Colours, standards and guidons


In military organizations, the practice of carrying colours, standards or guidons, both to act as a rallying point for troops and to mark the location of the commander, is thought to have originated in Ancient Egypt some 5,000 years ago. The Roman Empire also made battle standards a part of their vast armies. It was formalized in the armies of Europe in the High Middle Ages, with standards being emblazoned with the commander's coat of arms.
General use

As armies became trained and adopted set formations, each regiment's ability to keep its formation was potentially critical to its, and therefore its army's, success. In the chaos of battle, not least due to the amount of dust and smoke on a battlefield, soldiers needed to be able to determine where their regiment was.
Regimental flags are generally awarded to a regiment by a head-of-State during a ceremony. They were therefore treated with reverence as they represented the honour and traditions of the regiment. Colours may be inscribed with the names of battles or other symbols representing former achievements (see battle honours).
Regiments tended to adopt "colour guards", composed of experienced or élite soldiers, to protect their colours. As a result, the capture of an enemy's standard was considered as a great feat of arms.
They are never capriciously destroyed – when too old to use they are replaced and then laid-up in museums, religious buildings and other places of significance to their regiment. However, in most modern armies, standing orders now call for the Colours to be intentionally destroyed if they are ever in jeopardy of being captured by the enemy.
Due to the advent of modern weapons, and subsequent changes in tactics, Colours are no longer carried into battle, but continue to be used at events of formal character.
Colours
North, Central and South Americas
Argentina
The Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic's military Colours of the Argentine Army, Argentine Navy and Argentine Air Force are the Flag of Argentina as the National War Colour and the Unit Colour. The National War Colour is a variation of the Argentine national flag made for military use, while the Unit Colour differs per service arm and unit. The Army's older regiments tend to have their unit colour based on designs used before while the Regiment of Mounted Grenadiers tend to have the Flag of the Army of the Andes as a second National War Colour.
Only the Regiment of Patricians uses company colors. Cadet squadron colours are used by the Argentine Air Force Academy.
Brazil
Units of the Brazilian Armed Forces carry a stand of two Colours, differing per service.
The standard of the Army measures 80 × 120 cm, white with the Army coat of arms in the centre, trimmed with gold fringe. The name of the service is inscribed in gold letters on a green scroll beneath the shield. Above the shield is a knight's helmet with red and sky blue mantling. The staff is topped by a nickel-plated lance-head finial, 32 cm high. Below the lance-head, there is a cravat (laço militar) divided lengthwise, sky blue and red, with a gold fringe at the end, tied in a bow and fastened with a cockade of blue with the Southern Cross in white stars, red, and blue. Ten red streamers with campaign honours inscribed in sky blue letters are also attached below the lance-head. The staff is 212 cm long, not including the lance-head, and 3.5 cm in diameter. It is covered in sky blue velvet with a red spiral strip. The colour belt is 10 cm in width, covered with sky blue velvet with red velvet stripes. The Navy's flag uses dark blue colours, the Air Force flag ultramarine blue.
Brazilian military units also carry the national flag as a National Colour. This is in the dimensions 90 × 128 cm. It is mounted on the same size staff and with the same finial as the Army standard, but the cravat is divided lengthwise yellow and green, with a gold fringe at the end, tied in a bow and fastened with a cockade of blue with the Cruzeiro do Sul in white stars, yellow, and green. The staff is covered in green velvet with a yellow spiral strip. The colour belt is 10 cm in width, covered with green velvet with yellow velvet stripes of width and number varying with the rank of the organization's commander.
Chile
Units of the Chilean Army carry one main Colour, known as the estandarte de combate (combat standard). This is the same as the national flag, but with an embroidered star and with the unit designation, honorific title, founding date and place, and, depending on the unit, other historic information and honours embroidered diagonally across the fly in gold. The flag is also trimmed with gold fringe. It is mounted on a staff with a gilt condor finial; below the finial is a cravat in the national colours with decorations attached. In addition to the military Colour, particularly distinguished units, and long serving units may carry a second Colour known as a bandera coronela (colonel's colour). This is a red field with a large white five-pointed star. In the angles of the star are the names and dates of battle honours surrounded by laurel wreaths, all in gold, while in an arc above the star is the designation of the unit, also in gold. The flag is also surrounded by gold fringe.
The Chilean Air Force, the Chilean Navy, the Carabineros de Chile and the Chilean Gendarmerie all use the estandarte de combate as their main colour, and do not use the bandera coronela at all. The design is the same as in the Army's.
Colombia
The main state colours of the Military Forces of Colombia and the National Police of Colombia is the Flag of Colombia with the Coat of arms of Colombia in the centre inside a circle with a red border, used by all the services. These flags also carry medals and decorations attached to the flag. The MFC and the NPC also uses unit regimental colours and battle colors, that differ accordingly per service. All of them are gold fringed.
Mexico
The Mexican Armed Forces use the Flag of Mexico as the National Color, with the unit inscription below the Coat of arms of Mexico and the official name of the country (Estados Unidos Mexicanos, United Mexican States) above it.
United States

In the United States military, each branch has its own flag, an organizational colour, sometimes also called a ceremonial flag. Each of these is 4 ft 4 in × 5 ft 6 in, some using 2.5 in gold fringe during specific instances. The ceremonial flag is paraded with a National Colour of equal dimensions in a colour guard, with gold fringe as necessary. The National Color is never dipped in salute, but remains vertical at all times, while the organizational colours and any guidons are dipped as necessary. When the National Colour is not cased, all persons salute the Colors. The finial is a nickel or chrome-plated spearhead, though the Navy uses different finials on occasion.
Each service attaches campaign/battle streamers, sometimes known as battle honours, for actions in which the service as a whole has taken part. These can either be war service streamers, which are in the colours of the appropriate campaign medal and have the name of the campaign embroidered; or unit citation streamers, which have the name of the action embroidered and signify that the unit's performance in a specific action has been worthy of special mention. Units are also permitted to wear streamers of overseas awards they may have been presented with. These streamers are in the colours of the appropriate medal ribbon.[1] The streamers are 3 ft × 2.75 in. The Army, for instance, currently has 178 service streamers,[2] embroidering the name of each battle on each, as does the Air Force. The Marine Corps and Navy instead embroider award devices onto streamers to consolidate them, having 62 and 34, respectively.
United States Army

In the Army, most regiments, battalions of regiments, and separate battalions also have a stand of colours. The first is the National Color, which is a 36 in × 48 in version of the national flag trimmed with a 2.5 in wide gold fringe, and is the equivalent of the Queen's Colour in the British Army. The second is the Organizational Colour, which is the equivalent of the Regimental Colour; this is the same dimensions as the National Color, but is of a single colour representing the branch of the service that the unit is from; each branch also has its own fringe colour, which the Organizational Colour is trimmed with. In the centre of the Colour is the eagle from the Great Seal of the United States, but with the regimental coat of arms in the shield. The eagle has in its beak a scroll bearing the regimental motto, with the crest of the regiment's coat of arms above it and the regiment's name below. Attached to the Organizational Color will be the campaign and unit citation streamers awarded to the individual unit – these are equivalent to the battle honours embroidered directly onto the colours of British and Commonwealth units. The Organizational Color was carried in lieu of a National Color until shortly before the Civil War, when the Stars and Stripes became the National Color.[3] Civil War era units sometimes carried alternative Organizational Colors based on their home state flags or of other designs.
United States Marine Corps

In the Marine Corps, each battalion-sized unit or larger maintains a set of colors.[4][5] The organizational color identical to the Marine Corps battle color, excepting that the scroll will have the unit's name instead of "United States Marine Corps". It will also bear the streamers authorized to the unit, or scarlet and gold tassels if none are authorized.
Fringe is generally not seen on the National Colours when carried by Marine Corps unit (the exception being indoor parades). Instead, a red, white, and blue tassel is used to decorate.
United States Navy
While the Navy uses a number of maritime flags, such as the Ensign and Jack of the United States, the Flag of the United States Navy is normally seen only at ceremonies and parades. The display of streamers and fringe is consistent with that of the Marine Corps.
United States Air Force
U.S. Air Force (USAF) groups have the same National Colour as the Army; the Organizational Colour is ultramarine blue, with the group's coat of arms beneath the USAF crest, which is an eagle on a cloud background. The fringe is in gold.
Uruguay
Aside from the three state colours (the Flag of Uruguay, the Flag of Artigas and the Flag of the Treinta y Tres), the Uruguayan military also has regimental colours that differ per service and unit. The national colours have armed colour guards while the regimental colour has none at all.
Venezuela
In the National Bolivarian Armed Forces of Venezuela, aside from the Flag of Venezuela as the National Colour, there are also Organizational Colours for each of the 6 service branches and the Ministerial Colour of the Ministry of Defence and Unit Colours, which differ per service branch and arm. Every military unit from the Ministry of Defense down to all individual units have a stand of colours like in the United Kingdom, but differ from the battalion to the service and the national level. The national flag, until the 1940s, served also as the unit state colour in the same manner as the National Colour of the United States Army and the State/Sovereign's Colour in the Commonwealth of Nations, and was based on the national flag but with the unit inscription replacing the stars in the centre in white lettering. The Venezuelan National Militia is the only service branch that uses a battle colour, similar to the flag of the Cuban July 26 Movement: the colour is red and black with the service name on it in white, and a separate colour is used for the service headquarters at the Montana Barracks in Caracas. Starting from July 2013 onward it was granted permission to use a 4th colour for its battalions: red with the eyes of the late President Hugo Chávez and the inscription Chavez Vive (Chavez Lives On) below, topped with a scarlet star.
Since 2014 the National Armed Forces uses two additional colours (the National Militia its 5th and 6th): that of the Supreme Commander's Colour, which is red bearing the portrait of the late President Chávez surrounded by a wreath and the Armed Forces Motto (Independence and Socialist Fatherland, we will live on and triumph!) below and the inscription Supreme Commander of the Bolivarian Revolution (Comandante Supremo de la Revolucion Bolivariana) and the eight golden stars from the National Flag above it, plus the Memorial Colour of the Liberator and Father of the Nation (introduced in the summer of 2016), which is of the same colour facing but with the wreath containing the portrait of Simon Bolivar, the eight gold stars and his title above and the words Freedom, Sovereignty, Independence (Libertad, Soberania e Independencia) below the title, all in gold.
The colors used on the Unit Colours are as follows:
- Red: Ministry of Defence (formerly gray), Service units, Marine Corps, National Militia, Military Technical Academy, Presidential Honour Guard Brigade, Caracas HQ Battalion of the Ministry of Defence
- Dark Blue and Red: Venezuelan Army HQ and units directing to Army HQ, Division and Brigade Colours
- Yellow: Infantry, Jungle Infantry, Airborne Units
- Orange: Rangers
- Green: Army Engineers
- Dark Blue: Venezuelan Army Special Forces
- Black: Armor
- Burgundy Red: Artillery and Air Defence Artillery
- Gray: Logistics, National Armed Forces Communications and Electronics School
- Navy Blue: Navy
- Ultramarine Blue: Air Force
- Maroon: National Guard
- Dark Blue and White: Bolivarian Military University of Venezuela, Military Academy of the Bolivarian Army and Armed Forces Health Sciences Academy
- Light Blue and White: Venezuelan Naval Academy
- White : Venezuelan Army schools
Asia
China
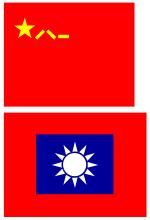
This details the two Chinas (People's Republic of China and Republic of China)
People's Republic of China
The People's Liberation Army is the overall body for the entire armed forces of the People's Republic of China, and is represented by a single flag, which serves as a ceremonial colour for all regiments and larger formations. This is based on the national flag, but has instead of the four smaller gold stars the Chinese characters for the numerals '8' and '1', which stands for the 1 August, which was the date in 1927 that the PLA was founded. When paraded, the flag is fringed with gold, and is mounted on a red and gold pole. However, each branch of the PLA has its own flag, based on the Army Flag:
- Ground forces: This is the Army Flag with the lower 40% coloured green.
- Navy: This is the Army flag except that the lower 40% has three blue and two white horizontal stripes of equal width.
- Air Force: This is the Army Flag with the lower 40% coloured air force blue.
- Rocket Forces: This is the Army Flag with the lower 40% being a gold stripe.
- Banners of the PLA
Republic of China
The army of the Republic of China (Taiwan) also has a single flag that it uses, which is red, with a blue rectangle in the centre and the white sun from the national flag. It has a red flagpole with silver spearhead finial and red tassels immediately underneath. Individual units use a variation of the Army Flag as their own identifying Colour; this features a white strip next to the hoist, which has the unit's name in black characters, as well as a golden fringe (as is the case since 1961 for all units of the Republic of China Armed Forces, but since 1947 were limited only to Army units above the regimental level). The Army Honor Guard color is in gold with the unit coat of arms in the center.
The Republic of China Navy's colors were red but with the seal of the Navy in a dark blue canton in the center until the 1980s, the honor guard company's colours only use both dark blue and the Navy seal, which are the same colours used today in other ROCN units.
For the Republic of China Marine Corps, its unit battle color mirrors that of the USMC but since the 1980s the unit name is on the white stripe near the hoist (just as the rest of the armed forces, formerly it was on a scroll similar to the USMC's).
The colors used by the Republic of China Air Force are in sky blue with the air force seal in the center (formerly it was red with the sky blue canton featuring the coat of arms, the old design only used today by the honor guard).
Units of the Republic of China Military Police, formerly using a blue color, now use a brown color with the ROCMP arms.
Units reporting to the Ministry of National Defense sport an orange colour with the coast arms of the Ministry in the center. Garrison colors are in blue with the Kuomintang emblem, a wheat wreath and 3 interlocked circles in yellow, red and blue respectively. Reserve units carry a red color whil the Taiwan Reserve uses a green one.
Only the following military academies sport their colors as the ROCAF color is used by the Republic of China Air Force Academy:
In all events whenever the ROCAF is involved, the ROC flag is used as the National Color.
Philippines
Philippine military colours are the Flag of the Philippines as the National Colour, the Organizational Colours, and the Unit Regimental Colour. The Flag of the Philippines is the National Colour of the Armed Forces of the Philippines, but unlike the US colour has no markings on the flag. The Organizational Colours are the flags of the AFP's four Major Service Commands while the Unit Regimental Colour differs per service arm and unit. Like the US, it also has 2nd order guidons for companies and troops, but these are also based on the Spanish military guidons and banners, not on the American ones, reflecting the long history of the military establishment here. These guidons are therefore not swallow tailed save for the PMA, the Philippine Army's Escort and Security Btn and some other units under the Philippine Army.
Thailand

Each unit of the Royal Thai Armed Forces is given a colour called the "Thong Chai Chalermphol" (Thai: ธงชัยเฉลิมพล) or Victory Colours. These are presented to each unit personally by the King of Thailand. The flags are divided into four different designs, for: Royal Thai Army, Royal Thai Navy, Royal Thai Air Force and King's Guard units.
Before their presentation the colours are ceremonially blessed in a religious ceremony attended by Buddhist monks and other high ranking dignitaries inside the Temple of the Emerald Buddha in Bangkok. During the ceremony amidst the chanting of the monks, the King will personally hammer the brass nails into the staff of each colour using a silver hammer. Each colour contains about 32-35 nails, in which the cloth is attached to the wooden staff. Within the same ceremony, the King will also take a strand of his own hair and conceal it within a compartment at the top of the staff, which is closed by a round silver screw top. The King will also attach each colour with its own ceremonial Buddha image, and bless each colour with holy water. The ceremony is steeped in Buddhist and Brahmic heritage, it symbolizes and cements the King's role as Chief Kshatriya (กษัตริย์) or Warrior ruler of his realm. It also emphasizes his constitutional role as Head and Chief of the Thai Armed Forces (จอมทัพไทย: Chomthap Thai).
These colours are similar to the Flag of Thailand and therefore are treated like the State Colours of the Commonwealth, but are not lowered to the ground but above it to the tune of Sansoen Phra Barami (the Royal Anthem) when salutes are rendered by these Colours to the Thai Royal Family (most especially the King and Queen) in all military events that they attend.
-
.svg.png)
Royal Thai Army Unit Colour
-
.svg.png)
Royal Thai Navy Unit Colour
-
.svg.png)
Royal Thai Air Force Unit Colour
-
.svg.png)
Colours of the Royal Guard units
Commonwealth realms
A moth-eaten rag on a worm-eaten pole,
It does not look likely to stir a man's Sole,
'Tis the deeds that were done 'neath the moth-eaten rag,
When the pole was a staff, and the rag was a flag.
Sir Edward Hamly on seeing some old Colours
of the
So long as its colors remain, and there is one man left to carry them, a regiment can never die; they can recruit it again around that one man, and the regiment will continue on its road to future glory with the same old traditions behind it and the same atmosphere surrounding it that made brave men of its forbears. So although the colors are not exactly the soul of a regiment, they are the concrete embodiment of it, and are even more sacred than the person of a reigning sovereign.
Talbot Mundy, *The Soul of a Regiment*
The Colours of the Infantry are a set of large flags, unique to each regiment, that the ordinary soldier would be able to identify straight away.
United Kingdom
Line infantry and foot guards

In regiments of infantry of the British Army and the armies of other Commonwealth countries, each battalion carries two colours, which collectively are called a stand. These are large flags, usually 36 in × 45 in, and mounted on a pike which is 8 ft 7½ in long; the King's/Queen's Colour is usually a version of the country's national flag, often trimmed with gold fabric, and with the regiment's insignia placed in the centre. The Regimental Colour is a flag of a single colour, usually the colour of the uniform facings (collar/lapels and cuffs) of the regiment, again often trimmed and with the insignia in the centre. Most regiments that are designated as 'royal' regiments (that is either have the word 'Royal' or the sponsorship of a royal personage in their name) have a navy blue Regimental Colour. Irish regiments, today the Royal Irish Regiment, have a dark green Regimental Colour.
The colours of the five regiments of Foot Guards have the pattern of the line infantry reversed, with the Queen's Colour being crimson with the regimental insignia and honours and the Regimental Colour a variation of the Union Flag with the battle honours embroidered.
Additional Colours
- The Grenadier, Coldstream and Scots Guards each have at least one State Colour; this is usually crimson with various regimental devices and honours, and the Royal Cypher at the corners of it. They are only used by Guards of Honour from any unit from these regiments, not found by the Queen's Guard, mounted on State occasions when The Queen is present. They are only lowered to the Queen and the Duke of Edinburgh and on State occasions only when the Queen is present, even if the Guard of Honour is mounted in honour of some other personage. The colour design is larger than the normal colours of the Guards Division used in ceremonies.
- The 1st Battalion, Princess of Wales's Royal Regiment, as the linear descendant, bears the Third Colour initially born by the 2nd Regiment of Foot, later renamed the Queen's Royal Regiment (West Surrey) which, for one reason or another, was never taken away from the regiment in the 18th century when new regulations on colours were implemented.
- The 1st Battalion, Royal Regiment of Fusiliers bears the Drummer's Colour awarded after the Battle of Wilhelmsthal to the 5th Regiment of Foot, (later The Royal Northumberland Fusiliers) of which it is the direct descendant.
- The 3rd Battalion, Yorkshire Regiment (Duke of Wellington's), as the linear descendent, carries the honorary Queen's and Regimental Colours that were given to the 76th Regiment of Foot by the Honourable East India Company following their actions at Delhi and Allyghur.
- The Royal Highland Fusiliers 2nd Battalion, Royal Regiment of Scotland carries the Assaye Colour awarded as an honorary colour to the 74th Regiment of Foot following the Battle of Assaye, which is paraded every year on Assaye Day.
- The Honourable Artillery Company has both a stand of Colours (Queen's and Regimental) and Guns. The latter are also regarded as colours and accorded the same compliments just as the Royal Artillery regard their guns as their Colours.
Rifle regiments
By tradition, rifle regiments do not carry colours; this goes back to their formation, when they were used as skirmishers and sharpshooters. While individual units may have had banners or pennants to distinguish themselves from other units, regiments as a whole never needed a full stand of Colours. Today, the two rifle regiments in the British Army, The Rifles and the Royal Gurkha Rifles carry their battle honours on their drums, while the Royal Green Jackets also had theirs inscribed on their cap badge; this tradition is maintained by The Rifles, who wear the Maltese Cross badge of the Royal Green Jackets, inscribed with the regimental honours, as the belt badge. In place of a Regimental Colour, the Gurkhas carry the Queen's Truncheon.
Colours in the cavalry regiments
In the British Army's cavalry units, the Queen's Cavalry Standard and the Regimental Standard (for the heavy cavalry) and the Queen's Cavalry Standard and Regimental Guidons (for the light cavalry) are the equivalents to the line infantry colours. The Queen's Standard is crimson with the Royal coat of arms and cypher, plus the regimental honours, while the Regimental (Squadron/Union) Standard has an adaptable background colour per unit (the colour is sometimes scarlet) and includes sometimes the Union Badge below the crown and the Royal Cypher at the sides of the badge, with the unit honours below. The light cavalry Guidon is swallow-tailed and includes the regimental coat of arms and honours. Before the 1950s, however, Timpani in the drumhorses (and later snare, bass and tenor drums in the dismounted bands) carried the regimental honours and insignia of the light cavalry regiments.
Embellishments
Woven onto the colours are battle honours; the Queen's Colour has honours from the First World War and Second World War, while the Regimental Colour has honours from other campaigns. The Regimental Colour will also have other distinctions, including antecedent emblems and unique honours; one significant example is the Sphinx emblem carried by regiments who took part in the Egypt campaign of 1801. If the regiment has more than a single battalion, then there will be identifying marks on the colours to show which battalion they belong to. There are various other embellishments that can be added to the colours on various occasions:
- On anniversaries of various battle honours, and certain other events, a laurel wreath is added to the top of the pike.
- Battle honour equivalents awarded by foreign countries may be added to the colours, subject to permission being given by the head of state. In the Commonwealth, three infantry battalions are permitted to display the four-foot-long blue streamer that signifies the Presidential Unit Citation/Distinguished Unit Citation, which is the highest collective award given by the United States of America:
In the UK, 41 Commando, Royal Marines and the 1st Battalion, Gloucestershire Regiment were also awarded the PUC and permitted to display the streamer of their regimental colours.
Because of their importance to the regiment, prior to a new stand of colours being presented, they are consecrated.
Royal Hospital, Chelsea
The Royal Hospital, Chelsea had neither colours nor other distinctive device during its entire history, until 2002 when The Queen presented the Hospital with the Sovereign's Mace. This is now paraded by a party of In-Pensioners at all of the Royal Hospital's ceremonial events
Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines has a single pattern Queen's Colour, which is the Union Flag with the foul anchor and the reigning sovereign's cypher interlaced in the centre. Above is a scroll with the single battle honour Gibraltar surmounted by St Edward's Crown. Below is the globe (which represents the many Battle Honours the Royal Marines had earned) surrounded by a laurel wreath (which represents the Battle of Belle Isle) and below this is a scroll with the Corps' motto. Each of the four commandos (the battalion-sized formations that make up the bulk of the corps) has a Queen's Colour, with the only difference being the colour of the cords and tassels. Each commando also has its own Regimental Colour. The Regimental Colour is a dark blue flag (because the Corps is classed as a 'royal regiment') with a small Union Flag at the pike head. The Colour carries similar central embellishments as the Queen's Colour, with the exception that the cypher of George IV replaces that of the reigning monarch and the unit numeral is below. The Royal Cypher is at the other corners. The Regimental Colours also have the coloured cords and tassels, which are gold combined with the following colours:
- 40 Commando: Light Blue
- 42 Commando: White
- 43 Commando: Old Gold and Scarlet
- 45 Commando: Red
The former 41 Commando was awarded the Distinguished Unit Citation for its service in the Korean War, and was thus permitted to carry the streamer on its Regimental Colour.
The Royal Navy

The Colours of Her Majesty's ships in the Royal Navy consist of:
- a White Ensign (worn at the stern, or from the gaff or main yardarm when at sea);
- a Union Jack (worn at the ship's jackstaff at the bow when not underway or when the ship is dressed);
- a Masthead pennant (worn at the masthead, except when displaced by an admiral's flag or commodore's broad pennant).
In addition, each principal command in the Royal Navy also has its own Queen's Colour which is a variation of the White Ensign, with its dimensions altered to mirror those of the Colours of infantry regiments. In the centre is the Royal Cypher of the reigning monarch within the Garter, surmounted by the crown.
Unlike the Colours of regiments in the Army, every Queen's Colour of the Royal Navy is identical. The following units hold a Queen's Colour of the Royal Navy:
- Naval Aviation Command (ACOS(AV), HMS Heron)
- Submarine Command (CAPTFASFLOT, HMS Neptune)
- Fleet (CINCFLEET HQ)
- Britannia Royal Naval College
- Surface Flotilla (MWS, HMS Collingwood)
- Royal Naval Reserve (COMMARRES, HMS Vivid)
The Royal Air Force

RAF Colours are made of sky blue silk and measure approximately 36" x 36". The following colours have been awarded:
- RAF College, Cranwell, approved 27 December 1947, presented 6 July 1948.
- The RAF in the UK, approved 27 December 1947, presented, 16 May 1951.
- No. 1 School of Technical Training RAF, approved 27 December 1947, presented 25 July 1952.
- RAF Regiment, presented 17 March 1953.
- Near East Air Force, presented 14 October 1960, laid up 31 May 1976.
- Far East Air Force, presented 13 July 1961, laid up 30 January 1972.
- Central Flying School, presented 26 June 1969.
- RAF Germany, presented 16 September 1970, laid up 27 June 1993.
- Royal Auxiliary Air Force, presented 12 June 1989.
- RAF Halton, presented 31 October 1997.
The Queen's Colour for the Royal Air Force in the United Kingdom is a variation of the RAF Ensign with its dimensions altered. The RAF Roundel is moved to the lower fly, with its place in the centre again taken by the Royal Cypher surmounted by the crown. Other colours feature the unit's badge in the centre with the Royal Cypher and crown in the first quarter.
The RAF's Squadron Standards are its counterpart to the Regimental Colours. They are in air force blue with a gold fringe surrounding it, with the Squadron insignia and honours.
Australia, Canada and New Zealand

The naval and air forces of all three of these countries also have similar Colours based on their own ensigns. Rules stipulated by the Canadian Department of Defence state that the First, or Senior Colours symbolizes the unit's loyalty to the Crown; authorization to possess a Queen's Colour may only be granted, and the Colour presented, by the Queen or her vice-regal representative. The design based on the flag of Canada reflects the custom established for infantry line regiments in the mid-18th century, when the Sovereign's Colour was based on the national flag, as was the practice in British and French units in Canada.[7]
Navy
- Royal Australian Navy: The Queen's Colour of the RAN is the Australian White Ensign – it is a reverse of the Australian National Flag (white with blue stars), with the Royal Cypher and Garter band positioned between the Commonwealth Star and the stars representing the Southern Cross. (See former Colours at Naval Chapel, Garden Island NSW.) The RAN possesses two Colours, the first is the Fleet Colour held on behalf of the fleet units by Fleet Headquarters, HMAS Kuttabul. The second, known as the Establishment Colour, is held by HMAS Cerberus on behalf of the shore establishments.
- Royal Canadian Navy: The Queen's Naval Colour is a variation of the Canadian Naval Ensign (which used to be the Canadian Forces naval Jack) – it is white, with the Canadian flag in the canton, the cypher from the Queen's personal flag for the Commonwealth (a crowned "E" surrounded by a wreath of roses) in the centre, and the symbol of the navy in the lower fly. The edge of the Colour is trimmed in gold. Until 1979 the RCN possessed two identical colours: one for the Atlantic fleet and one for the Pacific fleet. Since then, a single Colour has been held at Naval Service Headquarters.
- Royal New Zealand Navy: Since 1968 the RNZN Queen's Colour is a variant of the Naval Ensign of New Zealand - itself the Flag of New Zealand but in white, with the Royal Cypher and Garter band situated near the Southern Cross.
Army
- While the colours of the Australian Army infantry regiments follow the British tradition, starting in the 1960s colours based on the Australian national flag are now used as the Queen's Colour. Armoured units carry Standards and Guidons – flags smaller than Colours and traditionally carried by Cavalry, Lancer, Light Horse and Mounted Infantry units. The 1st Armoured Regiment is the only unit in the Australian Army to carry a Standard, in the tradition of heavy armoured units. Guidons are also carried by aviation units. Only the Royal Australian Artillery uses guns. Non-combat units (combat service support corps) do not have Colours, but have Standards or Banners instead. The Royal Military College, Duntroon also has an additional colour, the Sovereign's Banner, carried yearly by the RMC's Champion Company from the Corps of Staff Cadets formed from the best cadet company for the year, which on parades takes precedence over the other companies as the Sovereign's Company.[8] The Army itself since 2001 has a banner known as the Army Banner, carried on all events of the service (as the Army is the protector of the traditions of the Flag of Australia, and thus does not have its own service colour). It is trimmed with gold fringe, has gold and crimson cords and tassels, and is mounted on a pike with the usual British royal crest finial.[9] The Army Banner bears the Australian Coat of Arms on the obverse, with the dates "1901–2001" in gold in the upper hoist. The reverse bears the "rising sun" badge of the Australian Army, flanked by seven campaign honours on small gold-edged scrolls: South Africa, World War I, World War II, Korea, Malaya-Borneo, South Vietnam, and Peacekeeping. It was presented to the Army in celebration of its 2001 centennial year.
- In the Canadian Army, regiments designated horse guards and dragoon guards, along with the Canadian Special Operations Regiment, have regimental standards. Royal Canadian Armoured Corps standards have a crimson field and the CSOR standard has a tan field. Other RCAC regiments have crimson regimental guidons. Each battalion of the Royal Canadian Infantry Corps, except those of rifle regiments, has a stand of two colours: a queen's colour and a regimental colour. For foot guards, the queen's colours have a crimson field, and the regimental colours are based on the Canadian national flag. For other infantry regiments, the queen's colours are based on the national flag, and the regimental colours are of the regimental facing colour.
Air Force
- Royal Australian Air Force: The Queen's Colour of the RAAF is the Royal Australian Air Force Ensign. It is similar to that of the RAF – however, in addition to the RAAF roundel, which is in the lower fly, it has the Commonwealth Star in the lower hoist and the stars of the Southern Cross in the upper fly, with the Royal Cypher in the centre. The flag has a border of golden wattle as well as golden fringe.
- Royal Canadian Air Force: The Queen's Air Force Colour is the Royal Canadian Air Force Ensign. It is significantly different from the standard in that it is not based on the ensign but instead is similar to the Queen's Colour of infantry regiments: it is a silk national flag of Canada with a red circlet on the maple leaf inscribed with the name of the command, surrounding the royal cipher, and ensigned with the royal crown. Uniquely among Commonwealth air forces, the Canadian air force also has a Command Colour, analogous to an infantry Regimental Colour. This is light blue with the command badge in the centre and a gold maple leaf in each corner, stems outward. Also like army units, squadrons with 25 years or more of active service receive unit colours with battle honours surrounding the unit badge on the same light blue background edged with flowers.
Sri Lanka

When Sri Lanka declared itself a republic in 1972 the units that had a Queen's Colour retired them. These were replaced by the new President's Colour, which was first awarded in 1972. The following colours have been awarded:
- Army
- Regiments
- Sri Lanka Light Infantry – 1978
- Gemunu Watch – 1980
- Gajaba Regiment – 2007
- Establishments
- Army Training Centre – 1972, laid up 20 August 1992
- Sri Lanka Military Academy – 1997
- Air Force
- Sri Lanka Air Force – 1976
- SLAF Regiment – 2009
- Squadrons
- No. 1 Flying Training Wing – 2001
- No. 2 Heavy Transport Squadron – 2009
- No. 4 (VIP) Helicopter Squadron – 2009
- No. 9 Attack Helicopter Squadron – 2009
- No. 10 Fighter Squadron – 2009
- Stations
- SLAF Katunayake – 2001
- Navy
- Naval and Maritime Academy – 2000
Malaysia
The same format of Sovereign's and Regimental Colours also apply in Malaysia. The King's Colours and Regimental Colours of the Malaysian Armed Forces are the flags given by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong in his responsibilities as Supreme Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces and by the 8 other state monarchs, to units recognized as Royal units and to flags of large formations (the King's Colour) and to units now receiving their new regimental colours (the Unit Regimental Colour).
The King's Colour is yellow with the national arms surrounded by paddy on the centre, thus Malaysia is one of only two Commonwealth countries, the other being Brunei, that does not use its national flag for use as a senior Colour (the flag is the senior colour of the entire Armed Forces establishment). The sides are emblazoned with the battle honours of the unit. On the canton the service emblem of either service of the Armed Forces (Army, Navy and Air Force) can be seen. The Regimental Colour, however, differs by service arm or branch (the latter case being used in the Army) and unit. Both flags have gold fringes surrounding them. These colours are only present in formal parades.
During the Merdeka Parade and on Armed Forces Day on 21 September, as the armed services on parade do not wear their dress uniforms, only the 1st Battalion, Royal Malay Regiment, which wears dress uniforms, is present with its King's and Regimental Colours, but for the rest of the services on public parade the following order then applies:
- Service Colour/Regimental Camp Flag
- Flag of Malaysia (National Colour)
- Colour of the Malaysian Armed Forces
Singapore
Singaporean military colours of the Singapore Armed Forces are divided today into Service State Colours and Unit Regimental Colours. Until 1997 there were also Service Regimental Colours and Unit State Colours. The State Colours are similar to the Flag of Singapore but differ per service. But Regimental Colours are different, and they differ per unit or service arm (save for the flags of the Air Force and Navy that show their respective service colours instead and some SAF service-wide commands like the Military Police). Their common design is that of the regimental or command arms at the centre of the colour used. Both are gold fringed and are brought out on major occasions only.
European countries
Belgium
Infantry units have a drapeau / vaandel, a square vertical tricolour of black, yellow, and red within a 15 mm wide gold border, the whole being 90 cm square. The names of battle honours for which the unit was cited are embroidered in gold in French on the obverse and in Dutch on the reverse, in straight lines.
Denmark
.svg.png)
Danish Navy, Army and Air Force units carry a unit colour (Danish: regimentsfane) and for the Life Guards a battalion colour (bataljonsfane), which measures 105 × 140 cm, former horse units a slightly smaller guidon.[10] The flag is a variation of the Dannebrog, with a curvilinear white Dannebrog cross, called the Mantova cross, set with its centre about one-half the width of the hoist from the hoist edge. The royal cypher is embroidered in gold over the centre of the cross, the unit badge in gold in the upper hoist, and the unit number, name or both in gold in the lower hoist. Some regiments have additional marks in the upper fly. The Jyske Dragonregiment, for instance, has Prince Henrik's cipher in the upper fly. The finial is an ornate gold openwork spearhead with the royal cypher in the centre. Attached below the spearhead can be one or more campaign streamers (fanebånd). The colour is decorated with a gold cord with two tassels and bordered with a thin strip of gold cord. The sleeve holding the colour to the pike is attached with ornamental nails, the first three of which represent the sovereign, the Fatherland, and the Union.
Finland
Units of Finnish Defence Forces have a single Colour. The Colours are either active or traditional. An active Colour belongs to a brigade or an equivalent unit in the FDF. A traditional Colour belongs to a battalion or a regiment that has formerly been separate but is now part of a brigade. The difference between an active and traditional Colour is the way of presenting them. The active Colour has always a guard of two officers, while a traditional Colour is borne without one. The military oath is always given in the presence of the active Colour of the unit.
The Finnish military vexillology is a mixture of Scandinavian and Russian tradition. The Colours are usually modelled after Swedish regimental flags of the 17th century, but some units carry flags modelled after Russian or German colour traditions. The Colour often bears the emblem of the province where the unit is located with an appropriate symbol of the service branch. No battle honours were awarded for units during the Second World War but some units have battle honours from the Finnish Civil War.
Units and institutions of the Finnish Defence Force which have not been awarded a colour of their own use the unadorned swallow-tailed Flag of Finland as their State Colour, and the oath of service for NCOs and volunteer enlisted personnel assigned to these are given in its presence.
-

Colour of the Finnish Guard Jaeger Regiment. Note the Imperial Russian-style design of the flag which is symbolic of the lineage of the regiment as part of the Russian imperial guard
-

Colour of the Armoured Brigade features the black and silver colours of Finnish armoured troops while the main emblem is a cuirassier helmet symbolizing armoured force.
-

Colour of Pori Brigade has the blue and yellow colours of Satakunta, and the coats of arms of Satakunta and Finland Proper on its two sides. The colour carries the ribbon of the Order of the Cross of Liberty as a streamer.
-

The traditional colour of the Kymen jääkäripataljoona (Kymi Jaeger Battalion), nowadays a part of Karelia Brigade, is of the form defined for light infantry. The Kymi Jaeger Battalion follows the traditions of the 3rd Bicycle Battalion and carries that number on its colour, and the Order of the Cross of Liberty both as a streamer and as the point of the staff.
-

The traditional colour of Itä-Suomen Viestipataljoona (Eastern Finland Signals Battalion), part of Karelia Brigade, has the branch colours of signals corps: purple and gold. The device featuring Western Capercaillie is a throwback to the earlier designation as Central Finland Signals Battalion. The main device, the three lightning bolts, is symbolic of communication.
-

The traditional Colour of the 7. Pintatorjuntalaivue (7th Surface Combat Flotilla) of the Coastal Navy features a blue Lion of Finland with a fish tail, striking with a trident.
-

The Colour of the Finnish Defence Forces International Centre features a Lion of Finland holding a herald's staff in addition to the sword. The shade of blue of the colour is the same as in the flag of United Nations.
-

The Colour of the Karelian Air Command features, like all Finnish Air Force Colours, a swastika within a winged circle. The identifying device is a small coat of arms of Karelia
France
In January 1188, in a meeting between Henry II of England and Philip II of France, where it was agreed that both would go on a crusade, and that Henry II would use a white cross and Philip II would use a red cross.[11] Later on, this usage was inverted, and the English took to using a red cross on white, and the French a white cross on red.
Background
As the use of regimental colours spread in Europe, the habit developed of using a symmetric white cross as the basis of the design of the French regimental flags, and by the 18th century almost every regiment had a white cross. The regiments were distinguished by the colours of the cantons
After the French Revolution and the appearance of the new Tricolore, crosses disappear in 1794 and various arrangements of the tricolour come into use. Napoleon standardizes first in 1804 to a white field chape-chausse of red and blue, and in 1812 to the modern French flag.
-

French, white-cross, and English, red cross, fighting at the battle of Formigny during the Hundred Years' War.
-
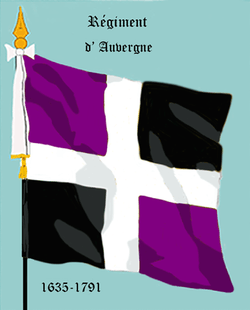
Regiment of Auvergne.
-

Regiment of Normandy.
-

King's Regiment (Régiment du Roi).
-

The pre-revolutionary regimental flags inspired the flag of Quebec (here, the Compagnies Franches de la Marine).
-

French Imperial regimental flag with its Eagle (1804-1812).
-

Regimental flag of the 1st Regiment of Grenadiers of the French Imperial Guard (1812).
About battle honours on current colours

Somehow, the French Armed Forces of today are not officially considered to be the successors of the Royal Army and Navy, although many of their individual units are de facto. Accordingly, battles fought and won by the Royal Army and Navy before the French Revolution (such as Patay, Fontenoy, Chesapeake, Porto Praya and so on) do not appear as battle honours on regimental colours. The names of battles of the old times, however, which are rightly still considered as most glorious by the modern French Army, are honoured by being given to ships or armoured vehicles, and remembered by anniversaries.
As a paradoxical example, the 1st Infantry Regiment Picardie (founded 1479, during the reign of Louis XI) which is one of the oldest regiments with continuous service of all European armies, has fought an impressive number of fierce battles since the 15th century, as one may imagine... yet, officially, its battle honours record starts only in 1792:
- Valmy 1792
- Fleurus 1794
- Moeskirch 1800
- Biberach 1800
- Miliana 1842
- Guise 1914
- Verdun – L'Yser 1916-1917
- La Somme 1916
- L'Ourcq 1918
- Résistance Berry 1944
- AFN 1952-1962.
Latest official regulations
The following official documents relate to the colours of the Land Army (armée de Terre) :
- recommendation (circulaire) 808 EMM/CAB of 5 December 1985 rules what sorts of units can be given colours, abiding to previous regulations of joint services;
- decision 12350/SGA/DPMA/SHD/DAT of 14 September 2007 deals with the inscriptions of battle honours upon the flags and standards of the units of the Army, the Defence Health service and the Military Fuel Service;[12]
- government order of 19 November 2004 relates to the award of the AFN 1952-1962 battle honour to flags and standards of Army and Services units.[13]
Land Army in general
- Regimental colours of units which are traditionally on foot, such as Infantry regiments of the line, Marine Infantry, Foreign Legion Infantry, Paratroops Infantry, Engineers, Signal Corps and Military Colleges are called drapeaux (flags).
- Regimental colours of the (traditionally) mounted units of the Armoured Cavalry Branch and other cavalry units such as Dragoon Paratroopers, Hussar Paratroopers, Legion Cavalry, Artillery (including Marine Artillery, Legion Artillery, etc.), Transportation, Army Aviation, and Materiel, are called étendards (standards).

Regimental colours are 90 cm × 90 cm Tricolore silk square flags – standards are smaller: 64 cm × 64 cm – surrounded by a golden fringe. Both are set on a stave (2.11 m long and 32 mm diameter – staves for standards are slightly shorter) ended by a 38 cm pike-shaped finial with a cartouche bearing the initials "RF" for République française on one side, and the name or number of the unit on the other side.
The cravate hanging from the pike is made of two tricolour silk ribbons, 90 cm long and 24 cm wide, ended by an 8 cm gold fringe on which the unit number or monogram is embroidered in gold, encircled by an oak and laurel wreath. French decorations and fourragères[14] awarded to the unit are pinned or tied to the cravate; foreign awards and decorations are borne on a red velvet cushion.
All writings on the colour are embroidered in gold, as well the unit number (or monogram) encircled in antique oak and laurel wreath in each corner of the flag.
Obverse of a colour:
- RÉPUBLIQUE FRANÇAISE
- (NAME OF THE UNIT)
Reverse of a colour:
- HONNEUR (Honour)
- ET (and)
- PATRIE (Fatherland)
- (BATTLE HONOURS)
Rifle battalions (chasseurs à pied)

By tradition, all the battalions of the rifles (the bataillons de chasseurs à pied together with the chasseurs alpins) share a single collective colour. Individual battalions have pennants (fanions) and the flag of the rifles (Drapeau des chasseurs) is given to be held each year in turn to a different rifle battalion. As a result, the single flag displays all the battle honours earned by every rifle battalion.
Other specific colours

- Since 1844, the obverse of Foreign Legion regimental colours do not carry the motto "Honneur et Patrie" but "Honneur et Fidélité" (Honour and Fidelity). This motto was originally written on the flags of the Swiss regiments in French service, such as the Régiment de Diesbach (85th Infantry of the line).
- The École polytechnique, as a military college, also has a colour which does not carry "Honneur et Patrie" but instead "Pour la Patrie, les Sciences et la Gloire" (For the Fatherland, Sciences and Glory). The reverse of École polytechnique's colour has one battle honour written under the motto: Défense de Paris – 1814, awarded in 1901 by President Émile Loubet.
- Since 1880, the motto of the Paris Fire Brigade (which is a military unit belonging to the Engineering Arm), "Dévouement et Discipline" (Devotion and Discipline), is written under "Honneur et Patrie".
- The reverse of the Saint-Cyr Military College's colour has seven lines: Honneur / et / patrie / Ils s'instruisent pour vaincre / Premier / bataillon / de France (Honour / and / Fatherland / They study for victory / First / battalion / of France).
The National Navy

The Colours worn by the ships of the National Navy (Marine nationale) consist of the National Ensign and the jack:
- the National Ensign[15] is flown at the stern and at the bowsprit if not replaced there by the FNFL jack or a military award jack;
- the FNFL jack is flown at the ship's jackstaff if the ship has fought with the Free French Naval Forces, or is named after such a ship;
- military award jacks may also be flown at the ship's jackstaff if the ship has received mention in dispatches (in which case crew members wear the corresponding fourragère).
Currently, only eight individual National Navy units do have colours[16] other than the National Ensign or the FNFL jack. Under recommendation 808 EMM/CAB of 5 December 1985, naval units to which colours can be bestowed must be those with manpower equivalent to that of a regiment, which are specialised in combat or services on land (or corps which have inherited their traditions from such units), and naval instruction centres or colleges. The flags are quite similar to those of Land Army units, the difference being the wreaths in corners which encircle anchors instead of name of unit, except for the Naval Gunners (initials CM) and the Fleet Engineering Cadets College (initials EAMF).
As of today, these units are (between brackets is where the colours are currently kept):
- the 1er Régiment de fusiliers marins (École des fusiliers marins) – the 1st Naval Fusiliers Rgt. (Naval Fusiliers College);
- the Demi-brigade de fusiliers marins (Compagnie de fusiliers marins de Cherbourg) – the Naval Fusiliers Half-Brigade (Cherbourg Naval Fusiliers Company);
- the Canonniers marins (Centre d' instruction naval de Saint-Mandrier) – the Naval Gunners (Saint-Mandrier Naval Instruction Centre);
- the École navale (Groupe des écoles du Poulmic) – the Naval College (Poulmic Schools Group);
- the École militaire de la flotte (Groupe des écoles du Poulmic) – the Fleet Military College (Poulmic Schools Group);
- the École des mousses (Centre d'instruction naval de Brest) – the Cabin Boys College (Brest Naval Instruction Centre);
- the École des apprentis mécaniciens de la flotte (Centre d' instruction naval de Saint-Mandrier)' – the Fleet Engineering Cadets College (Saint-Mandrier Naval Instruction Centre);
- the Bataillon de marins pompiers de Marseille (Bataillon de marins pompiers de Marseille) – the Marseille Marine Fire Battalion (The Marseille Marine Fire Battalion).
The Air Army

The colours of Air Army (armée de l'Air) units are by all means similar to those of the Land Army from which it separated as an independent military arm in 1933. Colours are generally not bestowed to Air Army units smaller than escadres (wings), land combat regiments, air force bases, instruction centres or air colleges.
The National Gendarmerie
The units of the National Gendarmerie (Gendarmerie nationale) have colours which are very similar to those of the Land Army. Each region (formerly legion), instruction centre, college or Republican Guard Regiment has its flag or standard, altogether 56 flags and 2 standards. The reverse of colours of the Departmental Gendarmerie units and Gendarmerie instruction centres have the same motto as the Land Army units (Honneur et Patrie) but the colours of the Mobile Gendarmerie have their own particular motto: Valeur et Discipline (Valour and Discipline). Most subordinate or smaller units use 50 cm large x 40 cm high pennants.
The National Gendarmerie also has a common flag, under the guard of the Director-general, on which five battle honours are registered:
- Hondschoote 1793;
- Villodrigo 1812;
- Taguin 1843;
- Sébastopol 1855;
- Indochine 1945-1954.
French influence
Nations of the former French Empire
Many of today's armed forces of independent countries that once were part of the French Empire share customs and traditions closely similar if not identical to those of the French military regarding organisation of military arms, army and navy rank structures and uniform styles. Indeed, in countries where the decolonisation process had been conducted through peaceful political negotiations (chiefly French West Africa and French Equatorial Africa), French colonial units were sometimes directly inherited by the former colonies where they had been raised to form the basis of the new national armies. This legacy not only included colour etiquette (the way colours are respected, taken care of and paraded), but also design, adapted to new national flag designs.
On the contrary, in countries where independence came as the aftermath of bloody wars of liberation, such as in Vietnam and Algeria, due to the Cold War context, French military culture was strongly rejected often only to be replaced by communist Soviet or Chinese style military culture (colours, ranks, uniforms, parade pace, etc.).
Other Nations
As one of the World's great powers together with Great Britain, France did not only exercise its influence by conquest but also by the prestige of its military. At the height of European colonial expansion in the 19th century, France's army and Britain's navy were each regarded as the most powerful forces ever on land and at sea. This lead many a military to copy both powers' military and naval cultures. As most navies in the World adopted the British naval looks (double-breasted navy blue jacket and peaked cap for officer, blue jean collar for ratings, etc.), numerous land armies adopted French-inspired uniforms during the 1860s and 1870s (both Union and Confederate armies during the American Civil War, the Chilean Army of the War of the Pacific, the Russian Imperial Army, etc.) and even sometimes imported types of French units (e.g. Zouave regiments). France's influence on military fashion dimmed for the time being after the most unexpected French defeat ending the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871 and many armies then changed to adopt Prussian military style (as a perfect example of this trend, Chilean soldiers traded their kepis for pickelhauben).
As far as regimental colours are concerned, French influence was mainly to be seen in armies of smaller European powers with strong cultural, economical or political ties to France, notably in such countries whose national flag itself was patterned after the French national flag, such as Belgium or Romania.
- widths="150px"
-

Djiboutian colours: French influence through legacy.
-

Belgian colours: French influence through common culture.
-

Romanian colours: French influence through prestige.
Germany

Units of the Bundeswehr have only a single Colour. The Truppenfahne is a square version of the national flag with the Bundesadler (national shield) overall in the centre. The flag is surrounded by a black, red, and gold lacework border and edged on three sides by gold fringe. The finial is a gilt bronze openwork spearhead surrounding a black and silver Iron Cross. Below the finial, a streamer is attached with the unit badge at the top and its designation embroidered in gold at the end. These streamers are red for army (Heer) units, blue for the navy (Marine), and white for the air force (Luftwaffe). The streamer is the same length as the hoist of the flag.[17]
Greece

Traditionally, Army infantry and tank/cavalry regiments have a single colour or war flag (Greek: Πολεμική Σημαία). This is blue, with a white cross and features St George and the Dragon in the centre.[18] The flag has no distinguishing features for individual regiments, although battle honours are sometimes added to the flag; the regiment's identity is inscribed on the flagstaff. The pattern has been in use since the 1830s, with no changes between the periods of monarchy or republic. The Hellenic Army Academy has also been awarded a war flag, its cadets having participated in the Battle of Crete in 1941. Similar flags exist also for the Air Force, featuring the archangel Michael. Recently war flags were assigned to the Army NCO Academy and the Police Academy.
Unlike Army, Police and Air Force, the Hellenic Navy uses the Flag of Greece as both the naval ensign and national colour.
Holy See

The flag of the Swiss Guard, the army of the Vatican City, consists of four quarters. The Coat of Arms of the current pope is in the first quarter, while the arms of Pope Julius II are in the fourth quarter. In the second and third quarters are horizontal stripes of red, yellow and blue, the colours of the unit's uniforms.
The flag also has the coat of arms of the commander within a wreath, on a background of the colour of his canton. The design of the flag changes with the election of a new pope and the appointment of a new commander.
Italy
The Colour (bandiera di guerra) for army units (other than cavalry) is a square version of the national tricolour in silk, 99 cm × 99 cm. It is mounted on a pike 2.2 m long, made of wood covered with green velvet and decorated with ornate brass nails arranged in a spiral. The pike is topped by a 35 cm high finial consisting of an ornate gilt brass spearhead chased with a five pointed star and the monogram RI (for Repubblica Italiana), which is in turn mounted atop a gilt brass ball on which is the name and date of establishment of the unit. The pike is adorned with two silver cords 67 cm long, each with a 10 cm long silver tassel and a blue silk cravat 8 cm × 66 cm with an 8 cm silver fringe at each end, to which the unit's decorations are pinned, the ribbons of the decorations overlapping so that the medals hang down the cravat.
Netherlands
In the Dutch armed forces, the Colour is orange (except for the colour of the midshipsmans' corps, which is red). On the obverse is the royal cypher of the monarch that gave the regiment its (original) colour, with the unit's name underneath, both in gold; around the four edges is a laurel branch. On the reverse is the arms of the Kingdom of the Netherlands without the mantle. The shield is blue and is strewn with small upright rectangles; the main device is a crowned rampant lion, holding a sword in its upper paw. The lion and rectangles are gold, whilst the blade of the sword is silver. Supporting the shield on either side is a gold rampant lion, facing outwards towards the viewer. There is a gold crown above the shield; whilst below it is a blue scroll with the motto Je Maintiendrai in gold. The shield and lions are surrounded by a wreath of green palm and oak leaves, and there is another wavy gold laurel wreath around the edge. Battle honours are added in the corners of the obverse; if additional honours are awarded, they are placed on streamers that are attached to the pike until the presentation of a new Colour. The Military Order of William or other decorations are attached to the pike when awarded. The pike has a finial of a lion on a block holding a sword and a bunch of seven arrows. Traditionally a colour is 87 cm x 87 cm (with a pike of 2.50 m in length), but armoured infantry regiments carry colours that measure 60 cm x 60 cm (with a pike of 2.20 m in length). Guards regiments carry the same colour, with some differing details.[19]
Norway
Norwegian infantry units have a stand of colours – the first (King's Colour) is the national flag, while the second (Regimental Colour) is unique to each unit:
- Infantry: Norwegian line infantry units carry regimental colours, either of a solid colour or divided vertically into two or three stripes, with the Norwegian lion in the centre, the name of the unit, and battle honours embroidered on the field. The colours vary by regiment and derive either from historic associations with predecessor regiments or from the colours of the regiment's oldest known uniform.
- Guards: The Royal Norwegian Guards regiment has a regimental colour that is all white, again with the lion in the centre, and with the Royal Cypher of the reigning monarch in each corner.
Poland
The standard military colours of the Polish Armed Forces are in red and white, with the design tracing back to the Polish Second Republic, a standardized form based on earlier colours. The motto of the Armed Forces, "God, Honor and Fatherland" are at the reverse while the Polish military eagle (which differs per service) is at the centre of the obverse. The unit's name is inscribed on the obverse.
Portugal

All regiments of the Portuguese Army have a National Colour – Estandarte Nacional – which is based on the National Flag of Portugal. Regiments and battalions also have regimental heraldic colours based on the unit's coat of arms.
National Colours are also carried by major units of the Portuguese Navy, Portuguese Air Force and Portuguese National Republican Guard (GNR).
The official standard for the National Colours was established in 1911 and states that they should measure 120 cm in the hoist by 130 cm in the fly, the National Arms being surrounded by two olive branches tied by a scroll with the motto "Esta é a Ditosa Pátria Minha Amada" (This is my loved blessed Motherland). The colours used by the land units of the Navy, the Air Force and the GNR follow closely this standard. However, the colours used by the Army and by the ships crews of the Navy are smaller (90 cm by 90 cm), with these last ones having the additions of cross of the Order of Christ in the canton.
Romania
According to the Romanian General Staff, "The military colors (drapel de luptă) are the symbol of military honor, bravery and glory. They evoke the past struggle of the Romanian people for national liberty and the traditions of unity, reminding each soldier of his sacred duty to serve the Fatherland with trust, and to defend at all costs the unity, sovereignty and independence of Romania".
The military colours are granted to military units by presidential decree, on the advice of the Minister of National Defence, the Minister of Internal Affairs or the director of the Romanian Intelligence Service. According to the Ministry of National Defence, the complete description of this military insignia is as follows:
.png)
The military colours of Romania are made of double silk cloth and have dimensions of 100 × 66 cm (2:3 ratio). The canvas has the colours of the Romanian flag and its obverse is identical with the reverse. The national coat of arms, measuring 29 × 21.5 cm, is applied in the middle of the yellow stripe, 18 cm above its base. In each corner, 5 cm from the edge of the canvas, is sewed a wreath of oak leaves, which surrounds the weapon signs, all of golden thread:
- two crossed swords for land forces
- a helicopter blade juxtaposed over a pair of wings in downward flight, a radar and a crossed rocket and telescope for aerial forces
- an anchor for naval forces.
- the letter J in a rhombus over two crossed swords for gendarmerie units
- the emblem of the Romanian Intelligence Service for its units
The three sides of the flag not attached to the pole are decorated with fringes of golden thread (5–7 cm long) and tassels of the same material (10–12 cm long) hang from the corners of the fly. The flag is attached to the pole by an antioxidant metal rod 70 cm long.
The pole, of brown wood, is 240 cm high and 3.5 cm in diameter. A brass cylinder is at the base, 4 cm long and closed on the bottom. The rod is attached to the pole by a brass ring, gilt on its lower part, and a 6 cm high cylindrical protective tube of the same material and gilt on its upper part. The ring (3.2 cm high) is inscribed with the name of the unit. Another brass cylinder is placed on the tip of the pole, 6 cm long and of brass. The eagle, of gilt copper, sheet, 15 cm high and 11.5 cm wide, is placed over this. Looking rightward, the eagle's wings are pointed downward and it holds the thunderbolts of Jupiter in its talons. It is placed on a parallelepipedic support of the same metal (10 × 3.5 × 2 cm), which has a 3.4 cm high ornament on its lower part. The support is screwed onto the brass cylinder and has inscribed into the front the motto "Onoare şi Patrie" ("Honor and Fatherland"). The name of the respective unit is engraved into the reverse.
Other features of the military colours are a tie for attaching decorations, six sashes for the troops in the flag's guard and a protective cover of impermeable fabric.
The military colours of navy vessels are identical to their ensign. The ensign is in turn identical to the national flag, being made of ordinary canvas in various dimensions, according to the ship's rank, size and place of hoisting.
Russia and Soviet Union
Until Peter the Great assumed the office and throne of Tsar in 1685, various flag designs were used by land and naval units of Imperial Russia.
In the 18th century the Imperial Russian Army started to have colours of its own. Starting from the 1730s, Cross style flags in the colours of the various military units appeared in various units: large flags for the infantry and the other arms and small flags for the cavalry and horse artillery. These flags mirrored the Commonwealth military colours of today, with one colour set as the state colour and the rest as the regimental and battalion or squadron colours. 1797 regulations introduced new designs for the infantry—for regular units, the state color being white with the state emblem and the company, battalion and/or regimental colors using the assigned colors of their units, for the Imperial Guard a different emblem was used, and the design was identical. New colors were issued in 1800, but only Guards units used them.
Regulations set in 1813 unified infantry unit colors into one. Guards units used the orange and black of the Order of Saint George with the facing colors and unit emblem at the center.
All these years, the cavalry colors were different.
Naval flags, until 1861-62 (with a brief break in the late 1790s) whilst using the St. Andrew's cross in blue on white, mirrored the British Royal Navy.

From 1942 onwards, each regiment in the armed forces of the Soviet Union (especially the Army and Air Force) had its own colour, which was produced to a standard design:
- Obverse: red field, a red star yellow bordered and the full name and number of a military unit/school below. Each unit has its own inscription.
- Reverse: red field, a gold hammer and sickle and the motto "For our Soviet Motherland!" (За нашу советскую родину!, Za nashu sovyetskuyu rodinu)
The colour was gold fringed.
The former designs had a red star on the reverse with the name of the Central Executive Committee and later, the Supreme Soviet of the USSR surrounding it, and the obverse had the unit inscription below the coat of arms of the Soviet Union, which had the Soviet Union state motto (Workers of the world, unite!) and the red star with the hammer and sickle inside (both were on the flag of the Soviet Union) above it (the latter was near the hoist). Naval flags until 1935 sported different designs. (Distinguished units would be given a second color, the Revolutionary Red Banner of Honor, by the all-Union CEC (before 1924 by the All-Russian Central Executive Committee).)
The Soviet Navy colours had the 1935 official design with them (it was later revised in 1950), with additions for units honoured with the Order of the Red Banner, but in 1964 the Supreme Commander's and Defence Minister's own naval colour and the colours of the Navy Commander-in-Chief (formerly the Minister for the Navy) and Chief of Naval Operations were issued with different designs used, with the addition of the Armed Forces General Staff's own naval colour. The first colour was red with the USSR state arms, the next two had the arms with blue stripes indicating office rank, and the final two were adaptations of the naval ensign (with a different ensign with the rank) plus the stripes. The 1935 design (that of a white field with a blue lower stripe and the red star plus the hammer and sickle above the blue stripe) replaced a much earlier, post-revolutionary naval colours design adopted in 1925. In 1944 a different flag was issued to the Navy for its land based units – the same design used by the Army with a different obverse having the unit name below the naval ensign.
Early flags even had the RKKA and RKKF insignia (the Army General Staff, represented by crossed blue rifles and later became the General Staff's naval colour until 1964, the Naval General Staff and the Army Naval Operations Staff, later the flag of the People's Comissariat for the Navy on its 1938 creation and was issued with two new colours for the Navy Commissar and Deputy Comissar) beside the hammer and sickle, even the flags of the People's Commissar for National Defence and that of the Navy General Staff and the various flags of naval officers which had the ensign on a canton surrounded by a red field, derived from the Navy Commissar's. The cruiser Aurora since 1968 has had a different version of the ensign, flanked by the Order of the Red Banner and of the Order of the October Revolution on the top sides of the star, as the Aurora was the only naval recipient of the latter order in 1967 while in 1918, the Order of the Red Banner was conferred to the ship.
Regimental colours of the Guards units
The colours of those regiments that were classed as "Guards" was slightly different as per 1942 regulations. These had the portrait of Lenin, the Za nashu motto and the abbreviation "USSR" (СССР, SSSR) on the obverse and the small star with hammer and sickle in its centre, unit's name and a motto on the reverse of the colour. The mottoes were different for every regiment (for example, those regiments made Guards in the Great Patriotic War bore the motto "Death to the German invaders", Смерть Немецким захватчикам, Smyert' Nyemyetskim zahvatchikam). In some Guards Armies and Corps, different designs on the obverse and reverse were used. Even the Lenin portrait was different in these colours. All of them were gold fringed.
The Navy's Guards units still had the 1935 design, with the addition of the Guards ribbon below, except for units which were honoured with the Order of the Red Banner and became Guard units later. The difference is in the red five-pointed star, in which Red Banner Guard unit flags had applied the Guards ribbon below aside from the Order of the Red Banner on the star for units that had the order bestowed on their colours earlier. Units which used the 1944 regimental colour design but adapted for the navy's guards units[20] included air and marine units which still had the obverse of Army and Air Force guards units standards.
Colours of the present-day Russian Armed Forces
Since the birth of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation in the aftermath of the dissolution of the USSR, the old Soviet unit colours were retained. Starting in 1998, the traditional Imperial Russian Armed Forces flag designs were reinstated; however, the new designs began to appear in the early years of the 21st century in the Army and Air Force. But the Russian Navy's old naval colour (St. Andrew's cross in blue on a white field) began to be used again in 1992. It has several variations, and the old jack colour of the Soviet Navy (pre-1935) soon became its jack colour, with the red star with the hammer and sickle removed. The unit colours (especially those of the Navy honour guards) have the same design with the unit insignia at the centre of it while Guards units and bemerited and decorated units apply a different version of the colour.
The new Army and Air Force unit colours are square shaped, have St. Andrew's cross in the colors of the Ribbon of Saint George, and with the unit insignia in the middle of the observe and the national arms at the reverse, with the service branch emblem on the corners. These colours are the basis for similar ones used today in the various Russian uniformed services.
Spain

- Standard Colours: Units of the Spanish Armed Forces have a single colour based on the national flag. This has the coat of arms in the centre of the flag, surrounded by the regiment's name in black lettering. Red and yellow tassles are attached to the finial which have the battle honours embroidered on them. Formerly a white regimental colour with the unit insignia on the middle of a red Cross of Burgundy or at the sides was used by these units until the adoption of the present colours design in 1843.
- Coronelas: Up until the early years of the 20th century, some Spanish regiments had a coronela, or King's Colour in addition to their Regimental Colour based on the national flag. Although officially the only colour is the standard one, some older regiments continue to carry a copy of their old coronela which are used on some occasions to maintain regimental traditions. However, the coronelas no longer have any official standing and are not used on official occasions. The design of such colours are white with the royal arms at the centre and the unit insignia and honours at the sides.
- Second Order Colours-Regimental/Wing Guidons and Banners:In the Spanish Armed Forces, Guidons and Banners are second order colours, but are more smaller (Guidons are medium square shaped while Banners are small square shaped). Guidons are used by battalions, squadrons and groups (even vessels) in the Armed Forces while the banners are used by companies, troops, flights and batteries. All have different and unique designs with some of these having the old Burgundy cross on them. These have also the unit insignia at the centre. Like the Regimental Colour the finials of these colours have the attached unit battle honours and decorations.
Turkey
The Flag of Turkey is used by the Turkish Armed Forces as a National Colour, and thus has distinguishing featurers:
- the golden TC (Turkish monogram for Republic of Turkey) on the top left corner, surrounded by golden rays
- the regimental name, abbreviated, below the crescent and star in white
Ukraine
Maroon and gold are the colors used in the military colors used in the Armed Forces of Ukraine, with origins in the Imperial Russian Army's Cossacks and Ukrainian units. In the observe the Coat of arms of Ukraine is at the center of an Orthodox Cross - both symbols form the emblem of the Armed Forces - with a St. Andrew's Cross under it with the same emblem in the sides. The unit's name is in the reverse. The same design is used in the National Guard of Ukraine but in blue, and the secondary cross is absent. Active duty NG units sport dark blue colors with the cross and the coat of arms at the corners.
Yugoslavia and post-Yugoslav nations
The first Yugoslav military colours came about when the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was established in 1918. These were the square versions of the Flag of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia with the state coat of arms and the motto of the Yugoslav Royal Army. The unit names were attached to a ribbon at the pole. The colours were inspired by the military colours of Serbia and of the Croat, Slovene and Bosnian military units of resistance against Austria-Hungary during the First World War.
With the birth of the communist Partisans in 1941 in time for the Second World War, their flags showed the same Pan-Slavic colours on them (arranged according to nationality) but this time a red star was added in the middle. The naval units had a different ensign used and these flags became the basis for the military colours of Democratic Federal Yugoslavia at the time of its 1943 proclamation.
By the time, these flags had the unit name on the pole pennants and were gold fringed. The Partisan General Staff had their own version of it.
Postwar colours (from 1947, when the nation became a Federal People's Republic) used various flag design with the Yugoslav People's Army motto in Serbo-Croatian (For the freedom and independence of the socialist fatherland) both in Cyrillic and Latin and differed per unit or service arm of the YPA, but was longer and were gold fringed. Just as before, the unit name stayed on the attached ribbon. Both the Flag of Yugoslavia and the flag of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia were used as National Colours in parades. Unique colours were issued to the Navy, to YPA reserve units and the Territorial Defense Forces of the republics.
Today all the nations comprising the former Yugoslavia have separate colour traditions per armed forces, but keep their unique appearance.
Guidons and standards
Commonwealth of Nations
The standard is the colours-equivalent for the heavy cavalry (e.g., horse guards and dragoon guards). At 27 in × 30 in, on an 8 ft 6 in long pole, it is much smaller than infantry colours, so that it can be carried by a soldier on horseback.

The guidon is the equivalent for the light cavalry (e.g., dragoons, light dragoons, hussars and lancers). It is swallow-tailed, 27 in × 41 in, with an 8 ft 6 in long pole.
The word guidon is a corruption of the French guyde homme – 'the guide man'.[21] Originally each troop had its own, but this was quickly reduced to a single, regimental one. With the increased dispersion of troops required in the light cavalry role, their operational function had ceased by the 1830s and they were discontinued. The regiment's kettledrums, with the battle honours woven onto the drum banners (with the exception of 3rd The King's Own Hussars and its successors, where they are uncovered, with the battle honours engraved onto the kettledrums themselves) became the focal point of the regiment's loyalty. In 1952 King George VI reintroduced the guidons of the light cavalry for ceremonial purposes.
Both the standard and the guidon are usually of crimson trimmed in gold and with the regiment's insignia in the centre. The regiment's battle honours are emblazoned on both the obverse and reverse, up to a maximum of 22 on each side.
Denmark
Cavalry (armour) units carry an estandart (standard), of similar design to the infantry fane, but smaller and square, with the cross centred on the field. The royal cypher is in the upper hoist and the initials of the regiment in the lower hoist.
France
In the French Army, mounted units carry étendards (standards). Mounted units include Armoured corps and Cavalry, Artillery, Transportation, Army Aviation, Supplies. The étendard is a 64 × 64 cm square flag similar to the drapeaux carried by the units of foot.
Italy
In the Italian Army, cavalry units carry a stendardo (standard) of the same pattern as the bandiera di guerra, but which measures 60 cm × 60 cm.
The Netherlands
The four Hussar regiments of the Royal Netherlands Army carry a standaard (standard), of similar design to the infantry colour, but smaller (50 cm x 50 cm).
Portugal
In the Portuguese Armed Forces parlance, a guidon (Portuguese: guião) is a small square flag, normally used to identify a battalion size unit. The present guidon design - similar in all branches of the Armed Forces - consists in the quadrature of the coat of arms of the unit or of its mother unit, framed by a bordure in various geometric shapes. The colors of the bordure can be used to identify a sub-unit inside its mother unit.
Besides guidons, the Portuguese military units also use two other types of heraldic flags, the standard (estandarte) and the pennant (flâmula). The standard is also a square flag used normally to identify regiment size units, while the pennant is a swallow-tailed or triangular flag used normally to identify company size units.
These types of heraldic flags are also used by some of the Portuguese security forces.
United States
In the United States armed forces, guidons are much more prevalent, with units below battalion size being authorized to use them. In the US Army, these are swallow tailed flags that are 20 in × 27 in, and are in the colour of the branch of the service the unit is from, with the branch's insignia the most prominent device. Also on the guidon is included the unit's identifying letter, and the number(s) of its parent unit. War service and campaign streamers are not attached to these guidons, but unit citation streamers can be.
Guns
In regiments of the (British) Royal Artillery, and artillery regiments of other Commonwealth countries, the guns are afforded the status of colours.[22] This is due to the difficulty of artillery regiments being able to carry flags onto the battlefield, and the fact that the guns themselves were the rallying points for the soldiers manning them. As a consequence, whenever artillery regiments parade, the etiquette that would normally be applied to the colours is applied to the guns. During the Battle of Balaclava gunners abandoned their guns, in effect abandoning their colours, causing disgrace.
Because the guns have the status of colours, gunners of commonwealth countries will attempt to prevent their guns falling intact into enemy hands both for practical reasons (so that the guns can not be turned and used against their own side) and for the honour of the regiment.[23] For example, the last action of gunners of the Royal Artillery during the fall of Singapore was to destroy their guns.[24][25]
The Honourable Artillery Company, the oldest regiment in the British Army, and not part of the Royal Artillery, is the only artillery regiment to have both colours and guns, which are treated with equal respect.
In Singapore, however since its independence the Singapore Army's artillery arm (the Singapore Artillery) uses Colours instead of Guns (this is also the case for the Malaysian Army, Pakistan Army, Royal Cambodian Army and the Royal Thai Army, whose artillery units use Colours and not Guns on parade). But in the Venezuelan Army, Guns and Colours are both used for the field artillery, but the colours are attached to the lead vehicle on parades.
Etiquette
- The Regimental Colour (or Standard or Guidon) is always paraded whenever the regiment is on a formal parade. However, the Queen's Colour is only paraded on certain occasions.
- Compliments (for example saluting and presenting arms) are always paid to the (uncased) Colours.
- When the Colours are being paraded, they are carried either by a subaltern or warrant officer, dependent on the regiment. On parade, the Colours always have an armed escort, the Colour Party, who would normally be non-commissioned officers. In the infantry this role usually falls to Colour Sergeants.
- When the Colours are not being paraded, most regiments house them in their Officers' Mess. They are cased and secured every night.
- When a regiment is presented with new Colours, the old Colours, which will now never again be paraded, are laid up (i.e.: put on permanent display) in a place sacred to the Regiment (for example the Regimental Chapel).
Ceremonies of colours
Royal Navy
The British Royal Navy and other navies of the Commonwealth of Nations call the flag-raising ceremony that happens every morning when a ship is in harbour colours. In British home waters, colours is conducted at 0800 (eight bells in the morning watch) from 15 February to 31 October inclusive, and at 0900 (two bells in the forenoon watch) during the winter.
When sunset is at or before 2100, flags are lowered at sunset at the ceremony of sunset. When sunset is after 2100, the evening flag lowering ceremony is called evening colours and carried out at 2100.
United States Navy
The United States Navy performs the same ceremonies, called "Morning Colors" and "Evening Colors", at 0800 and sunset each day. When Colors is played aboard Navy and Marine Corps bases, those outdoors must stop to render proper courtesies by saluting if in uniform or, if out of uniform, by standing at attention, until "Carry On" is sounded. Marines and sailors driving on base during this time are expected to stop their vehicles and stand at attention until the ceremony is over.
Yacht Clubs
Many traditional Yacht Clubs worldwide also conduct morning and evening colour ceremonies. At 0800 each morning and at sunset during the club's active sailing season the ceremony is performed by the launchmen or harbourmaster.
- First, a bell is sounded as an alert for all members and guests present to stand at attention.
- A cannon is then shot and the national ensign hoisted (or lowered if sunset).
- At the conclusion of the ceremony the most senior officer present says: "As you were" and members and guests may carry on.
See also
- The finial is the top piece of the pike or lance which the colour/guidon/standard is attached to.
- Glossary of vexillology
- Historical colours, standards and guidons
- Honor guard
- Trooping the Colour
- War flag
- With flying colours
Notes
- ↑ Campaign Streamers, Commendation Streamers, and Awards and Decorations of the United States Military
- ↑ U.S. Army Press Release, Army to award campaign participation credit and streamers for global war on terror. Retrieved 16 August 2006.
- ↑ "U.S. Army FM 3-21.5" (PDF).. Retrieved 16 August 2006.
- ↑ "Flag Manual" (PDF). Mco P10520.3B. 15 September 1989.
- ↑ McMillan, Joseph (2001). "Flags of the U.S. Marine C". Seaflags. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ↑ "Regimental Colours, Banners, and Flags Past and Present". Regimental website of the Lincoln and Wetland Regiment. Major A.D. Woolley. Retrieved 22 July 2011. External link in
|work=(help) - ↑ Department of National Defence; Cadet Instructors Cadre; pg. 33 Archived 6 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ http://www.army.gov.au/Army-life/Army-careers/RMCD/RMCD-history-and-traditions/The-colours
- ↑ "Army Flags (Australia)". Flags of the World. Archived from the original on 3 April 2007. Retrieved 3 April 2007.
- ↑ http://forsvaret.dk/ghr/om%20ghr/kendetegn/fane_estandart/Pages/default.aspx
- ↑
- "On January 1188 there was a meeting between Henry II and Phillip II under an old tree at Gisors on the border between France and Normandy. The meeting was attended also by Phillip of Alsace, the Count of Flanders. The two rivals agreed to stop the wars between them and swear to "take the cross" (i.e. to go in a crusade). They also agreed to establish symbols to the different corps: white cross for the Plantagenet corps of Henry II, a red cross for the Capetian corps of Phillip II, and a green cross for the Flemish."
- ↑ Bulletin officiel des armées, 27, 9 novembre 2007
- ↑ (A) NORDEF0452926A, by Minister of Defence Mme Michèle Alliot-Marie.
- ↑ The modern fourragère of the French Army is awarded to all members of military units which have been awarded a mention in despatches. It should not be confused with unit awards of particular decorations, where the medal itself is hung on the colour of the unit. For example, there are many units wearing the fourragère of the Médaille militaire, whereas only six units wore the medal on their colours. See also the article dealing with the Croix de guerre.
- ↑ The ensign of the National Navy differs from the French national flag by its slightly darker blue shade, and by the dimensions of the stripes: while the stripes of the national flag has 1:1:1 proportions, the naval ensign has 30:33:37.
- ↑ Les drapeaux de la Marine on the French Ministry of Defence and Veterans Affairs website (pdf download)
- ↑ Imperial German Empire Army Colours
- ↑ Presidential Decree 348 /17-4-1980, On the war flags of the Armed Forces and the Gendarmerie Corps, Gazette issue A-98/1980, pp. 1486.
- ↑ "Nederlands Instituut voor Militaire Historie | Ministerie van Defensie". Nimh.nl. Retrieved 2012-08-01.
- ↑ Soviet Army colours (In Russian)
- ↑ The medieval "guidon, a name derived from the Fr. Guyd-homme, was somewhat similar to the standard, but without the cross of St George, rounded at the end, less elongated and altogether less ornate. It was borne by a leader of horse, and according to a medieval writer 'must be two and a half yards or three yards long, and therein shall no armes be put, but only the man's crest, cognisance, and devyce.'" (Swinburne 1911, p. 457,458)
- ↑ "[ARCHIVED CONTENT] The Royal Artillery – British Army Website". Army.mod.uk. Retrieved 2012-08-01.
- ↑ "The Regiment -Firepower – The Royal Artillery Museum – Royal Arsenal in Woolwich". Firepower. Retrieved 2012-08-01.
- ↑ "History 1919–1942". Fort Siloso. Retrieved 2012-08-01.
- ↑ Did Singapore Have to Fall: Churchill and the Impregnable Fortress – Kevin Blackburn – Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2012-08-01.
References
- BR1834 – Royal Naval Handbook of Ceremonial and Drill
 Swinburne, H Lawrence (1911). "Flag". In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 10 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 457, 458.
Swinburne, H Lawrence (1911). "Flag". In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica. 10 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 457, 458.