HIST3H3
Histone H3.1t is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST3H3 gene.[2][3]
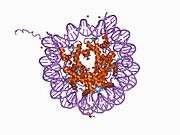
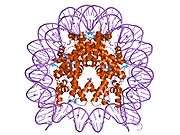
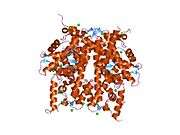
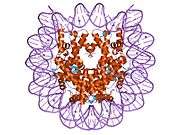
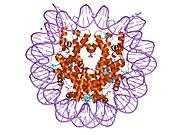
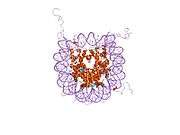
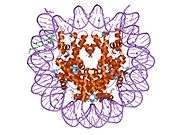
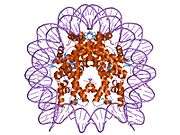
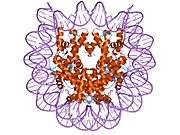
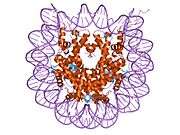
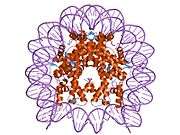
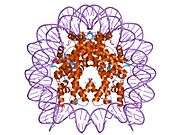
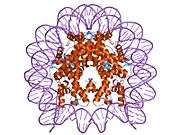
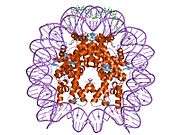
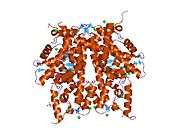
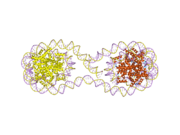
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H3 family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails; instead, they contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is located separately from the other H3 genes that are in the histone gene cluster on chromosome 6p22-p21.3.[4]
References
Further reading
- Govin J, Caron C, Rousseaux S, Khochbin S (2005). "Testis-specific histone H3 expression in somatic cells.". Trends Biochem. Sci. 30 (7): 357–9. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2005.05.001. PMID 15922600.
- Bernués J, Espel E, Querol E (1986). "Identification of the core-histone-binding domains of HMG1 and HMG2.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 866 (4): 242–51. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(86)90049-7. PMID 3697355.
- Ishimi Y, Ichinose S, Omori A, et al. (1996). "Binding of human minichromosome maintenance proteins with histone H3.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (39): 24115–22. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.39.24115. PMID 8798650.
- Mizzen CA, Yang XJ, Kokubo T, et al. (1997). "The TAF(II)250 subunit of TFIID has histone acetyltransferase activity.". Cell. 87 (7): 1261–70. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81821-8. PMID 8980232.
- Witt O, Albig W, Doenecke D (1997). "Testis-specific expression of a novel human H3 histone gene.". Exp. Cell Res. 229 (2): 301–6. doi:10.1006/excr.1996.0375. PMID 8986613.
- Rodriguez P, Munroe D, Prawitt D, et al. (1997). "Functional characterization of human nucleosome assembly protein-2 (NAP1L4) suggests a role as a histone chaperone.". Genomics. 44 (3): 253–65. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4868. PMID 9325046.
- Albig W, Doenecke D (1998). "The human histone gene cluster at the D6S105 locus.". Hum. Genet. 101 (3): 284–94. doi:10.1007/s004390050630. PMID 9439656.
- El Kharroubi A, Piras G, Zensen R, Martin MA (1998). "Transcriptional activation of the integrated chromatin-associated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (5): 2535–44. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.5.2535. PMC 110633
 . PMID 9566873.
. PMID 9566873.
- Zhang Y, Sun ZW, Iratni R, et al. (1998). "SAP30, a novel protein conserved between human and yeast, is a component of a histone deacetylase complex.". Mol. Cell. 1 (7): 1021–31. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80102-1. PMID 9651585.
- Lorain S, Quivy JP, Monier-Gavelle F, et al. (1998). "Core histones and HIRIP3, a novel histone-binding protein, directly interact with WD repeat protein HIRA.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (9): 5546–56. PMC 109139
 . PMID 9710638.
. PMID 9710638.
- Becker W, Weber Y, Wetzel K, et al. (1998). "Sequence characteristics, subcellular localization, and substrate specificity of DYRK-related kinases, a novel family of dual specificity protein kinases.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (40): 25893–902. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.40.25893. PMID 9748265.
- Carrier F, Georgel PT, Pourquier P, et al. (1999). "Gadd45, a p53-responsive stress protein, modifies DNA accessibility on damaged chromatin.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (3): 1673–85. PMC 83961
 . PMID 10022855.
. PMID 10022855.
- Sassone-Corsi P, Mizzen CA, Cheung P, et al. (1999). "Requirement of Rsk-2 for epidermal growth factor-activated phosphorylation of histone H3.". Science. 285 (5429): 886–91. doi:10.1126/science.285.5429.886. PMID 10436156.
- Thomson S, Clayton AL, Hazzalin CA, et al. (1999). "The nucleosomal response associated with immediate-early gene induction is mediated via alternative MAP kinase cascades: MSK1 as a potential histone H3/HMG-14 kinase.". EMBO J. 18 (17): 4779–93. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.17.4779. PMC 1171550
 . PMID 10469656.
. PMID 10469656.
- Hsieh YJ, Kundu TK, Wang Z, et al. (1999). "The TFIIIC90 subunit of TFIIIC interacts with multiple components of the RNA polymerase III machinery and contains a histone-specific acetyltransferase activity.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 19 (11): 7697–704. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.11.7697. PMC 84812
 . PMID 10523658.
. PMID 10523658.
- Cheung P, Tanner KG, Cheung WL, et al. (2000). "Synergistic coupling of histone H3 phosphorylation and acetylation in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation.". Mol. Cell. 5 (6): 905–15. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80256-7. PMID 10911985.
- Buggy JJ, Sideris ML, Mak P, et al. (2001). "Cloning and characterization of a novel human histone deacetylase, HDAC8.". Biochem. J. 350 (1): 199–205. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3500199. PMC 1221242
 . PMID 10926844.
. PMID 10926844.
- Deng L, de la Fuente C, Fu P, et al. (2001). "Acetylation of HIV-1 Tat by CBP/P300 increases transcription of integrated HIV-1 genome and enhances binding to core histones.". Virology. 277 (2): 278–95. doi:10.1006/viro.2000.0593. PMID 11080476.
- Seo SB, McNamara P, Heo S, et al. (2001). "Regulation of histone acetylation and transcription by INHAT, a human cellular complex containing the set oncoprotein.". Cell. 104 (1): 119–30. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00196-9. PMID 11163245.
PDB gallery |
|---|
|
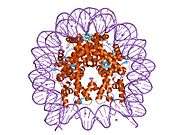
| 1aoi: COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT |
| 1eqz: X-RAY STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE AT 2.5 A RESOLUTION |
| 1f66: 2.6 A CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE CONTAINING THE VARIANT HISTONE H2A.Z |
| 1hq3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HISTONE-CORE-OCTAMER IN KCL/PHOSPHATE |
| 1kx3: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146, at 2.0 A Resolution |
| 1kx4: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP146b, at 2.6 A Resolution |
| 1kx5: X-Ray Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle, NCP147, at 1.9 A Resolution |
| 1m18: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA |
| 1m19: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA |
| 1m1a: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA |
| 1p34: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3a: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3b: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3f: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3g: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3i: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3k: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3l: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3m: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3o: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3p: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1s32: Molecular Recognition of the Nucleosomal 'Supergroove' |
| 1tzy: Crystal Structure of the Core-Histone Octamer to 1.90 Angstrom Resolution |
| 1u35: Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle containing the histone domain of macroH2A |
| 1zbb: Structure of the 4_601_167 Tetranucleosome |
| 1zla: X-ray Structure of a Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA peptide bound to the nucleosomal core |
| 2aro: Crystal Structure Of The Native Histone Octamer To 2.1 Angstrom Resolution, Crystalised In The Presence Of S-Nitrosoglutathione |
| 2cv5: Crystal structure of human nucleosome core particle |
| 2f8n: 2.9 Angstrom X-ray structure of hybrid macroH2A nucleosomes |
| 2fj7: Crystal structure of Nucleosome Core Particle Containing a Poly (dA.dT) Sequence Element |
| 2hio: HISTONE OCTAMER (CHICKEN), CHROMOSOMAL PROTEIN |
| 2hue: Structure of the H3-H4 chaperone Asf1 bound to histones H3 and H4 |
| 2io5: Crystal structure of the CIA- histone H3-H4 complex |
| 2nzd: Nucleosome core particle containing 145 bp of DNA |
|
|
 . PMID 9566873.
. PMID 9566873. . PMID 9710638.
. PMID 9710638. . PMID 10022855.
. PMID 10022855. . PMID 10469656.
. PMID 10469656. . PMID 10523658.
. PMID 10523658. . PMID 10926844.
. PMID 10926844.