Global warming in Antarctica
The effects of global warming in Antarctica may include rising temperatures and increasing snow melt.[1]
Effects
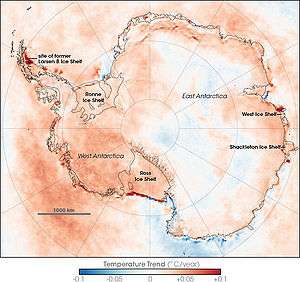
The continent-wide average surface temperature trend of Antarctica is positive and significant at >0.05 °C/decade since 1957.[2][3][4][5] The West Antarctic ice sheet has warmed by more than 0.1 °C/decade in the last 50 years, and is strongest in winter and spring. Although this is partly offset by fall cooling in East Antarctica, this effect is restricted to the 1980s and 1990s.[2][3][4]
Research published in 2009 found that overall the continent had become warmer since the 1950s, a finding consistent with the influence of man-made climate change:
- "We can't pin it down, but it certainly is consistent with the influence of greenhouse gases from fossil fuels", said NASA scientist Drew Shindell, another study co-author. Some of the effects also could be natural variability, he said.[6]
British Antarctic Survey
The British Antarctic Survey, which has undertaken the majority of Britain's scientific research in the area, has the following positions:[7]
- Ice makes polar climate sensitive by introducing a strong positive feedback loop.
- Melting of continental Antarctic ice could contribute to global sea level rise.
- Climate models predict more snowfall than ice melting during the next 50 years, but models are not good enough for them to be confident about the prediction.
- Antarctica seems to be both warming around the edges and cooling at the center at the same time. Thus it is not possible to say whether it is warming or cooling overall.
- There is no evidence for a decline in overall Antarctic sea ice extent.[8]
- The central and southern parts of the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula have warmed by about 2.4 °C. The cause is not known.
- Changes have occurred in the upper atmosphere over Antarctica.

The area of strongest cooling appears at the South Pole, and the region of strongest warming lies along the Antarctic Peninsula. A possible explanation is that loss of UV-absorbing ozone may have cooled the stratosphere and strengthened the polar vortex, a pattern of spinning winds around the South Pole. The vortex acts like an atmospheric barrier, preventing warmer, coastal air from moving into the continent's interior. A stronger polar vortex might explain the cooling trend in the interior of Antarctica.
In their latest study (September 20, 2007) NASA researchers have confirmed that Antarctic snow is melting farther inland from the coast over time, melting at higher altitudes than ever and increasingly melting on Antarctica's largest ice shelf.[9]
There is also evidence for widespread glacier retreat around the Antarctic Peninsula.[10]
Researchers reported December 21, 2012 in Nature Geoscience that from 1958 to 2010, the average temperature at the mile-high Byrd Station rose by 2.4 degrees Celsius, with warming fastest in its winter and spring. The spot which is in the heart of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is one of the fastest-warming places on Earth.[11][12][13]
References
- ↑ The Danger of a Runaway Antarctica March 31, 2016
- 1 2 Retrieved=2009-01-22
- 1 2 Retrieved=2009-01-22
- 1 2 Retrieved=2009-01-22
- ↑ Retrieved=2009-01-22
- ↑ Antarctica study challenges warming skeptics, Jan 21, 2009
- ↑ "Climate Change Positions". British Antarctic Survey. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ↑ In Antarctica, melting may beget ice; Disintegration of floating glaciers could be responsible for freezing of seawater March 29, 2013 Vol.183 #9 Science News
- ↑ "NASA Researchers Find Snowmelt in Antarctica Creeping Inland" September 20, 2007
- ↑ IPCC 2007, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, 2007, page 376.
- ↑ West Antarctica warming fast; Temperature record from high-altitude station shows unexpectedly rapid rise December 21, 2012 Science News
- ↑ Figure 1: Map of Antarctica and annual spatial footprint of the Byrd temperature record.
- ↑ Bromwich, D. H.; Nicolas, J. P.; Monaghan, A. J.; Lazzara, M. A.; Keller, L. M.; Weidner, G. A.; Wilson, A. B. (2012). "Central West Antarctica among the most rapidly warming regions on Earth". Nature Geoscience. 6 (2): 139. Bibcode:2013NatGe...6..139B. doi:10.1038/ngeo1671.