natur.496..323V. doi:10.1038/nature12055. PMID 23598340.
- ↑ Kong C, Zeng W, Ye S, Chen L, Sauer DB, Lam Y, et al. (2012). "Distinct gating mechanisms revealed by the structures of a multi-ligand gated K(+) channel". eLife. 1: e00184. doi:10.7554/eLife.00184. PMC 3510474
 . PMID 23240087.
. PMID 23240087. - ↑ Deller MC, Johnson HA, Miller MD, Spraggon G, Elsliger MA, Wilson IA, et al. (2015). "Crystal Structure of a Two-Subunit TrkA Octameric Gating Ring Assembly". PloS One. 10 (3): e0122512. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122512. PMC 4380455
 . PMID 25826626.
. PMID 25826626. - ↑ Clayton, GM; Altieri, S; Heginbotham, L; Unger, VM; Morais-Cabral, JH (5 February 2008). "Structure of the transmembrane regions of a bacterial cyclic nucleotide-regulated channel.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105 (5): 1511–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711533105. PMC 2234175
 . PMID 18216238.
. PMID 18216238. - ↑ Ren, D; Navarro, B; Xu, H; Yue, L; Shi, Q; Clapham, DE (14 December 2001). "A prokaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel.". Science. 294 (5550): 2372–5. doi:10.1126/science.1065635. PMID 11743207.
- ↑ Payandeh, J; Scheuer, T; Zheng, N; Catterall, WA (10 July 2011). "The crystal structure of a voltage-gated sodium channel.". Nature. 475 (7356): 353–8. doi:10.1038/nature10238. PMC 3266868
 . PMID 21743477.
. PMID 21743477. - ↑ Shaya, D; Findeisen, F; Abderemane-Ali, F; Arrigoni, C; Wong, S; Nurva, SR; Loussouarn, G; Minor DL, Jr (23 January 2014). "Structure of a prokaryotic sodium channel pore reveals essential gating elements and an outer ion binding site common to eukaryotic channels.". Journal of Molecular Biology. 426 (2): 467–83. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.010. PMC 3947372
 . PMID 24120938.
. PMID 24120938. - ↑ Zhang, X; Ren, W; DeCaen, P; Yan, C; Tao, X; Tang, L; Wang, J; Hasegawa, K; Kumasaka, T; He, J; Wang, J; Clapham, DE; Yan, N (20 May 2012). "Crystal structure of an orthologue of the NaChBac voltage-gated sodium channel.". Nature. 486 (7401): 130–4. doi:10.1038/nature11054. PMC 3979295
 . PMID 22678295.
. PMID 22678295. - ↑ McCusker, EC; Bagnéris, C; Naylor, CE; Cole, AR; D'Avanzo, N; Nichols, CG; Wallace, BA (2012). "Structure of a bacterial voltage-gated sodium channel pore reveals mechanisms of opening and closing.". Nature Communications. 3: 1102. doi:10.1038/ncomms2077. PMC 3493636
 . PMID 23033078.
. PMID 23033078. - ↑ Shi, N; Ye, S; Alam, A; Chen, L; Jiang, Y (23 March 2006). "Atomic structure of a Na+- and K+-conducting channel.". Nature. 440 (7083): 570–4. doi:10.1038/nature04508. PMID 16467789.
- ↑ Durell, SR; Guy, HR (2001). "A family of putative Kir potassium channels in prokaryotes.". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 1: 14. PMC 64639
 . PMID 11806753.
. PMID 11806753. - ↑ Derebe, MG; Sauer, DB; Zeng, W; Alam, A; Shi, N; Jiang, Y (11 January 2011). "Tuning the ion selectivity of tetrameric cation channels by changing the number of ion binding sites.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (2): 598–602. doi:10.1073/pnas.1013636108. PMC 3021048
 . PMID 21187421.
. PMID 21187421. - ↑ Sauer, DB; Zeng, W; Raghunathan, S; Jiang, Y (4 October 2011). "Protein interactions central to stabilizing the K+ channel selectivity filter in a four-sited configuration for selective K+ permeation.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (40): 16634–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.1111688108. PMC 3189067
 . PMID 21933962.
. PMID 21933962.
External links
- "Voltage-gated Ion Channels". IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR005821