Gymnopilus junonius
| Gymnopilus junonius | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Agaricales |
| Family: | Cortinariaceae |
| Genus: | Gymnopilus |
| Binomial name | |
| Gymnopilus junonius (Fr.) P.D.Orton (1960) | |
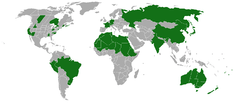 | |
| Approximate range of Gymnopilus junonius | |
| Synonyms | |
| Gymnopilus junonius | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| gills on hymenium | |
| cap is convex | |
| hymenium is adnate | |
| stipe has a ring | |
| spore print is reddish-brown | |
| ecology is saprotrophic | |
|
edibility: psychoactive or inedible | |
Gymnopilus junonius is a species of mushroom in the family Cortinariaceae. Commonly known as Laughing Gym, Laughing Cap, Laughing Jim, or the Spectacular Rustgill, this large orange mushroom is typically found growing on tree stumps, logs, or tree bases. Some subspecies of this mushroom contain the neurotoxic oligoisoprenoid gymnopilin.
Taxonomy
This species was formerly known as Gymnopilus spectabilis, or Pholiota spectabilis v. junonia (Fr.) J.E Lange.[1] The 'Gymn' in the present nomen means 'naked', and 'Juno' was the wife of Jupiter.[2] In Korea, this mushroom is called Hwanggalsaek Michigwang-i Beoseot, which translates to "bronze clown mushroom".
Description
The cap ranges from 7 to 20 cm across, is convex, and is bright yellow-orange in younger specimens and orange/brown or reddish brown in older ones, with a dry scaly surface. The stem is 2.5 to 26.5 cm long, 1 to 4 cm thick, and often narrows near the base. The frail ring is dusted with rusty orange spores, the flesh is yellow and the gill attachment to the stem is adnate to sub-decurrent. It has a bitter taste, stains red with KOH and turns green when cooked in a pan. The spore print is rusty orange. It occasionally bruises blue, especially smaller specimens or "runts". This mushroom usually grows in clusters from several to several dozen individuals, but sometimes grows solitary.
Similar species
This mushroom is often mistaken for Gymnopilus ventricosus, which contains no psilocybin.
Distribution and habitat
Gymnopilus junonius is a very widely distributed mushroom which grows in dense clusters under large or old trees, the most common being the silver maple. This mushroom grows just about everywhere that decaying wood can be found, [3] but is most common in moist, lowland wooded areas near rivers.
Biochemistry
This mushroom has subspecies which contain the hallucinogen psilocybin. Specimens found in Korea or the eastern part of US are more likely to contain psilocybin than similar mushrooms found in the western part of the US or Europe. This mushroom contains bis-noryangonin and hispidine, which are structurally related to alpha-pyrones found in kava.[4] Japanese researchers have found oligoisoprenoids, or neurotoxins in this mushroom.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Roger Phillips (2006). Mushrooms. Pan MacMillan. ISBN 0-330-44237-6.
- ↑ Arora D. (1986). Mushrooms Demystified. Ten Speed Press. ISBN 0-89815-169-4.
- ↑ Guzmán, Gastón; Allen, John W.; Gartz, Jochen (1998). "A Worldwide geographical Distribution of the neurotropic fungi, an analysis and discussion" (PDF). Ann. Mus. civ. Rovereto Sez. 14: 189–280. Referred to in the paper as Gymnopilus spectabilis.
- ↑ Hatfield, G.M.; Brady, L.R. (1969). "Occurrence of bis-noryangonin in Gymnopilus spectabilis". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 58 (10): 1298–1299. doi:10.1002/jps.2600581039. PMID 5388695.
- ↑ Tanaka, Masayasu; Hashimoto, Kimiko; Okunoa, Toshikatsu; Shirahama, Haruhisa (1993). "Neurotoxic oligoisoprenoids of the hallucinogenic mushroom, Gymnopilus spectabilis". Phytochemistry. 34 (3): 661–664. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(93)85335-O.
- C.J. Alexopolous, Charles W. Mims, M. Blackwell et al., Introductory Mycology, 4th ed. (John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken NJ, 2004) ISBN 0-471-52229-5
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gymnopilus junonius. |
- Tom Volk's Fungi of the Month - Gymnopilus spectabilis
- Mushroom Expert - Gymnopilus junonius
- Guzmán-Dávalos, Laura; Mueller, Gregory M.; Cifuentes, Joaquín; Miller, Andrew N.; Santerre, Anne (Nov–Dec 2003). "Traditional infrageneric classification of Gymnopilus is not supported by ribosomal DNA sequence data" (PDF). Mycologia. 95 (6): 1204–1214. doi:10.2307/3761920. JSTOR 3761920. PMID 21149021.