HLA-DRB1
| HLA-DRB1
|
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Human UniProt search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|
1BX2, 1YMM, 2WBJ,%%s1A6A,%%s1AQD, 1DLH, 1FYT, 1HXY, 1JWM, 1JWS, 1JWU, 1KG0, 1KLG, 1KLU, 1LO5, 1PYW, 1R5I, 1SEB, 1SJH, 1T5W, 1T5X, 2FSE, 2G9H, 2IAM, 2IAN, 2ICW, 2IPK, 2OJE, 2XN9, 3L6F, 3PDO, 3PGC, 3PGD, 3QXA, 3QXD, 3S4S, 3S5L, 4AEN, 4AH2, 4C56, 4E41, 4FQX, 4GBX, 4I5B, 4OV5, 4X5W, 4X5X,%%s1D5M, 1D5X, 1D5Z, 1D6E, 1J8H, 2SEB, 3O6F, 3T0E, 4IS6, 4MCY, 4MCZ, 4MD0, 4MD4, 4MD5, 4MDI, 4MDJ, 4Y19, 4Y1A
| | |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases |
HLA-DRB1, DRB1, DRw10, HLA-DR1B, HLA-DRB, SS1, HLA-DRB1, major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 |
|---|
| External IDs |
HomoloGene: 136635 GeneCards: HLA-DRB1
|
|---|
|
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species |
Human |
Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez |
|
|
|---|
| Ensembl |
|
|
|---|
| UniProt |
|
|
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) |
Chr 6: 32.55 – 32.59 Mb |
n/a |
|---|
| PubMed search |
[1] |
n/a
|
|---|
| Wikidata |
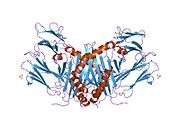
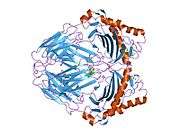
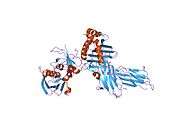
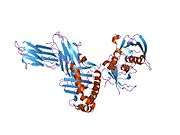
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRB1 gene.[2] DRB1 encodes the most prevalent beta subunit of HLA-DR. Several alleles of DRB1 (shared epitope alleles)[3] are associated with an increased incidence of rheumatoid arthritis.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. The class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DRA) and a beta chain (DRB), both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins to T helper cells. Class II molecules are constitutively expressed in professional antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages),[2] and could be induced in non-professional APCs.
Gene structure and polymorphisms
The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa. It is encoded by 6 exons, exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DR molecule the beta chain contains all the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities. Hundreds of DRB1 alleles have been described and typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation.[2]
Gene expression
DRB1 is expressed at a level five times higher than its paralogues DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. DRB1 is present in all individuals. Allelic variants of DRB1 are linked with either none or one of the genes DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. There are 4 related pseudogenes: DRB2, DRB6, DRB7, DRB8 and DRB9.[2]
See also
References
Further reading
- Turesson C, Matteson EL (Jan 2006). "Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 81 (1): 94–101. doi:10.4065/81.1.94. PMID 16438485.
- Ahmad T, Marshall SE, Jewell D (Jun 2006). "Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease: the role of the HLA complex". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 12 (23): 3628–35. PMID 16773677.
- Schmidt H, Williamson D, Ashley-Koch A (May 2007). "HLA-DR15 haplotype and multiple sclerosis: a HuGE review". American Journal of Epidemiology. 165 (10): 1097–109. doi:10.1093/aje/kwk118. PMID 17329717.
PDB gallery |
|---|
|
| 1aqd: HLA-DR1 (DRA, DRB1 0101) HUMAN CLASS II HISTOCOMPATIBILITY PROTEIN (EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN) COMPLEXED WITH ENDOGENOUS PEPTIDE |
| 1bx2: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-DR2 (DRA*0101,DRB1*1501) COMPLEXED WITH A PEPTIDE FROM HUMAN MYELIN BASIC PROTEIN |
| 1d5m: X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-DR4 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE AND SEB |
| 1d5x: X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-DR4 COMPLEXED WITH DIPEPTIDE MIMETIC AND SEB |
| 1d5z: X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-DR4 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDOMIMETIC AND SEB |
| 1d6e: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-DR4 COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDOMIMETIC AND SEB |
| 1dlh: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN CLASS II MHC PROTEIN HLA-DR1 COMPLEXED WITH AN INFLUENZA VIRUS PEPTIDE |
| 1fv1: STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR THE BINDING OF AN IMMUNODOMINANT PEPTIDE FROM MYELIN BASIC PROTEIN IN DIFFERENT REGISTERS BY TWO HLA-DR2 ALLELES |
| 1fyt: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A COMPLEX OF A HUMAN ALPHA/BETA-T CELL RECEPTOR, INFLUENZA HA ANTIGEN PEPTIDE, AND MHC CLASS II MOLECULE, HLA-DR1 |
| 1h15: X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-DRA1*0101/DRB5*0101 COMPLEXED WITH A PEPTIDE FROM EPSTEIN BARR VIRUS DNA POLYMERASE |
| 1hqr: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A SUPERANTIGEN BOUND TO THE HIGH-AFFINITY, ZINC-DEPENDENT SITE ON MHC CLASS II |
| 1hxy: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN H IN COMPLEX WITH HUMAN MHC CLASS II |
| 1j8h: Crystal Structure of a Complex of a Human alpha/beta-T cell Receptor, Influenza HA Antigen Peptide, and MHC Class II Molecule, HLA-DR4 |
| 1jwm: Crystal Structure of the Complex of the MHC Class II Molecule HLA-DR1(HA peptide 306-318) with the Superantigen SEC3 |
| 1jws: Crystal Structure of the Complex of the MHC Class II Molecule HLA-DR1 (HA peptide 306-318) with the Superantigen SEC3 Variant 3B1 |
| 1jwu: Crystal Structure of the Complex of the MHC Class II Molecule HLA-DR1 (HA peptide 306-318) with the superantigen SEC3 Variant 3B2 |
| 1kg0: Structure of the Epstein-Barr Virus gp42 Protein Bound to the MHC class II Receptor HLA-DR1 |
| 1klg: Crystal structure of HLA-DR1/TPI(23-37, Thr28-->Ile mutant) complexed with staphylococcal enterotoxin C3 variant 3B2 (SEC3-3B2) |
| 1klu: Crystal structure of HLA-DR1/TPI(23-37) complexed with staphylococcal enterotoxin C3 variant 3B2 (SEC3-3B2) |
| 1lo5: Crystal structure of the D227A variant of Staphylococcal enterotoxin A in complex with human MHC class II |
| 1pyw: Human class II MHC protein HLA-DR1 bound to a designed peptide related to influenza virus hemagglutinin, FVKQNA(MAA)AL, in complex with staphylococcal enterotoxin C3 variant 3B2 (SEC3-3B2) |
| 1r5i: Crystal structure of the MAM-MHC complex |
| 1seb: COMPLEX OF THE HUMAN MHC CLASS II GLYCOPROTEIN HLA-DR1 AND THE BACTERIAL SUPERANTIGEN SEB |
| 1sje: HLA-DR1 complexed with a 16 residue HIV capsid peptide bound in a hairpin conformation |
| 1sjh: HLA-DR1 complexed with a 13 residue HIV capsid peptide |
| 1t5w: HLA-DR1 in complex with a synthetic peptide (AAYSDQATPLLLSPR) |
| 1t5x: HLA-DR1 in complex with a synthetic peptide (AAYSDQATPLLLSPR) and the superantigen SEC3-3B2 |
| 1ymm: TCR/HLA-DR2b/MBP-peptide complex |
| 1zgl: Crystal structure of 3A6 TCR bound to MBP/HLA-DR2a |
| 2fse: Crystallographic structure of a rheumatoid arthritis MHC susceptibility allele, HLA-DR1 (DRB1*0101), complexed with the immunodominant determinant of human type II collagen |
| 2g9h: Crystal Structure of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin I (SEI) in Complex with a Human MHC class II Molecule |
| 2iam: Structural basis for recognition of mutant self by a tumor-specific, MHC class II-restricted TCR |
| 2ian: Structural basis for recognition of mutant self by a tumor-specific, MHC class II-restricted TCR |
| 2icw: Crystal structure of a complete ternary complex between TCR, superantigen, and peptide-MHC class II molecule |
| center|border|180x180px|alt=|Image:PDB_2seb_EBI.jpg | Image:PDB_2seb_EBI.jpg |
| center|border|180x180px|alt=| | |
|
|