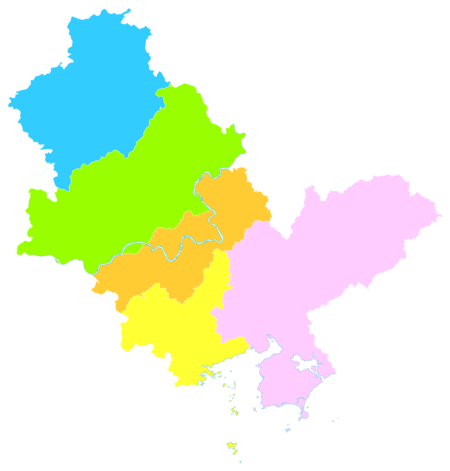
Huizhou
| Huizhou 惠州市 | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
|
West Lake of Huizhou | |
| Motto: A city to benefit people (惠民之州) | |
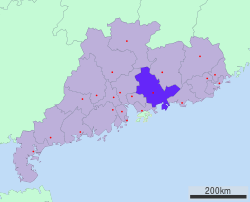 Location of Huizhou in Guangdong | |
 Huizhou Location in China | |
| Coordinates: 23°4′0″N 114°24′0″E / 23.06667°N 114.40000°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guangdong |
| City | 1988 |
| Municipal seat | Huicheng District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Secretary | Chen Yiwei (陈奕威) |
| • Mayor | Mai Jiaomeng (麦教猛) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 10,922 km2 (4,217 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,672 km2 (1,032 sq mi) |
| • Coastline | 223.6 km2 (86.3 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 15 m (49 ft) |
| Population (2010 census[1]) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,598,402 |
| • Density | 420/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,344,634 |
| • Urban density | 880/km2 (2,300/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 44,778,513 |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Postal code | 516000 |
| Area code(s) | 0752 |
| GDP | ¥2368.9 billion (2012) |
| GDP per capita | ¥38,650 (2012) |
| Licence Plate | 粤L |
| Website | http://www.huizhou.gov.cn/ |
Huìzhōu (Chinese: 惠州) is a city in southeast Guangdong Province, China. Huizhou borders the provincial capital of Guangzhou to the west, Shaoguan to the north, Heyuan to the northeast, Shanwei to the east, Shenzhen and Dongguan to the southwest, and Daya Bay of the South China Sea to the south. The city has about 4.6 million inhabitants and is administered as a prefecture-level city.
Economy
Huizhou gained benefit from the Chinese economic reform of the late 1980s. The blossoming of the real estate market attracted capital investment from Hong Kong and Taiwan.
In the provincial economic development strategy, Huizhou is regarded as a site for a world-class petrochemical industry, as well as a hub for developing information technology, and expanding exports and trade.
TCL Corporation has its headquarters in the city.
Development Zones
Huizhou Dayawan Economic and Technological Development Zone was approved by the State Council in 1993. It had an initial area of 9.98 km2 (3.85 sq mi), and in 2006, the State Council expanded the zone to 23.6 km2 (9.1 sq mi) in 3 phases. Industries encouraged in the zone include Automobile Production/Assembly, Chemical Production and Processing, Electronics Assembly & Manufacturing and more.[2]
- Huizhou Export Processing Zone
Huizhou Export Processing Zone was approved by Guangdong Provincial Government in June, 2005. Its parent zone is Huizhou Dayawan Economic and Technological Development Zone. The planned area is 3 km2 (1.2 sq mi). The zone is suitable for companies focused on electronics, auto parts, textile and chemicals.[3]
- Huizhou Zhongkai High-tech Industrial Development Zone
Huizhou Zhongkai High-tech Industrial Development Zone is connected with Shenzhen, Guangzhou and Dongguan by Huizhou-Shenzhen Highway, Guangzhou-Huizhou Highway and Dongguan-Huizhou Highway. Beijing-Kowloon Railway and Huizhou-Aotou Railway also run through the zone, linking it with Beijing, Hong Kong, and other cities along the railway. Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport is within one-and-a-half hour's drive from the zone. Huizhou Zhongkai HIDZ has established electronics, information technology and optical-, mechanical- and electronic-integration as its major industries. It also encourages investment in new materials, telecommunications, and other high-tech industries. The zone is one of the National Electronic Information Industry Bases and National Video and Audio Products Parks in China. The zone has attracted many large multinational companies. Major investors include Sony, SPG, Futaba, Coca Cola, LG and Siemens.[4]
Administration
The prefecture-level city of Huizhou administers 5 county-level divisions, including 2 districts and 3 counties.
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010 census) |
Area (km2) |
Density (/km2) |
| Huicheng District | 惠城区 | Huìchéng Qū | 1,579,818 | 1,488.45 | 1,061 |
| Huiyang District | 惠阳区 | Huìyáng Qū | 764,816 | 1,205.44 | 664 |
| Boluo County | 博罗县 | Bóluó Xiàn | 1,038,198 | 2,855.11 | 364 |
| Huidong County | 惠东县 | Huìdōng Xiàn | 908,390 | 3,526.73 | 258 |
| Longmen County | 龙门县 | Lóngmén Xiàn | 307,180 | 2,267.2 | 135 |
| Huizhou | |||||||||||||||||
|
"Huizhou", as written in Chinese | |||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 惠州 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postal | Waichow | ||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Benefit prefecture | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Transport
Huizhou is served by the Jingjiu Railway (also known as the Guangmeishan Railway in Guangdong) with two stations: Huizhou West and Huizhou.
The town is about 2 hour-drive by bus from Shenzhen Baoan International Airport. Huizhou airport reopened in 2015. A mass rapid transit linking it to Shenzhen was under construction as of 2011.
Language
The main language spoken by the local people in Huizhou is Huizhou Dialect as well as Hakka. As more newcomers from the other provinces come to work in Huizhou, Mandarin has become the other popular language in Huizhou.
Military
Huizhou is headquarters of the 42nd Group Army of the People's Liberation Army, one of the two group armies that comprise the Guangzhou Military Region responsible for the defense of China's southern coast and its border with Vietnam.
Education
Educational facilities in Huizhou include:
- Huizhou University
- Huizhou Radio and Television University
- Huizhou Nanshan School
Climate
| Climate data for Huizhou (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.2 (72) |
26.1 (79) |
29.3 (84.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.2 (88.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
20.4 (68.7) |
26.37 (79.47) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
11.7 (53.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
19.2 (66.6) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.0 (75.2) |
20.7 (69.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
11.6 (52.9) |
18.83 (65.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 37.3 (1.469) |
62.8 (2.472) |
87.0 (3.425) |
202.0 (7.953) |
226.7 (8.925) |
323.6 (12.74) |
255.1 (10.043) |
276.1 (10.87) |
173.0 (6.811) |
66.6 (2.622) |
28.2 (1.11) |
33.4 (1.315) |
1,771.8 (69.755) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 6.3 | 10.6 | 12.6 | 14.5 | 18.3 | 18.7 | 17.2 | 18.4 | 13.0 | 6.6 | 5.1 | 4.8 | 146.1 |
| Source: Weather China | |||||||||||||
Tourism

- Daya Bay
Daya Bay is located to the southeast of Huizhou City, on the South China Sea, with waters covering an area of nearly 500 km2 (190 sq mi). There are nearly 100 islands and reefs in the bay. The climate is described as a typical subtropical oceanic climate, with temperatures averaging 21.8 degrees over the year. Parts of the bay have been described by travelchinaguide.com as "an unpolluted, quiet paradise for those sea-lovers."[5]
- Beach Spa Huizhou's seashore hot springs are filled with geothermal minerals, and boast a temperature of nearly 70 degrees Celsius. These waters are said to have dozens of benefits to human health, due to the aforementioned minerals. The National Standards board has labelled the water as the best salt water hot spring spas.(citation needed)
- Sea-level city The Sea city was built in the 18th year of the Ming dynasty, under the Hongwu Emperor (AD 1385), giving it a history of over 600 years. It is found south of the Five Ridges known locally as the "living fossil of culture".(citation needed)
- Elephant Head Mountain Elephant head mountain scenic area is located in the south of Boluo County,18 kilometres away from the Huizhou city area, and covers an area of 33 km2 (13 sq mi). Elephant head mountain is formed in the Cretaceous period of igneous rock, and sports a main peak reaching an elevation of 1023 meters above sea level. The mountain bedrock forms a unique "stone egg" landscape.
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Huizhou is twinned with:
 Hallstatt, Austria[6]
Hallstatt, Austria[6] Milpitas, California, United States[7]
Milpitas, California, United States[7]
References
- ↑ "China: Administrative Division of Guăngdōng / 广东省". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ↑ "Huizhou Dayawan Economics Technology Development Zone". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ↑ "Guangdong Huizhou Export Processing Zone". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ↑ "Huizhou Zhongkai Hi-Tech Development Zone". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ↑ "Huizhou Travel Guide". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ↑ Wainwright, Oliver (7 January 2013). "Seeing double: what China's copycat culture means for architecture". The Guardian. London: Guardian News and Media Limited. Retrieved 2014-11-15.
- ↑ "Sister Cities". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Huizhou. |
- Government website of Huizhou (Chinese)