IgG4-related prostatitis
| IgG4-related prostatitis | |
|---|---|
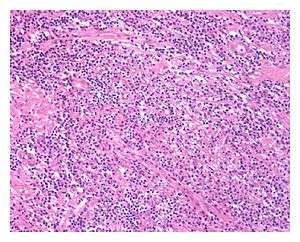 | |
| Low power view of IgG4-related prostatitis. The prostatic stroma shows a dense inflammatory infiltrate and fibrosis (H&E, 100x) | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Urology/Immunology |
| ICD-10 | N41.8 |
IgG4-related prostatitis is the term used to describe prostate involvement in men with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), which is an emerging fibroinflammatory disease entity which is characterised (i) by a tendency to tumefactive, or mass forming, lesions in multiple sites of the body and (ii) by usually a prompt response to steroid therapy.[1][2]
Men with IgG4-related prostatitis may present synchronously or metachronously with manifestations of IgG4-RD at other sites anywhere in the body.[3]
Symptoms
Several case studies on IgG4-related prostatitis have been reported. Patients have been noted to commonly present with lower urinary tract symptoms such as dysuria, pollakisuria, urinary urgency, and a feeling of incomplete emptying.[4][5] The clinical presentation is similar to that in benign prostatic hyperplasia or chronic prostatitis, although pain, as occurs in CP/CPPS, does not usually appear to be significant.
Investigations
Men with IgG4-related prostatitis may have similar findings to those that are frequently, but not always, seen in other organ manifestations of IgG4-related disease, such as elevated blood levels of IgG4, IgE and eosinophils.
FDG-PET scans have been reported to be useful as a diagnostic modality for detecting IgG4-related prostatitis in men with IgG4-RD.[6][7]
Histology
The diagnosis of IgG4-related prostatitis could be made from histological examination if prostate biopsy or surgery has been performed.[6] The hallmark histopathological features of established IgG4-related disease are storiform fibrosis, a dense lymphoplasmacytic (lymphocytes and plasma cells) infiltrate rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells, and obliterative phlebitis.[8]
However, identification depends on whether or not urologists and pathologists are aware of IgG4-related prostatitis/disease, as special immunostaining is required to identify the characteristic IgG4-positive plasma cells infiltration in prostatic tissue.[3]
Treatment
IgG4-related disease responds well, and often dramatically, to glucocorticoid therapy, provided that advanced fibrotic lesions have not resulted in irreversible damage, and this has included resolution of radiologic findings.[1] Men given glucocorticoids to treat IgG4-related disease at other anatomical sites sometimes report relief of their lower urinary tract symptoms, suggesting that IgG4-related prostatitis may be underdiagnosed.[6]
Cases are however likely to get misdiagnosed as benign prostatic hyperplasia and to get treated alternatively with medications such as alpha blockers. The efficacy of alpha blockers in IgG4-related prostatitis remains unclear.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 Rodolfo Montironi; Marina Scarpelli; Liang Cheng; Antonio Lopez-Beltran; Maurizio Burattini; Ziya Kirkali; Francesco Montorsi (December 2013). "Immunoglobulin G4-related disease in genitourinary organs: an emerging fibroinflammatory entity often misdiagnosed preoperatively as cancer". European Urology. European Association of Urology. 64 (1): 865–872. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.11.056. PMID 23266239.
- ↑ John H. Stone; Arezou Khosroshahi; Vikram Deshpande; John K. C. Chan; J. Godfrey Heathcote; Rob Aalberse; Atsushi Azumi; Donald B. Bloch; William R. Brugge; Mollie N. Carruthers; Wah Cheuk; Lynn Cornell; Carlos Fernandez-Del Castillo; Judith A. Ferry; David Forcione; Günter Klöppe; Daniel L. Hamilos; Terumi Kamisawa; Satomi Kasashima; Shigeyuki Kawa; Mitsuhiro Kawano; Yasufumi Masaki; Kenji Notohara; Kazuichi Okazaki; Ji Kon Ryu; Takako Saeki; Dushyant Sahani; Yasuharu Sato; Thomas Smyrk; James R. Stone; Masayuki Takahira; Hisanori Umehara; George Webster; Motohisa Yamamoto; Eunhee Yi; Tadashi Yoshino; Giuseppe Zamboni; Yoh Zen; Suresh Chari (October 2012). "Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations". Arthritis & Rheumatism. 64 (10): 3061–3067. doi:10.1002/art.34593. PMID 22736240.
- 1 2 3 Noboru Hara; Makoto Kawaguchi; Keisuke Takeda; Yoh Zen (28 Nov 2014). "Retroperitoneal disorders associated with IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (44): 16550–16558. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16550. PMC 4248198
 . PMID 25469023.
. PMID 25469023.
- ↑ Yukihiro Yoshimura; Shin-ichi Takeda; Yasuhiko Ieki; Eisuke Takazakura; Hisashi Koizumi; Kiyoshi Takagawa (1 Sep 2006). "IgG4-associated prostatitis complicating autoimmune pancreatitis". Internal Medicine. Tokyo: Japanese Society of Internal Medicine. 45 (15): 897–901. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.45.17522. PMID 16946571.
- ↑ Isao Nishimori; Takuhiro Kohsaki; Saburo Onishi; Taro Shuin; Shino Kohsaki; Yasuhiro Ogawa; Manabu Matsumoto; Makoto Hiroi; Hideaki Hamano; Shigeyuki Kawa (17 Dec 2007). "IgG4-related autoimmune prostatitis: two cases with or without autoimmune pancreatitis". Internal Medicine. Tokyo: Japanese Society of Internal Medicine. 46 (24): 1983–1989. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.46.0452. PMID 18084121.
- 1 2 3 Mohamad Zaidan; Julien Adam; Pascale Cervera-Pierot; Dominique Joly (Dec 2011). "The Case | A 69-year-old man with a 10-year history of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis". Kidney International. International Society of Nephrology. 80 (12): 1379–1380. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.357. PMID 22126986.
- ↑ Hiroyuki Takahashi; Hiroto Tsuboi; Hiroshi Ogishima; Masahiro Yokosawa; Hidenori Takahashi; Mizuki Yagishita; Saori Abe; Shinya Hagiwara; Hiromitsu Asashima; Tomoya Hirota; Naoto Umeda; Yuya Kondo; Takeshi Suzuki; Isao Matsumoto; Takayuki Sumida (June 2015). "[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography can reveal subclinical prostatitis in a patient with IgG4-related disease". Rheumatology. British Society for Rheumatology. 54 (6): 1113. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kev099. PMID 25863043.
- ↑ John H. Stone; Yoh Zen; Vikram Deshpande (February 2012). "IgG4-Related Disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 336 (6): 539–51. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1104650. PMID 22316447.