Hoesch reaction
| Houben–Hoesch reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Josef Houben Kurt Hoesch |
| Reaction type | Coupling reaction |
The Hoesch reaction or Houben–Hoesch reaction is an organic reaction in which a nitrile reacts with an arene compound to form an aryl ketone. The reaction is a type of Friedel-Crafts acylation with hydrogen chloride and a Lewis acid catalyst.
An example is the synthesis of 1-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)ethanone from phloroglucinol:[1]
A ketimine is isolated as an intermediate reaction product. The attacking electrophile is possibly[2] a species of the type R-C+=NHCl−. The arene must be electron-rich i.e. phenol or aniline type. A related reaction is the Gattermann reaction in which hydrocyanic acid not a nitrile is used.
The reaction is named after Kurt Hoesch[3] and Josef Houben[4] who reported about this new reaction type in respectively 1915 and 1926.
Mechanism
The mechanism of the reaction involves two steps. The first step is a nucleophilic addition to the nitrile with the aid of a polarizing Lewis acid, forming an imine, which is latter hydrolyzed during the aqueous workup to yield the final aryl ketone.
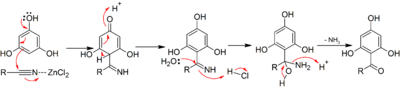
References
- ↑ Gulati, K. C.; Seth, S. R.; Venkataraman, K. (1935). "Phloroacetophenone". Organic Syntheses. 15: 70. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.015.0070.
- ↑ March, Jerry (1985), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (3rd ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN 0-471-85472-7
- ↑ Eine neue Synthese aromatischer Ketone. I. Darstellung einiger Phenol-ketone Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft Volume 48, Issue 1, Date: Januar–Juni 1915, Pages: 1122–1133 Kurt Hoesch doi:10.1002/cber.191504801156
- ↑ Über die Kern-Kondensation von Phenolen und Phenol-äthern mit Nitrilen zu Phenol- und Phenol-äther-Ketimiden und -Ketonen (I.) Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series) Volume 59, Issue 11, Date: 8. Dezember 1926, Pages: 2878–2891 J. Houben doi:10.1002/cber.19260591135
ethanone_from_phloroglucinol.png)