Geography of Saskatchewan
 | |
| Continent | North America |
|---|---|
| Region | Western Canada |
| Coordinates |
49°00′00″N 101°21′41″W / 49.00000°N 101.36139°W— 60°00′N 110°00′W / 60.000°N 110.000°W |
| Area | Ranked 7th among provinces |
| • Total | 651,036 km2 (251,366 sq mi) |
| • Land | 90.8% |
| • Water | 9.2% |
| Coastline | 0 km (0 mi) |
| Borders | Alberta, Manitoba, Northwest Territories, Montana and North Dakota |
| Highest point |
Cypress Hills 1,468 metres (4,816 ft) |
| Lowest point | Lake Athabasca shoreline |
| Longest river | Saskatchewan River |
| Largest lake |
Lake Athabasca 7935 km2 |
The geography of Saskatchewan (suskăch'uwun, –wän", săs"–, –oowun"), is unique among the provinces and territories of Canada in some respects. It is one of only two landlocked regions (Alberta is the other) and it is the only region whose borders are not based on natural features like lakes, rivers or drainage divides. The borders of Saskatchewan, which make it very nearly a trapezoid, were determined in 1905 when it became a Canadian province. The population in May 2012 was 1,072,853.[1] Saskatchewan has a total area of 651,036 square kilometers (251,366 sq mi) of which 591,670 km2 (228,450 sq mi) is land and 59,366 km2 (22,921 sq mi) is water.[2]
The province's name comes from the Saskatchewan River, whose Cree name is: Kisiskatchewani Sipi, meaning "swift flowing river".[3]
Saskatchewan can be divided into three regions: grassland (part of the Great Plains) in the south, aspen parkland in the center, and forest (taiga) in the north, part of the Canadian Shield. Its principal rivers are the Assiniboine River, North and South Saskatchewan.
Saskatchewan's economy is based on its abundant natural resources,[4] notably petroleum, natural gas, coal, potash, uranium and forests, and agriculture (wheat and other grains, and cattle ranching).
The original inhabitants of Saskatchewan were the Cree Indians in the south and central regions and the Dene in the north. The Hudson's Bay Company controlled the area named Rupert's Land beginning in 1670. The French established settlements in the region c. 1750, though the Hudson's Bay Company made the first permanent settlement in 1774. The Hudson's Bay Company ceded Rupert's Land in 1869 and, by 1870, the North West became a member of the Dominion of Canada as a part of the Northwest Territories. From 1882 into the early 1900s, the extension of the railroad brought in large numbers of European settlers. Saskatoon is the largest city and Regina is the second-largest city and capital.

Physical geography
Saskatchewan is an approximate trapezoid. Its western border runs concurrent with the 4th meridian or the 110°W longitude, separating Saskatchewan from the province of Alberta. This border extends in length for 1,225 kilometers (761 mi) and was established in 1905 when both provinces were formed.[5]
Saskatchewan's eastern border includes minor measurement errors from the 1880s, so that it does not lie perfectly on the 102°W longitude, but rather it is slightly west of that meridian from 60°N parallel to 55°47'N, then slightly east of that until the Canada–United States border – an irregular line (rather than a straight one) for its 1,225-kilometer (761 mi) distance.[6] When Saskatchewan was formed in 1905, Manitoba and the District of Keewatin were the neighboring areas to the east. Manitoba was enlarged in 1912 north to the 60th parallel, becoming Saskatchewan's only eastern neighbor. This remaining section of the border was determined by survey between 1961 and 1972.[5]
Saskatchewan's southern border with the United States sits approximately on the 49th parallel, as agreed in the Treaty of 1818—though minor measurement errors during the 1870s International Boundary Survey result in some variance between the actual Canada–United States border and the 49th parallel.[7] This boundary was not formally established until the 1867 survey.[5] This border extends 627 kilometers (390 mi) across southern Saskatchewan.
The Northwest Territories is north of the 60th parallel which forms the northern border of the province.[8] This border extends 445 kilometers (277 mi) across northern Saskatchewan.[5] The aforementioned measurement errors in the 1880s surveys place the Saskatchewan/Manitoba border approximately 400 meters (440 yd) west of the 102nd meridian and the accurately measured Northwest Territories/Nunavut border, just missing a true quadripoint of the Saskatchewan/Manitoba/Northwest Territories/Nunavut borders.
Geology
The geology of Saskatchewan can be divided into two main geological regions, the Pre-Cambrian or Canadian shield and the Phanerozoic or Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. Within the Canadian shield exists the Athabasca sedimentary basin. Meteorite impacts have altered the natural geological formation processes. The Quaternary period is the most recent geological process when the prairies were affected by glacial events.[9] There are six notable meteorite or comet impact craters in Saskatchewan. Carswell, Deep Bay and Gow Lake have affected the Canadian Shield area of the north. In the southern Phanerozoic crater are the Viewfield, Elbow and Maple Creek structures.[10] The Carswell structure is largest astrobleme at 35 kilometers (22 mi) in diameter.[11]
Historical geography
Archaeologists have dated the first human settlements to 9,500 BCE. The four groups inhabiting the area at the time of the first European contact were the Cree, Assiniboine, Salteaux and Dene.[12] Henry Kelsey of the Hudson's Bay Company is considered the first European person to see this area. The earliest trading posts were made by the French; however, the first permanent settlement was established at Cumberland House in 1774 by the HBC. In addition, several more ports were set up by British fur traders among the area's waterways. The forested area of the Canadian Shield was the favoured area for early settlement, and the economy was heavily dependent on hunting and trapping.
In 1870, the Hudson's Bay Company sold Rupert's Land and ceded its rights to the Canadian Government.[12] The region became a part of the Northwest Territories. The majority of the Canadians of indigenous descent in the Northwest Territories sold their lands to the government in the 1870s and were settled on reservations. Additional native peoples and Métis (people of mixed French and indigenous Canadian ancestry), led by Louis Riel, rebelled between 1884 and 1885 and were suppressed.
The arrival of settlements and the rail lines also brought agricultural economies and development in the Central Lowlands Area. The Great Plains or Palliser Triangle area to the south was mainly used for ranching economies. In the beginning of the 20th century, Saskatchewan farmers created cooperative organizations to maintain grain marketization. During the drought and depression of the 1930s, the population decreased as immigration nearly ended and numerous families left. During World War II, conservation programs and the increased demand for grain revived the economy.
Climate
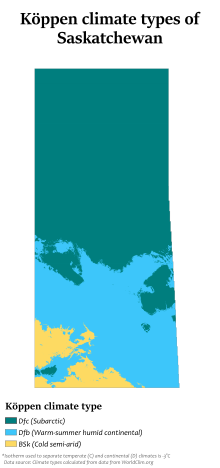



Being in the centre of the North America, Saskatchewan is far removed from the moderating effects of any large body of water and therefore has a temperate continental climate, Köppen climate classification types BSk, Dfb and Dfc. Hot to warm summers and cold winters mean that the annual temperature range can be up to 65 °C.[13] On average, Saskatchewan has 211 days per year when the temperature drops below freezing.[14] Plough winds, Supercell hail or high precipitation rain storms and tornadoes are eventful summer occurrences. Midale reached 45 °C (113 °F) on July 5, 1937, the highest recorded temperature in Canada,.[13]
Compared to average values from all thirteen Canadian provinces and territories,[14] Saskatchewan is the sunniest province or territory year round (2206 hours per year), has the second-lowest annual snowfall (145 centimetres (57 in)), the fourth-lowest total precipitation (428 centimetres (169 in)) and the second-hottest summer (22.5 °C (72.5 °F)). The number of frost-free days ranges from 95 days in the north (Prince Albert, for example) to as high as 124 days in the south (Estevan).[15]
Urban areas
Saskatchewan's capital is Regina. Its most populous city is Saskatoon. Other major cities include Estevan, Flin Flon (part), Humboldt, Lloydminster (part), Melfort, Melville, Moose Jaw, North Battleford, Prince Albert, Swift Current, Weyburn, and Yorkton.
|
|
Biosphere
Flora

The native flora of the Saskatchewan includes vascular plants, plus additional species of other plants and plant-like organisms such as algae, lichens and other fungi, and mosses.[18][18] Non-native species of plants are recorded as established outside of cultivation in Saskatchewan, of these some non-native species remain beneficial for gardening, and agriculture, where others have become invasive, noxious weeds.[19][20] Saskatchewan is committed to protecting species at risk in Canada.[21] The growing season has been studied and classified into plant hardiness zones depending on length of growing season and climatic conditions. Biogeographic factors have also been divided into ecoregions and floristic kingdoms across Saskatchewan, and natural vegetation varies depending on elevation, moisture, soil and weather.[22][23][24] The study of ethnobotany uncovers the interrelation between humans and plants and the various ways people have used plants for economic reasons, food, medicine and technological developments.[25][26]
The Government of Saskatchewan has declared 3 indigenous plants as provincial symbols.[27]

Red area Canadian Shield
Green area Central Lowlands
Southwest corner Great Plains
Fauna
The fauna of Saskatchewan include many land and aquatic species. From the multiplicity of invertebrates and vertebrates two have been chosen as symbols of Saskatchewan, the white-tailed deer and the sharp-tailed grouse.[28] Cenozoic vertebrate fossils reveal the geological evolution of the interior plains and its prehistoric biogeography.[29] Today, Saskatchewan's ecosystems range from the sub-arctic tundra of the Canadian Shield in north Saskatchewan to aspen parkland, and grassland prairie.[30] Fauna inhabit areas unique to their own specific and varied breeding, foraging and nesting requirements.[23] With a large land and water area, and small population density, the ecoregions of Saskatchewan provide important habitat for many animals, both endangered and not.[31]
Naturalists observing wildlife have enumerated shrinking and growing wildlife populations. They advocate programs and methods to preserve or re-introduce endangered species and identify programs of control for outbreaks of wildlife populations.[32]
A broad diversity of wildlife habitats are preserved as parks and reserves protecting the feeding and breeding grounds of protected and indigenous fauna of Saskatchewan.[29][33]
Hydrography
The total area of freshwater is 59,366 km2.[2][34] There are two main river basins, the Nelson and Churchill River Basins, both of which drain into Hudson Bay.[35]
Qu'Appelle and Souris, the North and South Saskatchewan, confluence is east of Prince Albert becoming the Saskatchewan which are all a part of the Nelson river basin. The Churchill River connects lakes and streams through the lower portion of the Canadian shield.[36] Rupert's Land a historical political division of Canada comprised all lands of the Hudson Bay drainage system between the years 1670 to 1870.[37][38]
Frenchman River does not flow east to Hudson Bay, but rather south to the Missouri River, which is part of the Missouri river basin catchment area. The Mackenzie River basin of north Saskatchewan flows north draining into the Arctic Ocean, which belongs to the Mackenzie river basin drainage area.[35][36]
There are over 10 thousand lakes across Saskatchewan, the main lake region being north of the tree line in the Canadian Shield.[39]
Saskatchewan's largest lake is Lake Athabasca which sits astride the Saskatchewan – Alberta border. The second in size is Reindeer Lake which is located on the Saskatchewan – Manitoba border. Other lakes of notable size would be Wollaston, Cree, Frobisher, and Lac La Ronge.[36] The deepest water point 220 meters (720 ft) is located in Reindeer Lake at the Deep Bay Structure site which was created by a meteor impact.[11][40]
Saskatchewan is also home to preserved wetlands which are partially submerged areas of land.[41]
Saskatchewan's waterways also contain bogs, as well as the salt water lakes. Quill Lake is Canada's largest saltwater lake, Chaplin Lake is a Western Hemispheric Shorebird Reserve Network and Little Manitou, an ehdorheic lake, is a popular tourist resort. Brine shrimp siheries have existed on sodium magnesium sulphate lakes such as Chaplin, Frederick, Ingebright, and Little Manitou lakes.[42][43]
Provincial and National Parks
Saskatchewan has 34 provincial parks that provide for recreational use or preserve wilderness, special environments or sites of historic importance.[44]
The province is also home to two of Canada's 36 National Parks. Grasslands National Park, which covers 907 square kilometres (350 sq mi) in southernmost part of the province, was established in 1981.[45] The other is Prince Albert National Park covering 3,874 square kilometres (1,496 sq mi) in central Saskatchewan, which was established in 1927.[46]
Economic geography
The economy of Saskatchewan has been associated with agriculture resulting in the moniker Bread Basket of Canada[47] and Bread Basket of the World.[48] According to the Government of Saskatchewan, approximately 95% of all items produced in Saskatchewan, depend on the basic resources available within the province. Various grains, livestock, oil and gas, potash, uranium, wood and their spin off industries fuel the economy.[49]
Saskatchewan's GDP in 2006 was approximately C$45.922 billion,[50]
Gallery
 View of Qu'Appelle River
View of Qu'Appelle River View of South Saskatchewan River
View of South Saskatchewan River The Saskatchewan River drainage basin.
The Saskatchewan River drainage basin. Lake Athabasca
Lake Athabasca Aerial view Wascana Lake
Aerial view Wascana Lake
 Saskatchewan Wetlands
Saskatchewan Wetlands Saskatchewan Wetlands Canada goose
Saskatchewan Wetlands Canada goose Paper birch, Saskatchewan's provincial tree
Paper birch, Saskatchewan's provincial tree Tamarack larch in fall colors, with black spruce
Tamarack larch in fall colors, with black spruce
See also
- The Saskatchewan Act
- Geography of Canada
- District of Assiniboia
- List of cities in Canada
- List of airports in Saskatchewan
- List of communities in Saskatchewan
- List of Canadian provincial and territorial symbols
- List of Saskatchewan rivers
- List of rural municipalities in Saskatchewan
- Symbols of Saskatchewan
References
- ↑ "Stats Canada 2006 census" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 17, 2007. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- 1 2 "The Atlas of Canada: Land and freshwater areas". Natural Resources Canada (Federal Government). Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑ "Provinces and Territories – The origins of their names". Natural Resources Canada. Archived from the original on January 23, 2009. Retrieved 2009-01-08.
- ↑ Reeves, Philip. "Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan: Mineral resources". Retrieved 2009-01-08.
- 1 2 3 4 Lewry, Marilyn (2006). "Boundary surveys". The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan. Canadian Plains Research Center, University of Regina. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ Thomson, Malcolm M.; Tanner, Richard W. (April 1977). "Canada's Prime Meridian". Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. 71: 204. 1977JRASC..71..204T.
- ↑ Widdis, Randy (2006). "49th Parallel". The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan. Canadian Plains Research Center, University of Regina. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ "The Atlas of Canada – Territorial Evolution, 1905". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2004-04-06. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ "Introduction to Saskatchewan's Geology". Government of Saskatchewan. Retrieved 2009-01-24.
- ↑ Macdonald, R. (2006). "Geology". The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan. Canadian Plains Research Center, University of Regina. Retrieved 2009-01-24.
- 1 2 Harper, Charles (2006). "Astroblemes". The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan Details. Canadian Plains Research Center, University of Regina. Retrieved 2009-01-24.
- 1 2 Cottrell, Michael. "Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan: History of Saskatchewan". Retrieved 2009-01-12.
- 1 2 Cote, Mark. "Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan: Climate". Retrieved 2009-01-08.
- 1 2 "Saskatchewan Weather Honours". Environment Canada. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ↑ "Summary of Agriculture in Saskatchewan". Government of Saskatchewan. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- 1 2 "Community Profiles from the 2006 Census, Statistics Canada". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. 2012-12-22. Retrieved 2009-01-09.
- 1 2 "Community Profiles from the 2011 Census, Statistics Canada". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. 2014-04-29. Retrieved 2015-04-29.
- 1 2 "University of Saskatchewan: Virtual Herbarium". Department of Biology. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ "Saskatchewan Conservation Data Centre". About Government/News Releases/March 1999/Wild Plants and Animals Protected. 2008. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ "Wild Plants and Animals Protected". About Agriculture/Production/Crops – Weeds/Invasive Alien Plant Program. Government of Saskatchewan. March 1999. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ "Wild Plants and Animals Protected". About Government/News Releases/March 1999/Wild Plants and Animals Protected. Government of Saskatchewan. March 1999. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ Haggett, Peter (2002). Encyclopedia of World Geography (Digitized online by Google books) (2, illustrated ed.). Marshall Cavendish. p. 355. ISBN 0-7614-7289-4. ISBN 9780761472896. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- 1 2 ThorpeWapple, Robert (1999), "Wildlife", in Kai-iu Fung; Bill Barry; Wilson, Michael, Atlas of Saskatchewan Celebrating the Millennium, Andrew B. Didiuk Alan Smith, Bernie Gollop, Jennifer Merkowsky, Peter Jonker (Millennium ed.), Saskatchewan: University of Saskatchewan, pp. 138–168, ISBN 0-88880-387-7
- ↑ Coupland, R.T. (1969). "Natural Vegetation of Saskatchewan". In J.H. Richards; K.I. Fung. Atlas of Saskatchewan. J.S. Rowe. Saskatoon, SK, CA: University of Saskatchewan. pp. 72–78.
- ↑ Elias, Professor Thomas S Elias,, Thomas S. (1983). Edible Wild Plants A North American Field Guide (Digitized online by Google books). Peter A. Dykeman. Cengage Learning. pp. 9–28 and 258. ISBN 0-442-22254-8. ISBN 9780442222543. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ Johnson, Derek; Linda Kershaw; Andy Mackinnon; Jim Pojar (1995). Plants of the Western Boreal Forest and Aspen Parkland (Digitized online by Google books). Lone Pine Publishing and the Canadian Forest Service. pp. 11–21. ISBN 1-55105-058-7. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ Government of Saskatchewan (June 2008). "Saskatchewan's Provincial Tree". Retrieved 2008-04-05.
- ↑ Government of Saskatchewan. "Symbols of Saskatchewan". Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- 1 2 "Royal Saskatchewan Museum: Publications: Earth Sciences" (Abstract published online by JSTOR 2000-2008). Royal Saskatchewan Museum. 2009. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ "Saskatchewan Conservation Data Centre". Saskatchewan Conservation Data Centre. 2002. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ "Narrative Descriptions of Terrestrial Ecozones and Ecoregions of Canada". The Green LaneTM, Environment Canada's World Wide Web site. Government of Canada. 2005-04-11. Archived from the original on January 15, 2009. Retrieved 2009-01-26.
- ↑ Sterling, Keir Brooks; C. Stuart Houston (1997). Biographical Dictionary of American and Canadian Naturalists and Environmentalists (Digitized online by Google books) (illustrated ed.). Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 267–269. ISBN 0-313-23047-1. ISBN 9780313230479. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ Maher, W.J. (1969). "Zoogeography". In J.H. Richards; K.I. Fung. Atlas of Saskatchewan. F.J. Atton, J.B. Gollop. Saskatoon, SK, CA: University of Saskatchewan. pp. 79–105.
- ↑ "Land and Freshwater area by province". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. 2005-02-01. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved 2007-04-05.
- 1 2 Benke, Arthur C. (2005). Rivers of North America: The Natural History. Academic Press. pp. 853–903. ISBN 0-12-088253-1. ISBN 9780120882533. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
|first2=missing|last2=in Authors list (help) - 1 2 3 "Saskatchewan (province) – MSN Encarta". Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ "The Atlas of Canada – Drainage Patterns". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2003-03-14. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ Smith, Shirlee Anne (2008). "Rupert's Land". Microsoft. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ "Saskatchewan Council for Archives and Archivists – The Saskatchewan Landscape". Saskatchewan Council for Archives and Archivists. University of Saskatchewan. 2004.
- ↑ "Geoscape Northern SaskatchewanGeoscience for our Canadian Shield Community – Meteorite impact". Government of Canada. 2008-01-07. Retrieved 2007-12-29.
- ↑ "The Atlas of Canada – Wetlands". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2003-03-14. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ Hammer, Ulrich Theodore; Cushing, Colbert E. (1986). Saline Lake Ecosystems of the World. Springer. pp. 55–57. ISBN 90-6193-535-0. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ "Canada Facts: Saskatchewan". Education Canada Network. Government of Canada. 1996–2008. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
- ↑ "Provincial Parks". Tourism Saskatchewan. Retrieved 2009-01-13.
- ↑ "Grasslands National Park of Canada". Parks Canada. Retrieved 2009-01-13.
- ↑ "Prince Albert National Park of Canada". Parks Canada. Retrieved 2009-01-13.
- ↑ Giannetta, J. "SASKATCHEWAN economy (oil and gas, mining, farming, forestry, food processing, dams and reservoirs, electricity)". Sask web pages. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- ↑ "Immigration to Canada: Saskatchewan". Abrams & Krochak – Canadian Immigration Lawyers. 2008. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- ↑ "Saskatchewan's Economy -". About Saskatchewan/Economy. Government of Saskatchewan. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- ↑ "Gross domestic product, expenditure-based, by province and territory". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. : 2008-11-06. Archived from the original on April 20, 2008. Retrieved 2009-01-16. Check date values in:
|date=(help)
Further reading
- Benke, Arthur C.; Colbert E. Cushing (2005). Rivers of North America: The Natural History (Digitized online by Googlebooks) (illustrated ed.). Academic Press. p. 859. ISBN 9780120882533. Retrieved 2009-01-21.
External links
- An outline map showing the boundaries and major lakes and rivers for Saskatchewan. Includes names for major political and geographical features.
For More Information on Saskatchewan click here