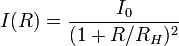Hubble–Reynolds law
Not to be confused with Hubble's law which relates galaxy redshifts and distances.
The Hubble–Reynolds law models the surface brightness of elliptical galaxies as
Where 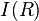 is the surface brightness at radius
is the surface brightness at radius 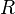 ,
, 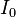 is the central brightness, and
is the central brightness, and 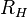 is the radius at which the surface brightness is diminished by a factor of 1/4. It is asymptotically similar to the De Vaucouleurs' law which is a special case of the Sersic profile for elliptical galaxies.[1]
is the radius at which the surface brightness is diminished by a factor of 1/4. It is asymptotically similar to the De Vaucouleurs' law which is a special case of the Sersic profile for elliptical galaxies.[1]
The law is named for the astronomers Edwin Hubble and John Henry Reynolds.
References
- ↑ Binney & Tremaine. Galactic Dynamics 2008.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/1/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.