International Docking System Standard
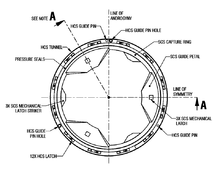
The International Docking System Standard (IDSS), is an international standard for spacecraft docking adapters. It was created by the International Space Station Multilateral Coordination Board, on behalf of the International Space Station partner organizations; NASA, Roscosmos, JAXA, ESA, and the Canadian Space Agency.
The IDSS was originally formulated in 2010.[1] The plan is for all cooperating agencies to make their future docking systems IDSS compatible.
Design
The IDSS docking mechanism is androgynous, uses low impact technology and allows both docking and berthing.[2] It supports both autonomous and piloted dockings and features pyrotechnics for contingency undocking. Once mated the IDSS interface can transfer power, data, commands, air, communication and in future implementations will be able to transfer water, fuel, oxidizer and pressurant as well.[3]
The passage for crew and cargo transfer has a diameter of 800 millimetres (31 in).[4]
Implementations
The NASA Docking System is NASA's implementation of the IDSS.[5] The International Docking Adapter is intended to convert older APAS-95 docking systems to the NASA Docking System.
The ESA's International Berthing and Docking Mechanism is their IDSS-compatible docking system.
References
- ↑ "New international standard for spacecraft docking". European Space Agency. Retrieved 2015-11-21.
- ↑ NASA Docking System (NDS) Technical Integration Meeting (2010-11-17)
- ↑ Parma, George (2011-05-20). "Overview of the NASA Docking System and the International Docking System Standard" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- ↑ "International Docking System Standard (IDSS) Interface Definitions Document (IDD) Revision D April 2015" (PDF). International Docking System Standard. ISS Multilateral Control Board. Retrieved October 31, 2015.
- ↑ Garcia, Mark. "Meet the International Docking Adapter". NASA. Retrieved 2015-11-21.