Green Cape Lighthouse
 Green Cape Lighthouse | |
 New South Wales | |
| Location |
Green Cape New South Wales Australia |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 37°15′41.01″S 150°2′57.58″E / 37.2613917°S 150.0493278°ECoordinates: 37°15′41.01″S 150°2′57.58″E / 37.2613917°S 150.0493278°E |
| Year first lit | 1883 |
| Deactivated | 1992 |
| Construction | concrete tower |
| Tower shape | square frusrum base with octagonal prism tower with balcony and lantern |
| Markings / pattern | white tower, black balcony |
| Height | 29 metres (95 ft) |
| Focal height | 44 metres (144 ft) |
| Original lens | 1st order Fresnel lens |
| Light source | mains power |
| Intensity | 1,000,000 cd |
| Range | 40 kilometres (25 mi) |
| Characteristic | Fl (2) W 10s. |
| Admiralty number | K2570 |
| NGA number | 6588 |
| ARLHS number | AUS-085 |
| Managing agent | Australian Maritime Safety Authority |
The Green Cape Lighthouse is a lighthouse located at the tip of Green Cape, a headland forming the northern boundary of Disaster Bay, in southern New South Wales, Australia. It is the southernmost lighthouse in New South Wales and Australia's first lighthouse built in concrete. At 29 metres (95 ft) it is also the second tallest lighthouse in New South Wales.[1] [2] It marks Green Cape on the northerly shore hugging sailing course.
History

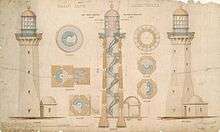
The need for lighthouse was approved in 1873, following a series of wrecks on the southern shore. After rounding Cape Howe, northerly ships would hug the shore to avoid the East Australian Current. Green Cape was the first major projection they would encounter. Original tenders were for a stone lighthouse and rubble quarters. However, with the soft local sedimentary, no one tendered. In 1870 the specifications were changed to concrete and a budget of £17,000 AUD was set.
The tower was designed by James Barnet in 1880[3] and the contract was awarded to Albert Aspinall who quoted £12,936 in December 1880. The tender was for the concrete tower, two houses of double brick with cement render, and associated structures.
Aspinall first had to find a way to move the materials from Eden to the site. The nearest safe anchorage was in Bittangabee Bay, north along the coast from Green Cape, where he built his storeroom and jetty. He then spent five months building a 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) wooden tramway from Bittangabee Bay to the cape. Materials were transported to the site on wooden trolleys pulled by horses. This first phase was complete in June 1881, and Aspinall commenced the construction.
Major problems were encountered when the site was found to lie on a 6 metres (20 ft)[4] white clay belt, forcing the foundation to be dug to 9 metres (30 ft). Work stopped in June 1883 due to financial difficulties, and Aspinall's creditors completed the project, which was lit on 1 November 1883.
The original apparatus, still mounted in the lantern, is a Chance Bros. 1st order revolving Fresnel lens dioptric. Its light characteristic was one flash every 50 seconds[5] and it was visible to 19 nautical miles (35 km; 22 mi).[6] The light source was a four-wick kerosene-burning lamp with an intensity of 100,000 cd.
On 31 May 1886, the SS Ly-Ee-Moon en route to Sydney from Melbourne, struck a reef close to the cape at night. 71 people died, with the lighthouse keepers only being able to save 15 people under the conditions. Flora MacKillop, the mother of Mary MacKillop, died in that accident.[7]
In 1910 the light source was replaced with a Douglas vaporised kerosene burner and a glass chimney around a silk mantle, made by Chance Bros.
In 1913 it was recommended to change the light characteristic to a white flash every 10 seconds. However, it took 16 years until this recommendation was accepted, in 1926. Previous to that, in 1923, light source was upgraded to a Ford Schmidt burner which increased the intensity of the light to 327,000 cd.
In 1962 the tower was electrified with diesel generators serving as the power source. The manual winding system was also replaced with an electric motor. The lightglove used provided a light intensity of 475,000 cd. In 1967 improved generators were installed together with a 1000 W Tungsten-halogen lamp with an intensity of 1,000,00 cd, visible over 20 nautical miles (37 km; 23 mi). The light characteristic was changed to two flashes every ten seconds. At some later point the power source was changed to the mains electricity.
 Green Cape Light. The current light is the skeletal tower to the right of the original tower. | |
| Location | Green Cape, New South Wales, Australia |
|---|---|
| Year first constructed | 1992 |
| Construction | metal skeletal tower |
| Tower shape | square pyramidal tower |
| Markings / pattern | white tower |
| Height | 49 feet (15 m)[8] |
| Focal height | 118 feet (36 m)[9] |
| Intensity | 37,500 cd |
| Range | 17 nautical miles (31 km; 20 mi) |
| Characteristic | Fl (2) W 15s. |
| Admiralty number | K2570 |
| NGA number | 6588 |
| ARLHS number | AUS-260 |
| Managing agent | NSW National Parks (Ben Boyd National Park) |
In 1992[10] a solar powered lens on a modern lattice skeletal steel tower was constructed right next to the historic tower, and the light was officially turned off on 17 March 1992. The new light operates a 36 W lamp with an intensity of 37,500 cd.
In February 2011, the lighthouse was recognised as an "Engineering Heritage National Landmark" by Engineers Australia.[11]
Structure
The original tower is built of concrete, and at the time it was the largest mass concrete structure in New South Wales. The form, octagonal on a square base, was chosen to ease the construction of the formwork.
The tower has a bluestone gallery. A small room is attached to the western side, originally meant to be an oil store.
Site operation
The current light is operated by the Australian Maritime Safety Authority. The site is managed by the Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water as part of the Ben Boyd National Park.
Visiting
The grounds are open to the public, and the tower is open to guided tours on some days of the week. Reservations for the guided tours are recommended. Accommodations are available in the two assistant keepers' cottages which sleep up to six people each.
See also
Notes
- ↑ According to "Lighthouses of Australia". "DECCW - Ben Boyd National Park - Accommodation" says it is the tallest.
- ↑ According to the British Admiralty List of Lights and Foghorns, Vol. K, there is no lighthouse in NSW taller than Greencape. There is a tower in Newcastle at Throsby 32 meters high but it is a light on top of a grey metal pole which can't really be regarded as a lighthouse.
- ↑ "Item details". recordsearch.naa.gov.au. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ↑ According to "Lighthouses of Australia". More than 7m according to Steve Merson
- ↑ According to Steve Merson. 60 seconds according to "SeaSide Lights"
- ↑ According to "SeaSide Lights" and Steve Merson. 34km according to "Lighthouses of America".
- ↑ "Flora Mackillop".
- ↑ According to Directory of Lighthouses. "SeaSide Lights" list the height of the old light, 95 feet (29 m), with the focal height of the new one, 118 feet (36 m).
- ↑ According to List of Lights. "39 m (118 ft)" according to Directory of Lighthouses, which is a unit conversion error.
- ↑ According to all sources except "SeaSide Lights" which says 1998.
- ↑ "Lighthouse receives national recognition". www.abc.net.au. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
References
- List of Lights, Pub. 111, The West Coasts of North and South America (Excluding Continental U.S.A. and Hawaii), Australia, Tasmania, New Zealand, and the Islands of the North and South Pacific Oceans (PDF). List of Lights. United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. 2009. p. 134.
- Rowlett, Russ. "Lighthouses of Australia: New South Wales". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- "The Green Cape Lighthouse". Lighthouses of New South Wales. Lighthouses of Australia Inc.
- Searle, Garry. "Green Cape". Lighthouses of New South Wales. SeaSide Lights.
- Steve Merson (July–August 2004). "Light the coast like a street with lamps". Lighthouses of Australia Inc Bulletin (4).
- "DECCW - Ben Boyd National Park - Accommodation". environment.nsw.gov.au. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Green Cape Lighthouse. |
- Australia’s iconic lighthouses, Australian Geographic, 26 July 2010
