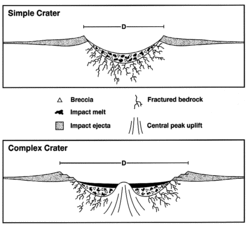
Impactite
Impactite (or impact glass) is rock created or modified by the impact of a meteorite.[1] Impactite includes shock-metamorphosed target rocks, melts (suevites) and mixtures of the two, as well as sedimentary rocks with significant impact-derived components (shocked mineral grains, tektites, anomalous geochemical signatures, etc.). In June 2015, NASA reported that impact glass has been detected on the planet Mars—such material may contain preserved signs of ancient life—if life existed.[2]
When a meteor strikes a planet's surface, the energy release from the impact can melt rock and soil into a liquid. If the liquid cools and hardens quickly into a solid, impact glass forms before the atoms have time to arrange into a crystal lattice. Impact glass is dark brown, almost black, and partly transparent.[3]
Some localities

- Alamo bolide impact (Late Devonian) of Nevada
- Alga crater on the planet Mars[2]
- Charlevoix crater of Québec
- Darwin glass from Tasmania
- Kärnäite from Lake Lappajärvi, Finland
- Manicouagan crater of Québec
- Neugrund crater of Québec
- Nördlinger Ries crater
- Rochechouart crater
- Wabar impact site
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Impactite. |
References
- ↑ http://adsabs.harvard.edu/full/1994LPI....25.1347S
- 1 2 3 Staff (8 June 2015). "PIA19673: Spectral Signals Indicating Impact Glass on Mars". NASA. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ↑ Temming, Maria. "Exotic Glass Could Help Unravel Mysteries of Mars". Retrieved 2015-06-15.