Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi
| Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi ا حمد رضا خا ن بریلوی احمد رضا خان | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Personal Details | |
| Title | Ala Hazrat |
| Born |
14 June 1856[1] Bareilly, North-Western Provinces, British Indian Empire |
| Died |
28 October 1921 (aged 65) Muhallah Sodagraan, Bareilly, UP, British Indian Empire |
| Nationality | British India |
| Era | Modern era |
| Region | South Asia |
| Religion | Islam |
| Jurisprudence | Hanafi[2] |
| Creed | Sunni[2] |
| Main interest(s) | Aqeedah, Fiqh, Tasawwuf |
|
Influenced by
| |
| Website | http://imamahmadraza.net/, http://www.raza.org.za, http://www.alahazrat.net , http://www.irshad-ul-islam.com/ |
Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi (Urdu: احمد رضاخان بریلوی, Hindi: अहमद रज़ा खान, 14 June 1856 CE or 10 Shawwal 1272 AH – 28 October 1921 CE or 25 Safar 1340 AH), also known as Imam Ahmed Raza Khan Qadri, was a Sufi Muslim scholar and reformer in British India,[3] and the founder of the Barelvi movement.[4][5][6] Raza Khan wrote on numerous topics, including law, religion, philosophy and the sciences. He was a prolific writer, religious poet, Sufi mystic, Mufti (jurist) producing nearly 1,000 works in his lifetime.[5]
Early life and family
Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi's father Naqi Ali Khan was the son of Raza Ali Khan.[7][8] Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi, Naqi Ali Khan (Father),[9] and Raza Ali Khan (Paternal grandfather).[9] Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi belonged to the Barech[7] tribe of Pushtuns. The Barech formed a tribal grouping among the Rohilla Pushtuns of North India who founded the state of Rohilkhand. The ancestors of Ahmed Raza Khan migrated from Qandahar during the Mughal rule and settled in Lahore.[7][8]
Ahmad Raza Khan was born on 14 June 1856 in Mohallah Jasoli, Bareilly Sharif, British India. His birth name is Muhammad.[10] Khan used the appellation "Abdul Mustafa" (slave [or servant] of Mustafa) prior to signing his name in correspondence.[11]
Bareilvi Sunnis Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi, by his writings and fatwas, defended Sufi practices and traditional Islam.[12] His writings, work of his students and their organizations defended the peaceful-Sufi version of Islam. Ahmed Raza Khan is regarded as Imam-e-Ahl-e-Sunnat (Leader of the Ahl-e-Sunnat) and Ala'hazrat.
This movement was founded when Ahmed Raza Khan Qadri saw an intellectual and moral decline of Muslims in British India.[13] It was a mass movement, defending popular Sufism, which grew in response to the influence of Deobandi and Wahabi extremist movement.[14]
Today the movement is spread across the globe with a huge number of followers in Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, South Africa, United States, and UK among other countries. The movement now has followers over 200 million[15] Muslims. Many religious schools, organizations and research institutions have been established that work on the teachings of Ahmed Raza Khan.[16]
The movement of Ahmed Raza Khan emphasizes primacy of Islamic law over adherence to Sufi practices and personal devotion to the Prophet Muhammad. Since partition of India and Pakistan in 1947, has addressed leading political issues for Muslims. The movement was largely a rural phenomenon when begun, but currently popular among urban, educated Pakistanis and Indians as well as South Asian diaspora throughout the world.[17]
Works
Books
Ahmed Raza Khan wrote several books on various topics in Arabic, Persian and Urdu, including the thirty-volume fatwa compilation Fatawa Razaviyya, and Kanzul Iman (translation of the Qur'an). Several of his books have been translated in other European and South Asian languages.[18][19]
Classification of 549 recovered books written by Ahmed Raza Khan:
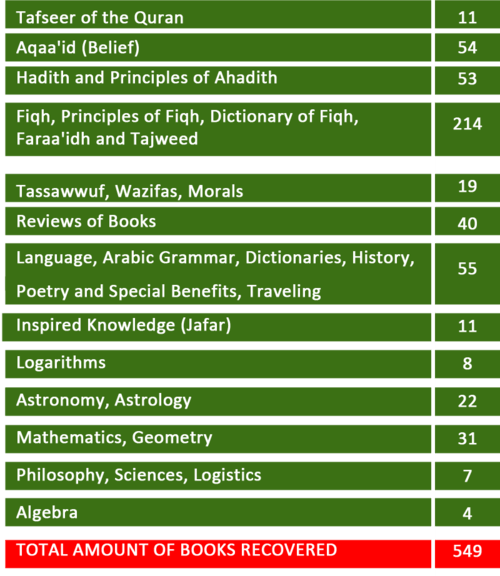
His main works include:
Kanzul Iman (translation of the Qur'an)
Kanzul Iman (Urdu and Arabic: کنزالایمان) is a 1910 Urdu paraphrase translation of the Qur'an by the Imam of Sunni Muslims Ahmad Raza Khan. It is associated with the Hanafi jurisprudence within Sunni Islam[20] and is considered widely read version of translation in the Subcontinent. It has been subsequently translated into other European and South Asian languages including English, Hindi, Bengali, Dutch, Turkish, Sindhi, Gujarati and Pashto.[19]
Husamul Haramain

Husamul Haramain or Husam al Harmain Ala Munhir kufr wal myvan (The Sword of the Haramayn at the throat of unbelief and falsehood) 1906, is a treatise written by Ahmad Raza Khan which declared infidels the founders of Deobandi, Ahle Hadith and Ahmadiyya movement on basis of what he considered to be the proper veneration of the Prophet Muhammad and finality of Prophethood in their writings and various book.[21][22][23][24] In defense of his verdict Imam Ahmad Raza Khan obtain confirmatory signatures from 268 traditional Sunni scholars in the South Asia,[25] and also got agreement from a number of ulama in Mecca and Medina. The treatise is published in Arabic, Urdu, English, Turkish and Hindi languages.[26]
Fatawa Radawiyyah

Fatawa-e-Razvia or Fatawa-e-Radaviyyah is the main fatwa (Islamic verdicts on various issues) book of his movement.[27][28] It has been published in 30 volumes and in approx. 22,000 pages. It contains solution to daily problems from religion to business and from war to marriage.[29][30]
Hadayake Bakhshish

He wrote devotional poetry in praise of Prophet and always discussed him in present tense.[31] His Na`at (Islamic poetry) is compiled in the book named Hidayake Bakhshish.[32] It includes the poems, which deal for the most part with the qualities of the Prophet, often have a simplicity and directness.[33] His emphasis on the spiritual life of the Prophet created a favorable climate for na'at writing.[34] His Urdu couplets titled, Mustafa jaane rahmat pe lakhon salaam (Millions of salutations on Mustafa, the Paragon of mercy) is read in movements mosques. It contains praise of the Prophet, his physical appearance (verses 33 to 80), his life and times, praise of his family and companions , praise of the awliya and saleheen (the saints and the pious).[35][36]
His other works include:[5][19]
- Ad Daulatul Makkiya Bil Madatul Ghaibiya
- Al Mu'tamadul Mustanad
- Al Amn o wa Ula
- Alkaukabatush Shahabiya
- Al Istimdaad
- Al Fuyoozul Makkiyah
- Al Meeladun Nabawiyyah
- Fauze Mubeen Dar Harkate Zameen
- Subhaanus Subooh
- Sallus Say yaaful Hindiya
- Ahkaam-e-Shariat
- Az Zubdatuz Zakkiya
- Abna ul Mustafa
- Tamheed-e-Imaan
- Angotthe Choomne ka Masla
Beliefs
Ahmed Raza Khan was A Muslim scholar, belonging to Sufi traditions. He supported Tawassul, Mawlid, Knowledge of Unseen for Prophet and other Sufi practices which were opposed by Wahabi and Deobandis.[31] [37] [38]
In this context he supported the following beliefs:
- Muhammad, although insan-e-kamil (perfect human), possessed a nūr or "light" that predates creation. This contrasts with the Deobandi view that Muhammad, was only a insan-e-kamil ("complete man"), a respected but physically typical human just like other humans.[39][40]
- Muhammad is haazir naazir (can be present in many places at the same time by the power given by Allah, :[41]
We do not hold that anyone can equal the knowledge of Allah Most High, or possess it independently, nor do we assert that Allah’s giving of knowledge to the Prophet (Allah bless him and give him peace) is anything but a part. But what a patent and tremendous difference between one part [the Prophet’s] and another [anyone else’s]: like the difference between the sky and the earth, or rather even greater and more immense.— Ahmed Raza Khan, al-Dawla al-Makkiyya (c00), 291.
He passed following judgements with regard to certain practices and faith in his book Fatawa-e-Razvia.[42][43] [44]
- Islamic Law Shari'ah is the ultimate law and following it is obligatory for all Muslims;
- To refrain from Bid'ah is of utmost importance;
- A Sufi without knowledge or a Shaykh without actions is a tool in the hands of the devil;
- It is impermissible to imitate the Kuffar, to mingle with the misguided [and heretics] and to participate in their festivals.
Opposition to other sects
Khan declared as infidels the founders of Deobandi, Ahle Hadith, Wahabi and Ahmadiyya sects on the basis of what he considered to be the proper veneration of the Prophet Muhammad and finality of Prophethood in their writings and various book.[21][22][23][24] In defense of his verdict Imam Ahmad Raza Khan obtained confirmatory signatures from 268 traditional Sunni scholars in the South Asia,[25] and also got agreement from a number of leading ulama in Mecca and Medina.[23]
Ahmadiyyah
Mirza Ghulam Ahmad of Qadian claimed to be the Promised Messiah and Mahdi awaited by some Muslims as well as a Ummati Nabi, a subordinate prophet to Muhammad who came to restore Islam to the Pristine form as praticed by Muhammad and early Sahaba.[45][46] Ahmed Raza Khan branded Mirza Ghulam Ahmad Qadiani a heretic and apostate and called him and his followers kuffar.[47]
Deobandis
When Ahmed Raza visited Mecca and Medina for pilgrimage in 1905, he prepared a draft document entitled Al Motamad Al Mustanad ("The Reliable Proofs"). In this work, Ahmad Raza branded Deobandi leaders such as Ashraf Ali Thanwi, Rashid Ahmad Gangohi, and Muhammad Qasim Nanotwi and those who followed them as kuffar. Ahmed Raza Khan collected opinions of the ulama of the Hejaz and compiled them in an Arabic language compendium with the title, Husam al Harmain ("The Sword of Two Sanctuaries"), a work containing 34 verdicts from 33 ulama (20 Meccan and 13 Medinese). This work, initiated a reciprocal series of fatwas between Barelvis and Deobandis lasting to the present.[48]
Shia
Khan wrote various books against beliefs and faith of Shia community and declared various practices of Shia as Kufr (Infidelity).[49] According to Imam Ahmad Raza, most Shiites of his day were apostates because they, according to him, repudiated necessities of religion.[50][51]
Wahhabism
Ahmed Raza Khan declared Wahabis as Kuffar and collected many fatwas of various scholars against the Wahabbi Movement founded by Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab who was predominant in the Arabian peninsula, just as he had done with the Ahmadis and Deobandis.[52]
Political views
Unlike other Muslim leaders in the region at the time, Khan and his movement opposed the Indian independence movement due to its leadership under Mahatma Gandhi, who was not a Muslim.[53]
Khan declared that India is darul Islam and here Muslims enjoys religious freedom, they are free to practice Islam. He said that Government has not imposed restrictions and prohibitions to follow Islam. According to him those arguing the contrary merely wanted to take advantage of the provisions allowing Muslims living under non- Muslim rule to collect interest from commercial transactions and had no desire to fight Jehad or perform Hijrat.[54] Therefore, he opposed labeling British India to be Dar al-Harb ("land of war"), which meant that waging holy war jehad and migration from India Hijrat were inadmissible as they would cause disaster to the community. The Fatawa of Deobandi Ulema on the other hand were ambiguous and contrary. Qasim Nanotwi declared India darul harab for the obligation of hijrat but darul Islam for the purpose of usury transactions. Rashid Ahmed Gangohi's decree are also confusing and non committal. This stand of Imam Ahmed Raza Qadri was similar to another reformer Sir Syed Ahmed Khan and Ubaidullah Ubaidi Suharwardy.[55]
Until just before the dawn of the British Raj, the Muslim League mobilized the Muslim masses to campaign for Pakistan[56] and many of Ahmed Raza Khan's followers played a significant and active role in the Pakistan Movement at educational and political fronts.[57]
Recognition
- On 21 June 2010, Muhammad al-Yaqoubi, a leading cleric and Sufi from Syria, declared on Takbeer TV's programme Sunni Talk that the Mujaddid of the Indian subcontinent was Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi, and said that a follower of Ahlus Sunnah wal Jamaah can be identified by his love of Khan, and that those outside of that those outside the Ahlus Sunnah are identified by their attacks on him.[58]
- Muhammad Iqbal (1877–1938), renowned poet and philosopher, said: "I have carefully studied the decrees of Imam Ahmed Raza and thereby formed this opinion; and his Fatawa bear testimony to his acumen, intellectual caliber, the quality of his creative thinking, his excellent jurisdiction and his ocean-like Islamic knowledge. Once Imam Ahmed Raza forms an opinion he stays firm on it; he expresses his opinion after a sober reflection. Therefore, the need never arises to withdraw any of his religious decrees and judgments. With all this, by nature he was hot tempered, and if this was not in the way, then Shah Ahmed Raza would have been the Imam Abu Hanifa of his age."[59] In another place he says, "Such a genius and intelligent jurist did not emerge."[60]
- Yusuf an-Nabhani (1849–1932), Mufti of Lebanon, upon reading the judgments of Khan, declared that he was a "giant Imam" and well learned man who was an expert in the sciences. Ismail Makki, Librarian of the Makkah Haram Library, said that Khan was the absolute Shaykh of all teachers. ‘Ali bin Hassan Maliki, Mufti of Mecca, called Khan the encyclopaedia of all religious sciences.[44]
- Professor Abdul Shakoor Shad, Kabul University, Afghanistan, said: “The research works of Imam Ahmed Raza Khan Barelwi are worth presenting. There is due need that Historical and Cultural Societies of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran together with other such institutions keep all his writings duly catalogued in their libraries.”[61]
Death
Ahmed Raza Khan barelvi died on 28 October 1921 CE (25th Safar 1340h) at the age of 65, in his home at Bareilly, India city on Friday.[44]
Legacy and Influences
- Ala Hazrat Express is an express train belonging to Indian Railways that runs between Bareilly and Bhuj in India.[62]
- The Indian government issued a commemorative postal stamp in honour of Ahmad Raza Khan on 31 December 1995.[63][64]
- Dawateislami owned Madani Channel broadcasts Special Transmission on the Birthday and Death Anniversary of Ahmed Raza Khan by the name of ''Faizan e Raza'' .
PhD Theses on Ahmed Raza Khan
More than twenty-one doctoral theses has been done on Ahmed Raza Khan in Pakistan, while more have been done around the world:
| Research Scholar | Topic | Language | University | Year of Approval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dr. Usha Saanpaal | Devotional Islam and Politics in British India | English | Columbia University, New York | 1990 |
| 2 | Dr. Syed Jameel Uddin Rathvi | Ala Hazrat Imam Ahmed Raza Khan and his 'Nathgoi' | Urdu | Dr. Harisingh Gour University, Sagar University | 1992 |
| 3 | Dr. Muhammad Imam Ud Deen (Johar Shafeeabad) | Hazrat Raza Barelvi as a Nasheed writer | Urdu | Bihar University, Muzaffar Pur | 1992 |
| 4 | Dr. Tayyeb Ali Raza Ansari | The Life and Achievements of Imam Ahmed Raza Khan | Urdu | Hinda University, Banaras | 1993 |
| 5 | Dr. Majeed Ullah Qadri | Detailed Comparision of Kanzul Imaan and other Quranic Translations | Urdu | Karachi University, Karachi | 1993 |
| 6 | Dr. Prof. Abdul Bari Siddiqui | The Life, Character and Reforming achievements | Sindhi | Sindh University, Jamshoro | 1993 |
Spiritual successors
There were many Mureeds (Disciples) and Khulafa (successors) of A'la Hadrat. They are 35 are in the other parts of the world and 30 in Indo-Pak Sub-Continent.[66][67]All of these sum up to more than 200 successors.[68]
Few of his Successor are:
- Maulana Hasan Raza Khan (The younger brother)
- Maulana Muhammad Raza Khan (Do)
- Maulana Hamid Raza Khan (elder son)
- Maulana Syed Ahmad Ashraf
- Maulana Zafruddin
- MUhaddithe Azam-e-Hind Syed Muhammad Kichhauchhavi.
- Maulana Abdul Ahad
- Maulana Hasnain Raza Khan (Nephew)
- Maulana Sultan Ahmad
- Maulana syed Ameer Ahmad
- Maulana Hafiz Yaqeenuddin
- Maulana Abdul Kareem
- Syed Noor Ahmad Chaatgami
- Maulana Munauwar Hussain
- Maulana waizuddin
- Maulana Abdul Rasheed
- Maulana Ghulam Muhammad Bihari
- Hakeem Syed Aziz Ghaus
- Nawab Mirza
- Maulana Abul Hasnaat Qadri
- Maulana Qalander Ali Suharwardi
- Maulana Syed Ayub Ali Razvi
- Maulana Abul Barkaat Qadri
- Maulana Muhammad Hussaini Firozpuri[69]
See also
- Dargah-e-Ala Hazrat
- Dawat-e-Islami
- Minhaj-ul-Quran
- Mohammad Abdul Ghafoor Hazarvi
- Mustafa Raza Khan
- Qamaruzzaman Azmi
- Raza Academy
- Syed Waheed Ashraf
References
- ↑ Hayat-e-Aala Hadhrat, vol.1 p.1
- 1 2 Rahman, Tariq. "Munāẓarah Literature in Urdu: An Extra-Curricular Educational Input in Pakistan's Religious Education." Islamic Studies (2008): 197–220.
- ↑ "Early Life of Ala Hazrat".
- ↑ See: He denied and condemned Taziah, Qawwali, tawaf of mazar, sada except Allah, women visiting at Shrines of Sufis.
- Illustrated Dictionary of the Muslim World (2011), p. 113. Marshall Cavendish, ISBN 9780761479291
- Globalisation, Religion & Development (2011), p. 53. Farhang Morady and İsmail Şiriner (eds.). London: International Journal of Politics and Economics.
- Rowena Robinson (2005) Tremors of Violence: Muslim Survivors of Ethnic Strife in Western India, p. 191. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications, ISBN 0761934081
- Roshen Dalal (2010) The Religions of India: A Concise Guide to Nine Major Faiths, p. 51. Revised edition. City of Westminster: Penguin Books, ISBN 9780143415176
- Barbara D. Metcalf (2009) Islam in South Asia in Practice, p. 342. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- The Columbia World Dictionary of Islamism (2007), p. 92. Oliver Roy and Antoine Sfeir (eds.), New York: Columbia University Press.
- Gregory C. Doxlowski and Usha Sanyal (Oct–Dec 1999). "Devotional Islam and Politics in British India: Ahmad Riza Khan Barelwi and His Movement, 1870–1920". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 119 (4): 707–709. doi:10.2307/604866. JSTOR 604866.
- Elizabeth Sirriyeh (1999) Sufis and Anti-Sufis: The Defense, Rethinking and Rejection of Sufism in the Modern World, p. 49. London: Routledge, ISBN 0-7007-1058-2.
- 1 2 3 Usha Sanyal (1998). "Generational Changes in the Leadership of the Ahl-e Sunnat Movement in North India during the Twentieth Century". Modern Asian Studies. 32 (3): 635. doi:10.1017/S0026749X98003059.
- ↑ Riaz, Ali (2008). Faithful Education: Madrassahs in South Asia. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press. p. 75. ISBN 978-0-8135-4345-1.
The emergence of Ahl-e-Sunnat wa Jama'at ... commonly referred to as Barelvis, under the leadership of Maulana Ahmed Riza Khan (1855–1921) ... The defining characteristic ... is the claim that it alone truly represents the sunnah (the Prophetic tradition and conduct), and thereby the true Sunni Muslim tradition.
- 1 2 3 "The blessed Genealogy of Sayyiduna AlaHadrat Imam Ahmad Rida Khan al-Baraylawi Alaihir raHmah | Alahzrat's Ancestral Tree". alahazrat.net. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- 1 2 "New Page 2". taajushshariah.com. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- 1 2 "Alahazrat Childhood". alahazrat.net. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ↑ Ala Hadhrat by Bastawi, p. 25
- ↑ Man huwa Ahmed Rida by Shaja'at Ali al-Qadri, p.15
- ↑ Mohammad Shahid Raza (1993). Islam in Britain: Past, Present and the Future. Volcano Press Limited. ISBN 978-1-870127-31-8.
- ↑ Marshall Cavendish Reference (2011). Illustrated Dictionary of the Muslim World. Marshall Cavendish. pp. 113–. ISBN 978-0-7614-7929-1.
- ↑ Robert L. Canfield (30 April 2002). Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective. Cambridge University Press. pp. 131–. ISBN 978-0-521-52291-5.
- ↑ "Search Results". oxfordreference.com.
- ↑ Usha Sanyal. Generational Changes in the Leadership of the Ahl-e Sunnat Movement in North India during the Twentieth Century. Modern Asian Studies (1998), Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ "Ahl al-Sunnah wa'l-Jamaah". oxfordreference.com.
- ↑ Skreslet, Paula Youngman, and Rebecca Skreslet. (2006). The Literature of Islam: A Guide to the Primary Sources in English Translation. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-8108-5408-6
- 1 2 3 Maarif Raza, Karachi, Pakistan. Vol.29, Issue 1–3, 2009, pages 108–09
- ↑ Paula Youngman Skreslet; Rebecca Skreslet (2006). The Literature of Islam: A Guide to the Primary Sources in English Translation. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 232–. ISBN 978-0-8108-5408-6.
- 1 2 "Trysts with Democracy". google.co.in.
- 1 2 "Muslimischer Nationalismus, Fundamentalismus und Widerstand in Pakistan". google.co.in.
- 1 2 3 Usha Sanyal Devotional Islam and Politics in British India: Ahmad Raza Khan Barelwi and His Movement, 1870–1920
- 1 2 Ismail Khan (19 October 2011). "The Assertion of Barelvi Extremism". Hudson Institute. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- 1 2 "Holy Quran's Judgement ? Part 2". google.co.in.
- ↑ "Islamic Reform in South Asia". google.co.in.
- ↑ "Jamia Rizvia of Bareilly to be upgraded to a university". milligazette.com.
- ↑ Maulana Shakir Noorie (10 October 2008). What is Sacrifice?: Qurbani kya hai?. Sunni. pp. 12–. GGKEY:G6T13NU1Q2T.
- ↑ "Dargah Ala Hazrat: Fatva Razabia is encyclopedia of Fatvas". jagran. 18 December 2014.
- ↑ David Emmanuel Singh (2012). Islamization in Modern South Asia: Deobandi Reform and the Gujjar Response. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 32–. ISBN 978-1-61451-246-2.
- 1 2 Ian Richard Netton (19 December 2013). Encyclopaedia of Islam. Routledge. pp. 88–. ISBN 978-1-135-17960-1.
- ↑ Raza, Muhammad Shahrukh. "sharah hadaiq e bakhshish - Books Library - Online School - Read - Download - eBooks - Free - Learning - Education - School - College - University - Guide - Text Books - Studies". Retrieved 24 November 2016.
- ↑ Contributions to Indian Sociology. Mouton. 1993.
- ↑ Muhammad Yusuf Abbasi (1992). Pakistani culture: a profile. National Institute of Historical and Cultural Research. ISBN 978-969-415-023-9.
- ↑ "Salaam by Imam Ahmed Raza Khan". 19 December 2007. Retrieved 24 November 2016.
- ↑ Noormuhammad, Siddiq Osman. "Salaam by Imam Ahmed Raza Khan". Retrieved 24 November 2016.
- ↑ Abdulkader Tayob; Inga Niehaus; Wolfram Weisse. Muslim Schools and Education in Europe and South Africa. Waxmann Verlag. pp. 64–. ISBN 978-3-8309-7554-0.
- ↑ Abdulkader Tayob; Inga Niehaus; Wolfram Weisse. Muslim Schools and Education in Europe and South Africa. Waxmann Verlag. pp. 76–. ISBN 978-3-8309-7554-0.
- ↑ Pakistan perspectives, Volume 7. Pakistan Study Centre, University of Karachi, 2002
- ↑ Akbar S. Ahmed (1999) Islam today: a short introduction to the Muslim world. I.B. Tauris Publishers, ISBN 978-1-86064-257-9
- ↑ N. C. Asthana & A.Nirmal (2009) Urban Terrorism : Myths And Realities. Publisher Pointer Publishers, ISBN 978-81-7132-598-6, p. 67
- ↑ Yoginder Sikand (24 August 2005). Bastions of The Believers: Madrasas and Islamic Education in India. Penguin Books Limited. pp. 73–. ISBN 978-93-5214-106-7.
- ↑ Sita Ram Sharma (1998). Politics and government of communalism. APH Publishing Corporation. ISBN 978-81-7024-933-7.
- 1 2 3 Usha Sanyal (1996). Devotional Islam and Politics in British India: Ahmad Riza Khan Barelwi and His Movement, 1870–1920. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-564862-1.
- ↑ "My Claim to Promised Messiahship - The Review of Religions". reviewofreligions.org. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ↑ Elucidation of Objectives: English Translation of Taudih-e-Maram: a Treatise by Hazrat Mirza Ghulam Ahmad
- ↑ Aziz, Zahid. (2008). A survey of the Lahore Ahmadiyya movement: history, beliefs, aims and work. Ahmadiyya Anjuman Ishaat Islam (AAIIL), UK. p. 43, ISBN 978-1-906109-03-5.
- ↑
- Siraj Khan, Blasphemy against the Prophet, in Muhammad in History, Thought, and Culture (Editors: Coeli Fitzpatrick and Adam Hani Walker), ISBN 978-1610691772, pp. 59-67
- R Ibrahim (2013), Crucified Again, ISBN 978-1621570257, pp. 100-101
- ↑ Sampark: Journal of Global Understanding. Sampark Literary Services. 2004.
- ↑ Fatawa-e-Razavia,Fatwa on Sunni marriage with shia, Book of Marriage; vol.11/pg345, Lahore edition
- ↑ http://www.islamic.pwp.blueyonder.co.uk/Fiqh/Sunni%20marriage%20with%20Shia.htm
- ↑ "Kafirs". web.archive.org. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ↑ R. Upadhyay, Barelvis and Deobandhis: "Birds of the Same Feather". Eurasia Review, courtesy of the South Asia Analysis Group. 28 January 2011.
- ↑ Ayesha Jalal (30 June 2009). Partisans of Allah: Jihad in South Asia. Harvard University Press. pp. 146–. ISBN 978-0-674-03907-0.
- ↑ M. Naeem Qureshi (1999). Pan-Islam in British Indian Politics: A Study of the Khilafat Movement, 1918–1924. BRILL. pp. 179–. ISBN 90-04-11371-1.
- ↑ Ingvar Svanberg; David Westerlund (6 December 2012). Islam Outside the Arab World. Routledge. pp. 220–. ISBN 978-1-136-11322-2.
- ↑ Imam, Muhammad Hassan. (2005). The Role of the Khulafa-e-Imam Ahmed Raza Khan in the Pakistan Movement 1920–1947. Diss. Karachi: University of Karachi.
- ↑ "Shaykh Yaqoubi Advocates Imam Ahmed Raza as a Mujaddid from Indian Subcontinent !!!!". Sunni Talk. Takbeer TV. 21 June 2010. Retrieved 19 August 2011.
- ↑ Arafat, 1970, Lahore.
- ↑ Weekly Uffaq, Karachi. 22–28 January 1979.
- ↑ "Bareilly".
- ↑ http://runningstatus.in/. "Ala Hazrat Express/14312 Live Running Train Status". runningstatus.in. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ↑ "Ala Hazrat Barelvi Commemorative Stamp". stampsathi.in. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ↑ Commemorative Stamps, India.
- ↑ Ala Hazrat ka Ilmi Pehlu. Zia ul Quran. 2005.
- ↑ Shah Ahmed Rida Khan – The "Neglected Genius of the East" by Professor Muhammad Ma'sud Ahmad M.A. P.H.D. – Courtesy of "The Muslim Digest", May/June, 1985, pp. 223–230
- ↑ "Website Bareilly".
- ↑ Maulana Ilyas Attar Qadri said in his Madani Muzarkara
- ↑ "Book".
Further reading
- Baraka, A. (2003). A Saviour in a Dark World (Article). The Islamic Times, March 2003. Stockport, UK: Raza Academy.
- Haroon, Muhammad. (1994). The World Importance of Imam Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi. Stockport, UK: Raza Academy. ISBN 9781873204122
- Imam, Muhammad Hassan. (2005). The Role of the Khulafa-e-Imam Ahmed Raza Khan in Pakistan Movement 1920–1947. Diss. Karachi: University of Karachi.
- Azimbadi, Badr. (2005).Great Personalities in Islam. Adam Publishers.
External links
- Imam Ahmed Raza Research Institute, Karachi
- Imam Ahmed Raza Academy, South Africa
- Alahazrat.net
- Raza Academy, Mumbai
- Full Biography of Ala Hazrat
- Who was Ahmad Raza Khan Barelwi?
- 315 Books of Imam Ahmed Raza Barelvi

