Hadrosaurid
| Hadrosaurids Temporal range: Late Cretaceous, 90–66 Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mounted skeleton of Parasaurolophus cyrtocristatus, Field Museum of Natural History | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | †Ornithischia |
| Suborder: | †Ornithopoda |
| Superfamily: | †Hadrosauroidea |
| Family: | †Hadrosauridae Cope, 1869 |
| Type species | |
| †Hadrosaurus foulkii Leidy, 1858 | |
| Subgroups | |
|
†Lapampasaurus | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Hadrosaurids (Greek: ἁδρός, hadrós, "stout, thick"), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is also known as the duck-billed dinosaurs, for the flat, duck-bill appearance of their mouths. The family, which includes ornithopods such as Edmontosaurus and Parasaurolophus, was a common herbivore in the Upper Cretaceous Period of what is now Asia, Europe, Antarctica, South America and North America.[1] Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Like the rest of the ornithischians, these animals had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Hadrosaurids are divided into two principal subfamilies: the lambeosaurines (Lambeosaurinae), which had hollow cranial crests or tubes, and the saurolophines, identified as hadrosaurines in most pre-2010 works (Saurolophinae or Hadrosaurinae), which lacked hollow cranial crests (solid crests were present in some forms). Saurolophines tended to be bulkier than lambeosaurines. Lambeosaurines are divided into Aralosaurines, Lambeosaurines, Parasaurolophines and Tsintaosaurines, while Saurolophines include Saurolophus, Brachylophosaurines and Kritosaurines.
Hadrosaurids were facultative bipeds, with the young of some species walking mostly on two legs and the adults walking mostly on four.[2][3] Their jaws were designed for grinding plants, with multiple rows of teeth replacing each other as the teeth wore down.[2]
Characteristics
The most recognizable aspect of hadrosaur anatomy is the flattened and laterally stretched rostral bones, which gives the distinct duck-bill look, and some members of the hadrosaurs also had massive crests on their heads, probably for display.[4] In some genera, including Edmontosaurus, the whole front of the skull was flat and broadened out to form a beak, which was ideal for clipping leaves and twigs from the forests of Asia, Europe and North America. However, the back of the mouth contained thousands of teeth suitable for grinding food before it was swallowed. This has been hypothesized to have been a crucial factor in the success of this group in the Cretaceous compared to the sauropods.
Skin impressions of multiple hadrosaurs have been found.[5] From these impressions, it has been determined that the hadrosaurs were scaled, and not feathered like some dinosaurs of other groups.
In 2009, paleontologist Mark Purnell conducted a study into the chewing methods and diet of hadrosaurids from the Late Cretaceous period. By analyzing hundreds of microscopic scratches on the teeth of a fossilized Edmontosaurus jaw, the team determined hadrosaurs had a unique way of eating unlike any creature living today. In contrast to a flexible lower jaw joint prevalent in today's mammals, hadrosaurs had a unique hinge between the upper jaws and the rest of its skull. The team found the dinosaur's upper jaws pushed outwards and sideways while chewing, as the lower jaw slid against the upper teeth.[6] This chewing method is called pleurokinesis. During pleurokinesis, the maxilla bones slide laterally outward from the mouth. This is accomplished with a hinge made of the joints between the premaxilla and maxilla bones and the lacrimal and prefrontal bones. Pleurokinesis allows for the teeth to more precisely grind against one another, for better shearing of plant material, and reduces the stress that chewing puts on the skull.[7] Analysis of the wear-patterns of the teeth has provided further insight into how these animals may have fed. On the teeth, there can be found four different sets of wear patterns that indicate the lower jaw would have moved directly up and down.[8] Furthermore, the wear patterns were parallel, revealing that the rows of teeth were extremely well aligned in the jaw.
Hadrosaurs, much like sauropods, are noted for having their manus united in a fleshy, often nail-less pad.[9]
Cranial differences between subfamilies
.jpg)
The two major divisions of hadrosaurids are differentiated by their cranial ornamentation. While members of the Lambeosaurinae subfamily have hollow crests that differ depending on species, members of the Saurolophinae (Hadrosaurinae) subfamily have solid crests or none at all. Lambeosaurine crests had air chambers that may have produced a distinct sound and meant that their crests could have been used for both an audio and visual display.
Discoveries
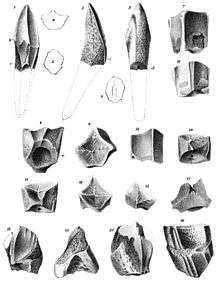
Hadrosaurids were the first dinosaur family to be identified in North America - the first traces being found in 1855-1856 with the discovery of fossil teeth. Joseph Leidy examined the teeth, and erected the genera Trachodon and Thespesius (others included Troodon, Deinodon and Palaeoscincus). One species was named Trachodon mirabilis. Ultimately, Trachodon included all sorts of cerapod dinosaurs, including ceratopsids, and is now considered an invalid genus. In 1858, the teeth were associated with Leidy's eponymous Hadrosaurus foulkii, which was named after the fossil hobbyist William Parker Foulke. More and more teeth were found, resulting in even more (now obsolete) genera.
When a second duck-bill skeleton was unearthed, Edward Drinker Cope incorrectly named it Diclonius mirabilis in 1883 instead of Trachodon mirabilis. But Trachodon, together with other poorly typed genera, was used more widely and, when Cope's famous "Diclonius mirabilis" skeleton was mounted at the American Museum of Natural History, it was labeled as a "Trachodont dinosaur". The duck-billed dinosaur family was then named Trachodontidae.
A very well preserved complete hadrosaurid specimen, AMNH 5060, (Edmontosaurus annectens) was recovered in 1908 by the fossil collector Charles Hazelius Sternberg and his three sons, in Converse County, Wyoming. Analyzed by Henry Osborn in 1912, it has come to be known as the "Trachodon mummy". This specimen's skin was almost completely preserved in the form of impressions.

Lawrence Lambe erected the genus Edmontosaurus ("lizard from Edmonton") in 1917 from a find in the lower Edmonton Formation (now Horseshoe Canyon Formation), Alberta. Hadrosaurid systematics were addressed in a 1942 monograph by Richard Swann Lull and Nelda Wright. They proposed the genus Anatosaurus for several species of dubious genera. Cope's famous mount at the AMNH became Anatosaurus copei. In 1990, Anatosaurus was moved to Edmontosaurus. One former Anatosaurus species was distinct enough from Edmontosaurus to be placed in a separate genus, named Anatotitan, so in 1990 the AMNH mount was re-labelled Anatotitan copei.
Paleontologists have found a hadrosaurid leg bone in Paleocene rocks, but it was probably reworked from a Cretaceous source.[10]
One of the most complete fossilized specimens was found in 1999 in the Hell Creek Formation of North Dakota and is now nicknamed "Dakota". The hadrosaur fossil is so well preserved that scientists have been able to calculate its muscle mass and learn that it was more muscular than thought, probably giving it the ability to outrun predators, such as Tyrannosaurus rex. Dakota is more than fossilized bones, it is a fossilized mummy. It comes complete with skin (not merely skin impressions), ligaments, tendons and possibly some internal organs. It is being analyzed in the world's largest CT scanner, operated by the Boeing Co.[11] The machine is usually used for detecting flaws in space shuttle engines and other large objects, but previously none as large as this. Researchers hope that the technology will help them learn more about the fossilized insides of the creature. They also found a gap of about a centimeter between each vertebra, indicating that there may have been a disk or other material between them, allowing more flexibility and meaning the animal was actually longer than what is shown in a museum.[12] Skin impressions have been found from the following hadrosaurs: Edmontosaurus annectens, Corythosaurus casuarius, Brachylophosaurus canadensis, Gryposaurus notabilis, Parasaurolophus walkeri, Lambeosaurus magnicristatus, Lambeosaurus lambei, Saurolophus osborni, Magnapaulia laticaudus and, Saurolophus angustirostris.[5]
Paleontologists from the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (INAH, Mexico's federal National Institute of Anthropology and History), identified a find in Mexico near the town of General Cepeda in the state of Coahuila, as a hadrosaur. Fifty of its tail vertebrae were found intact among other of its fossilized bones at the site.[13]
In September 2015, researchers from University of Alaska Fairbanks and University of Florida concluded that the remains of a duck-billed dinosaur found in the high arctic of Alaska is a new species of hadrosaur, provisionally named Ugrunaaluk kuukpikensis. It apparently survived in conditions much harsher than those of other dinosaurs.[14]
Classification
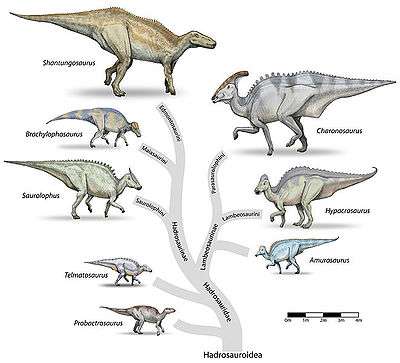
The family Hadrosauridae was first used by Edward Drinker Cope in 1869. Since its creation, a major division has been recognized in the group between the (generally crested) subfamily Lambeosaurinae and (generally crestless) subfamily Saurolophinae (or Hadrosaurinae). Phylogenetic analysis has increased the resolution of hadrosaurid relationships considerably (see Phylogeny below), leading to the widespread usage of tribes (a taxonomic unit below subfamily) to describe the finer relationships within each group of hadrosaurids. Recent phylogenies also support the monophyly of both the Saurolophinae and the Lambeosaurinae.[4] However, many hadrosaurid tribes commonly recognized in online sources have not yet been formally defined or seen wide use in the literature. Several were briefly mentioned under informal names, but not named as such, in the first edition of The Dinosauria. In this 1990 reference, "gryposaurs" included Aralosaurus, Gryposaurus, Hadrosaurus, and Kritosaurus; "brachylophosaurs" included Brachylophosaurus and Maiasaura; "saurolophs" included Lophorhothon, Prosaurolophus, and Saurolophus; and "edmontosaurs" included Edmontosaurus, and Shantungosaurus.[15]
Lambeosaurines have also been traditionally split into Parasaurolophini (Parasaurolophus) and Corythosaurini (Corythosaurus, Hypacrosaurus, and Lambeosaurus).[16] Corythosaurini and Parasaurolophini as terms entered the formal literature in Evans and Reisz's 2007 redescription of Lambeosaurus magnicristatus. Corythosaurini is defined as all taxa more closely related Corythosaurus casuarius than to Parasaurolophus walkeri, and Parasaurolophini as all those taxa closer to P. walkeri than to C. casuarius. In this study, Charonosaurus and Parasaurolophus are parasaurolophins, and Corythosaurus, Hypacrosaurus, Lambeosaurus, Nipponosaurus, and Olorotitan are corythosaurins.[17] In recent years Tsintaosaurini (Tsintaosaurus + Pararhabdodon) and Aralosaurini (Aralosaurus + Canardia) have also emerged.[18]
The use of the term Hadrosaurinae was questioned in a comprehensive study of hadrosaurid relationships by Albert Prieto-Márquez in 2010. Prieto-Márquez noted that, though the name Hadrosaurinae had been used for the clade of mostly crestless hadrosaurids by nearly all previous studies, its type species, Hadrosaurus foulkii, has almost always been excluded from the clade that bears its name, in violation of the rules for naming animals set out by the ICZN. Prieto-Márquez defined Hadrosaurinae as just the lineage containing H. foulkii, and used the name Saurolophinae instead for the traditional grouping.[4]
The closest relatives of the hadrosaurs are the Iguanodontidae.[19] The most notable difference between the Hadrosauridae and the Iguanodontidae are in the bones of their jaw.[19] Members of Iguanodontidae have a large maxilla bone in the upper jaw, while hadrosaurs have a smaller maxilla, complex teeth organization, and a large premaxilla in the upper jaw.[19] Hadrosaurs are defined as all of the descendants of the last common ancestor of Telmatosaurus and Parasaurolophus.[4]
Taxonomy
The following taxonomy includes dinosaurs currently referred to the Hadrosauridae and its subfamilies. Hadrosaurids that were accepted as valid, but not placed in a cladogram at the time of Prieto-Márquez's 2010 study,[20] are included at the highest level to which they were placed (either then, or in their description if they postdate the papers used here).
- Family Hadrosauridae
- Subfamily Hadrosaurinae
- Subfamily Saurolophinae
- Subfamily Lambeosaurinae
- Dubious hadrosaurids
Phylogeny
Hadrosauridae was first defined as a clade, by Forster, in a 1997 abstract, as simply "Lambeosaurinae plus Hadrosaurinae and their most recent common ancestor". In 1998, Paul Sereno defined the clade Hadrosauridae as the most inclusive possible group containing Saurolophus (a well-known saurolophine) and Parasaurolophus (a well-known lambeosaurine), later emending the definition to include Hadrosaurus, the type genus of the family, which ICZN rules state must be included, despite its status as a nomen dubium. According to Horner et al. (2004), Sereno's definition would place a few other well-known hadrosaurs (such as Telmatosaurus and Bactrosaurus) outside the family, which led them to define the family to include Telmatosaurus by default.
The following cladogram was recovered in a 2010 phylogenetic analysis by Prieto-Márquez.[20]
| |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Saurolophine cladogram
Hadrosauridae has not been subjected to as many phylogenetic analyses as other dinosaur groups, so other workers may find quite different phylogenies. Gates and Sampson (2007) published the following alternate cladogram of Saurolophinae (identified as "Hadrosaurinae" in the study) in their description of Gryposaurus monumentensis:[21]
| unnamed |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Lambeosaurine cladogram
The following cladogram is after the 2007 redescription of Lambeosaurus magnicristatus (Evans and Reisz, 2007):[17]
| Hadrosauridae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Paleobiology
Diet
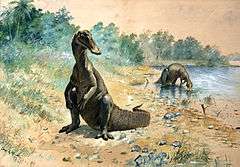
While studying the chewing methods of hadrosaurids in 2009, the paleontologists Vincent Williams, Paul Barrett, and Mark Purnell found that hadrosaurs likely grazed on horsetails and vegetation close to the ground, rather than browsing higher-growing leaves and twigs. This conclusion was based on the evenness of scratches on hadrosaur teeth, which suggested the hadrosaur used the same series of jaw motions over and over again.[8] As a result, the study determined that the hadrosaur diet was probably made of leaves and lacked the bulkier items, such as twigs or stems, that might have required a different chewing method and created different wear patterns.[22] However, Purnell said these conclusions were less secure than the more conclusive evidence regarding the motion of teeth while chewing.[6]
The hypothesis that hadrosaurs were likely grazers rather than browsers appears to contradict previous findings from preserved stomach contents found in the fossilized guts in previous hadrosaur studies.[6] The most recent such finding before the publication of the Purnell study was conducted in 2008, when a team led by University of Colorado at Boulder graduate student Justin S. Tweet found a homogeneous accumulation of millimeter-scale leaf fragments in the gut region of a well-preserved partially grown Brachylophosaurus.[23][24] As a result of that finding, Tweet concluded in September 2008 that the animal was likely a browser, not a grazer.[24] In response to such findings, Purnell said that preserved stomach contents are questionable because they do not necessarily represent the usual diet of the animal. The issue remains a subject of debate.[25]
Mallon et al. (2013) examined herbivore coexistence on the island continent of Laramidia, during the Late Cretaceous. It was concluded that hadrosaurids could reach low-growing trees and shrubs that were out of the reach of ceratopsids, ankylosaurs, and other small herbivores. Hadrosaurids were capable of feeding up to 2 m when standing quadrupedally, and up to 5 m bipedally.[26]
Coprolites (fossilized droppings) of some Late Cretaceous hadrosaurs show that the animals sometimes deliberately ate rotting wood. Wood itself is not nutritious, but decomposing wood would have contained fungi, decomposed wood material and detritus-eating invertebrates, all of which would have been nutritious.[27]
Reproduction
Neonate sized hadrosaur fossils have been documented in the scientific literature.[28] Tiny hadrosaur footprints have been discovered in the Blackhawk Formation of Utah.[28]
In the Dinosaur Park Formation

In a 2001 review of hadrosaur eggshell and hatchling material from Alberta's Dinosaur Park Formation, Darren Tanke and M. K. Brett-Surman concluded that hadrosaurs nested in both the ancient upland and lowlands of the formation's depositional environment. The upland nesting grounds may have been preferred by the less common hadrosaurs, like Brachylophosaurus and Parasaurolophus. However, the authors were unable to determine what specific factors shaped nesting ground choice in the formation's hadrosaurs. They suggested that behavior, diet, soil condition, and competition between dinosaur species all potentially influenced where hadrosaurs nested.[28]
Sub-centimeter fragments of pebbly-textured hadrosaur eggshell have been reported from the Dinosaur Park Formation. This eggshell is similar to the hadrosaur eggshell of Devil's Coulee in southern Alberta as well as that of the Two Medicine and Judith River Formations in Montana, United States. While present, dinosaur eggshell is very rare in the Dinosaur Park Formation and is only found in two different microfossil sites. These sites are distinguished by large numbers of pisidiid clams and other less common shelled invertebrates, like unionid clams and snails. This association is not a coincidence, as the invertebrate shells would have slowly dissolved and released enough basic calcium carbonate to protect the eggshells from naturally occurring acids that otherwise would have dissolved them and prevented fossilization.[28]
In contrast with eggshell fossils, the remains of very young hadrosaurs are actually somewhat common. Tanke has observed that an experienced collector could actually discover multiple juvenile hadrosaur specimens in a single day. The most common remains of young hadrosaurs in the Dinosaur Park Formation are dentaries, bones from limbs and feet, as well as vertebral centra. The material showed little or none of the abrasion that would have resulted from transport, meaning the fossils were buried near their point of origin. Bonebeds 23, 28, 47, and 50 are productive sources of young hadrosaur remains in the formation, especially bonebed 50. The bones of juvenile hadrosaurs and fossil eggshell fragments are not known to have preserved in association with each other, despite both being present in the formation.[28]
Development
The limbs of the juvenile hadrosaurs are anatomically and proportionally similar to those of adult animals.[28] However, the joints often show "predepositional erosion or concave articular surfaces",[28] which was probably due to the cartilaginous cap covering the ends of the bones.[28] The pelvis of a young hadrosaur was similar to that of an older individual.[28]
Evidence suggests that young hadrosaurs would have walked on only their two hind legs, while adults would have walked on all four.[2] As the animal aged, the front limbs became more robust in order to take on weight, while the back legs became less robust as they transitioned to walking on all four legs.[2] Furthermore, the animals’ front limbs were shorter than their back limbs.[2]
Daily activity patterns
Comparisons between the scleral rings of several hadrosaur genera (Corythosaurus, Prosaurolophus, and Saurolophus) and modern birds and reptiles suggest that they may have been cathemeral, active throughout the day at short intervals.[29]
Ichnology
Tiny hadrosaur footprints have been discovered in the Blackhawk Formation of Utah.[28]
See also
References
- ↑ Case, Judd A. (25 September 2000). "The first duck-billed dinosaur (Family Hadrosauridae) from Antarctica.". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dilkes, David W. (2001). "An ontogenetic perspective on locomotion in the Late Cretaceous dinosaur Maiasaura peeblesorum (Ornithischia: Hadrosauridae)". Canadian Journal of Earth Science 38.8.
- ↑ Fiorillo, A.R.; Tykoski, R.S. (2016). "Small hadrosaur manus and pes tracks from the Lower Cantwell Formation (Upper Cretaceous) Denali National Park, Alaska: implications for locomotion in juvenile hadrosaurs.". PALAIOS. doi:10.2110/palo.2016.049.
- 1 2 3 4 name=PM2010>Prieto-Márquez, A. (2010). "Global phylogeny of Hadrosauridae (Dinosauria: Ornithopoda) using parsimony and Bayesian methods." Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 159: 435–502.
- 1 2 Bell, P. R. (2012). Farke, Andrew A, ed. "Standardized Terminology and Potential Taxonomic Utility for Hadrosaurid Skin Impressions: A Case Study for Saurolophus from Canada and Mongolia". PLoS ONE. 7 (2): e31295. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031295. PMC 3272031
 . PMID 22319623.
. PMID 22319623. - 1 2 3 Boyle, Alan (2009-06-29). "How dinosaurs chewed". MSNBC. Retrieved 2009-06-03.
- ↑ Norman, John B.; Weishampel, David B. (1983). "Ornithopod Feeding Mechanisms: Their Bearing on the Evolution of Herbivory.". The American Naturalist.
- 1 2 Williams, Vincent S.; Barrett, Paul M.; Purnell, Mark A. (2009). "Quantitative analysis of dental microwear in hadrosaurid dinosaurs, and the implications for hypotheses of jaw mechanics and feeding". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106 (27): 11194–11199. doi:10.1073/pnas.0812631106. PMC 2708679
 . PMID 19564603.
. PMID 19564603. - ↑ "Hadrosaur Forelimb Study". Palaeo-electronica.org. Retrieved 2013-07-23.
- ↑ Fassett, J, Zielinski, R.A., and Budahn, J.R. (2002). Dinosaurs that did not die; evidence for Paleocene dinosaurs in the Ojo Alamo Sandstone, San Juan Basin, New Mexico. In: Koeberl, C., and MacLeod, K. (eds.). Catastrophic events and mass extinctions: impacts and beyond. Special Paper – Geological Society of America 356:307-336.
- ↑ (Reuters News) "Mummified dinosaur reveals surprises: scientists" 3 December 2007.
- ↑ Schmid, Randolph (2007-12-03). "Mummified Dinosaur May Have Outrun T Rex". Associated Press. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
- ↑ Cohen, Luc, et al, Paleontologists discover dinosaur tail in northern Mexico, Reuters, Tuesday, July 23, 2013
- ↑ "New Duck-billed Dinosaur Species Discovered in Alaska". Sci-News.com. Retrieved 2015-09-23.
- ↑ Weishampel, David B.; Horner, Jack R. (1990). "Hadrosauridae". In Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; Osmólska, Halszka. The Dinosauria (1st ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 534–561. ISBN 0-520-06727-4.
- ↑ Glut, Donald F. (1997). Dinosaurs: The Encyclopedia. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Co. p. 69. ISBN 0-89950-917-7.
- 1 2 Evans, David C.; Reisz, Robert R. (2007). "Anatomy and relationships of Lambeosaurus magnicristatus, a crested hadrosaurid dinosaur (Ornithischia) from the Dinosaur Park Formation, Alberta". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 27 (2): 373–393. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2007)27[373:AAROLM]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ↑ "PLOS ONE: Diversity, Relationships, and Biogeography of the Lambeosaurine Dinosaurs from the European Archipelago, with Description of the New Aralosaurin Canardia garonnensis".
- 1 2 3 You, Hai-lu; et al. (June 2003). "The earliest-known duck-billed dinosaur from deposits of late Early Cretaceous age in northwest China and hadrosaur evolution.". Cretaceous Research 24.3.
- 1 2 Prieto-Márquez, A. (2010). "Global phylogeny of Hadrosauridae (Dinosauria: Ornithopoda) using parsimony and Bayesian methods." Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 159: 435–502.
- ↑ Gates, Terry A.; Sampson, Scott D. (2007). "A new species of Gryposaurus (Dinosauria: Hadrosauridae) from the late Campanian Kaiparowits Formation, southern Utah, USA". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 151 (2): 351–376. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2007.00349.x.
- ↑ Bryner, Jeanna (2009-06-29). "Study hints at what and how dinosaurs ate". LiveScience. Retrieved 2009-06-03.
- ↑ Tweet, Justin S.; Chin, Karen; Braman, Dennis R.; Murphy, Nate L. (2008). "Probable gut contents within a specimen of Brachylophosaurus canadensis (Dinosauria: Hadrosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana". PALAIOS. 23 (9): 624–635. doi:10.2110/palo.2007.p07-044r.
- 1 2 Lloyd, Robin (2008-09-25). "Plant-eating dinosaur spills his guts: Fossil suggests hadrosaur's last meal included lots of well-chewed leaves". MSNBC. Retrieved 2009-06-03.
- ↑ This information comes from the aforementioned Alan Boyle source from June 29, 2009. However, this specific information is not included in the body of the article, but rather a response by Boyle to comments in the article. Since the comments were written by Boyle himself, and since they cite information he received specifically from Purnell, they are as legitimate a source of information as the article itself.
- ↑ Mallon, Jordan C.; Evans, David C.; Ryan, Michael J.; Anderson, Jason S. (2013). "Feeding height stratification among the herbivorous dinosaurs from the Dinosaur Park Formation (upper Campanian) of Alberta, Canada". BMC Ecology. 13: 14. doi:10.1186/1472-6785-13-14. PMC 3637170
 . PMID 23557203.
. PMID 23557203. - ↑ Chin, K. (September 2007). "The Paleobiological Implications of Herbivorous Dinosaur Coprolites from the Upper Cretaceous Two Medicine Formation of Montana: Why Eat Wood?". PALAIOS. 22 (5): 554. doi:10.2110/palo.2006.p06-087r. Retrieved 2008-09-10.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Tanke, D.H. and Brett-Surman, M.K. 2001. Evidence of Hatchling and Nestling-Size Hadrosaurs (Reptilia:Ornithischia) from Dinosaur Provincial Park (Dinosaur Park Formation: Campanian), Alberta, Canada. pp. 206-218. In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life—New Research Inspired by the Paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Edited by D.H. Tanke and K. Carpenter. Indiana University Press: Bloomington. xviii + 577 pp.
- ↑ Schmitz, L.; Motani, R. (2011). "Nocturnality in Dinosaurs Inferred from Scleral Ring and Orbit Morphology". Science. 332 (6030): 705–708. doi:10.1126/science.1200043. PMID 21493820.
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Hadrosaurid |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Hadrosauridae |
