Game design
Game design is the art of applying design and aesthetics to create a game to facilitate interaction between players for entertainment or for medical, educational, or experimental purposes. Game design can be applied both to games and, increasingly, to other interactions, particularly virtual ones (see gamification).
Game design creates goals, rules, and challenges to define a sport, tabletop game, casino game, video game, role-playing game, or simulation that produces desirable interactions among its participants and, possibly, spectators.
Academically, game design is part of game studies, while game theory studies strategic decision making (primarily in non-game situations). Games have historically inspired seminal research in the fields of probability, artificial intelligence, economics, and optimization theory. Applying game design to itself is a current research topic in metadesign.
History
Sports (see history of sports), gambling, and board games are known, respectively, to have existed for at least ten thousand, six thousand, and five thousand years.
Folk process
Tabletop games played today whose descent can be traced from ancient times include chess, go, pachisi, backgammon, mahjong, mancala, and pick-up sticks. The rules of these games were not codified until early modern times and their features gradually evolved and changed over time, through the folk process. Given this, these games are not considered to have had a designer or been the result of a design process in the modern sense.
After the rise of commercial game publishing in the late 19th century, many games which had formerly evolved via folk processes became commercial properties, often with custom scoring pads or preprepared material. For example, the similar public domain games Generala, Yacht, and Yatzy led to the commercial game Yahtzee in the mid-1950s.
Today, many commercial games, such as Taboo, Balderdash, Pictionary, or Time's Up!, are descended from traditional parlour games. Adapting traditional games to become commercial properties is an example of game design.
Similarly, many sports, such as soccer and baseball, are the result of folk processes, while others were designed, such as basketball, invented in 1891 by James Naismith.
New media
Technological advances have provided new media for games throughout history. The printing press allowed packs of playing cards, adapted from Mahjong tiles, to be mass-produced, leading to many new card games. Accurate topographic maps produced as lithographs and provided free to Prussian officers helped popularize wargaming. Cheap bookbinding (printed labels wrapped around cardboard) led to mass-produced board games with custom boards. Inexpensive (hollow) lead figurine casting contributed to the development of miniature wargaming. Cheap custom dice led to poker dice. Flying discs led to disc golf and Ultimate. Personal computers contributed to the popularity of computer games, leading to the wide availability of video game consoles and video games. Smart phones have led to a proliferation of mobile games.
The first games in a new medium are frequently adaptations of older games. Pong, one of the first widely disseminated video games, adapted table tennis. Later games will often exploit distinctive properties of a new medium. Adapting older games and creating original games for new media are both examples of game design.
Theory
Game studies or gaming theory is a discipline that deals with the critical study of games, game design, players, and their role in society and culture. Prior to the late-twentieth century, the academic study of games was rare and limited to fields such as history and anthropology. As the video game revolution took off in the early 1980s, so did academic interest in games, resulting in a field that draws on diverse methodologies and schools of thought. These influences may be characterized broadly in three ways: the social science approach, the humanities approach, and the industry and engineering approach.[1]
Broadly speaking, the social scientific approach has concerned itself with the question of "What do games do to people?" Using tools and methods such as surveys, controlled laboratory experiments, and ethnography researchers have investigated both the positive and negative impacts that playing games could have on people. More sociologically informed research has sought to move away from simplistic ideas of gaming as either 'negative' or 'positive', but rather seeking to understand its role and location in the complexities of everyday life.[2]
In general terms, the humanities approach has concerned itself with the question of "What meanings are made through games?" Using tools and methods such as interviews, ethnographies and participant observation, researchers have investigated the various roles that videogames play in people's lives and activities together with the meaning they assign to their experiences.[3]
From an industry perspective, a lot of game studies research can be seen as the academic response to the videogame industry's questions regarding the products it creates and sells. The main question this approach deals with can be summarized as "How can we create better games?" with the accompanying "What makes a game good?" "Good" can be taken to mean many different things, including providing an entertaining and an engaging experience, being easy to learn and play, and being innovative and having novel experiences. Different approaches to studying this problem have included looking at describing how to design games[4][5] and extracting guidelines and rules of thumb for making better games[6]
Strategic decision making
Game theory is a study of strategic decision making. Specifically, it is "the study of mathematical models of conflict and cooperation between intelligent rational decision-makers".[7] An alternative term suggested "as a more descriptive name for the discipline" is interactive decision theory.[8] The subject first addressed zero-sum games, such that one person's gains exactly equal net losses of the other participant or participants.[9] Today, however, game theory applies to a wide range of behavioral relations, and has developed into an umbrella term for the logical side of decision science.
The games studied in game theory are well-defined mathematical objects. To be fully defined, a game must specify the following elements: the players of the game, the information and actions available to each player at each decision point, and the payoffs for each outcome. (Rasmusen refers to these four "essential elements" by the acronym "PAPI".)[10] A game theorist typically uses these elements, along with a solution concept of their choosing, to deduce a set of equilibrium strategies for each player such that, when these strategies are employed, no player can profit by unilaterally deviating from their strategy. These equilibrium strategies determine an equilibrium to the game—a stable state in which either one outcome occurs or a set of outcomes occur with known probability.
Design elements
Games can be characterized by "what the player does."[11] This is often referred to as gameplay. Major key elements identified in this context are tools and rules that define the overall context of game.
Tools of play
Games are often classified by the components required to play them (e.g. miniatures, a ball, cards, a board and pieces, or a computer). In places where the use of leather is well established, the ball has been a popular game piece throughout recorded history, resulting in a worldwide popularity of ball games such as rugby, basketball, football, cricket, tennis, and volleyball. Other tools are more idiosyncratic to a certain region. Many countries in Europe, for instance, have unique standard decks of playing cards. Other games such as chess may be traced primarily through the development and evolution of its game pieces.
Many game tools are tokens, meant to represent other things. A token may be a pawn on a board, play money, or an intangible item such as a point scored.
Games such as hide-and-seek or tag do not utilise any obvious tool; rather, their interactivity is defined by the environment. Games with the same or similar rules may have different gameplay if the environment is altered. For example, hide-and-seek in a school building differs from the same game in a park; an auto race can be radically different depending on the track or street course, even with the same cars.
Rule development
Whereas games are often characterized by their tools, they are often defined by their rules. While rules are subject to variations and changes, enough change in the rules usually results in a "new" game. There are exceptions to this in that some games deliberately involve the changing of their own rules, but even then there are often immutable meta-rules.
Rules generally determine turn order, the rights and responsibilities of the players, and each player's goals. Player rights may include when they may spend resources or move tokens.
Victory conditions
Common win conditions are being first to amass a certain quota of points or tokens (as in Settlers of Catan), having the greatest number of tokens at the end of the game (as in Monopoly), or some relationship of one's game tokens to those of one's opponent (as in chess's checkmate).
Single or multiplayer
Most games require multiple players. However, single-player games are unique in respect to the type of challenges a player faces. Many games described as "single-player" may be termed actually puzzles or recreations. Unlike a game with multiple players competing with or against each other to reach the game's goal, a one-player game is a battle solely against an element of the environment (an artificial opponent), against one's own skills, against time, or against chance.
Storyline and plot
Stories told in games may focus on narrative elements that can be communicated through the use of mechanics and player choice. Narrative plots in games generally have a clearly defined and simplistic structure. Mechanical choices on the part of the designer(s) often drastically effect narrative elements in the game. However, due to a lack of unified and standardized teaching and understanding of narrative elements in games, individual interpretations, methods, and terminology vary wildly. Because of this, most narrative elements in games are created unconsciously and intuitively. However, as a general rule, game narratives increase in complexity and scale as player choice or game mechanics increase in complexity and scale. One example of this is removing a players ability to directly affect the plot for a limited time. This lack of player choice necessitates an increase in mechanical complexity, and could be used as a metaphor to symbolize depression that is felt by a character in the narrative.
Luck and strategy
A game's tools and rules will result in its requiring skill, strategy, luck, or a combination thereof, and are classified accordingly.
Games of skill include games of physical skill, such as wrestling, tug of war, hopscotch, target shooting, and stake, and games of mental skill such as checkers and chess. Games of strategy include checkers, chess, go, arimaa, and tic-tac-toe, and often require special equipment to play them. Games of chance include gambling games (blackjack, mah-jongg, roulette, etc.), as well as snakes and ladders and rock, paper, scissors; most require equipment such as cards or dice.
Most games contain two or all three of these elements. For example, American football and baseball involve both physical skill and strategy while tiddlywinks, poker, and Monopoly combine strategy and chance. Many card and board games combine all three; most trick-taking games involve mental skill, strategy, and an element of chance, as do many strategic board games such as Risk, Settlers of Catan, and Carcassonne.
Use as educational tool
By learning through play[lower-alpha 1] children can develop social and cognitive skills, mature emotionally, and gain the self-confidence required to engage in new experiences and environments.[12] Key ways that young children learn include playing, being with other people, being active, exploring and new experiences, talking to themselves, communication with others, meeting physical and mental challenges, being shown how to do new things, practicing and repeating skills and having fun.[13]
Play develops children's content knowledge and provides children the opportunity to develop social skills, competences and disposition to learn.[14] Play-based learning is based on a Vygotskian model of scaffolding where the teacher pays attention on specific elements of the play activity and provides encouragement and feedback on children's learning.[15] When children engage in real-life and imaginary activities, play can be challenging in children's thinking.[16] To extend the learning process, sensitive intervention can be provided with adult support when necessary during play-based learning.[15]
Development process
Development team
Game artist
A game artist is an artist who creates art for one or more types of games. Game artists are responsible for all of the aspects of game development that call for visual art.[17] Game artists are often noted in role-playing games, collectible card games and video games.[18]
Testing
Game testing, a subset of game development, is a software testing process for quality control of video games.[19][20][21] The primary function of game testing is the discovery and documentation of software defects (aka bugs). Interactive entertainment software testing is a highly technical field requiring computing expertise, analytic competence, critical evaluation skills, and endurance.[22][23] In recent years the field of game testing has come under fire for being excessively strenuous and unrewarding, both financially and emotionally.[24]
Strategies
Board games
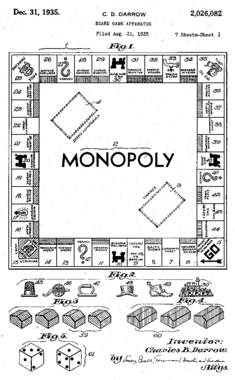
Board game design is the development of rules and presentational aspects of a board game. When a player takes part in a game, it is the player's self-subjection to the rules that creates a sense of purpose for the duration of the game.[25] Maintaining the players' interest throughout the gameplay experience is the goal of board game design.[26] To achieve this, board game designers emphasize different aspects such as social interaction, strategy, and competition, and target players of differing needs by providing for short versus long-play, and luck versus skill.[26] Beyond this, board game design reflects the culture in which the board game is produced.
The most ancient board games known today are over 5000 years old. They are frequently abstract in character and their design is primarily focused on a core set of simple rules. Of those that are still played today, games like go (c.400BC), mancala (c.700AD), and chess (c.600AD) have gone through many presentational and/or rule variations. In the case of chess, for example, new variants are developed constantly, to focus on certain aspects of the game, or just for variation's sake.
Traditional board games date from the nineteenth and early twentieth century. Whereas ancient board game design was primarily focused on rules alone, traditional board games were often influenced by Victorian mores. Academic (e.g. history and geography) and moral didacticism were important design features for traditional games, and Puritan associations between dice and the Devil meant that early American game designers eschewed their use in board games entirely.[27] Even traditional games that did use dice, like Monopoly (based on the 1906 The Landlord's Game), were rooted in educational efforts to explain political concepts to the masses. By the 1930s and 1940s, board game design began to emphasize amusement over education, and characters from comic strips, radio programmes, and (in the 1950s) television shows began to be featured in board game adaptations.[27]
Recent developments in modern board game design can be traced to the 1980s in Germany, and have led to increased popularity of "German-style board games" (also known as "Eurogames" or "designer games"). The design emphasis of these board games is to give players meaningful choices.[25] This is manifested by eliminating elements like randomness and luck to be replaced by skill, strategy, and resource competition, by removing the potential for players to fall irreversibly behind in the early stages of a game, and by reducing the number of rules and possible player options to produce what Alan R. Moon has described as "elegant game design".[25] The concept of elegant game design has been identified by The Boston Globe's Leon Neyfakh as related to Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi's concept of "flow" from his 1990 book, "Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience".[25]
Modern technological advances have had a democratizing effect on board game design, with services like Kickstarter providing designers with essential startup capital and tools like 3D printers facilitating the production of game pieces and board game prototypes.[28][29] A modern adaptation of figure games are miniature wargames like Warhammer 40,000.
Card games
The design of card games is constricted by the type of the deck of cards, like Tarot or the four-suited Latin decks. Card games can be played for fun, like Go Fish, or for profit like Poker.
In Asian cultures, special sets of tiles can serve the same function as cards, as in mahjong, a game similar to (and thought to be the distant ancestor of) the Western card game rummy. Western dominoes games are believed to have developed from Asian tile games in the 18th century.
Magic: The Gathering was the first collectible card game (or "trading card game") in 1993.
The line between card and board games is not clear-cut, as many card games, such as solitaire, involve playing cards to form a "tableau", a spatial layout or board. Many board games, in turn, uses specialized decks of cards as randomization devices, such as a sub-type of wargames called card-driven wargames.
Dice games

Dice games are among the oldest known games and have often been associated with gambling. The oldest known dice game is a backgammon set that was discovered by archaeologists excavating the site of the Burnt City, which was abandoned in 2100 BC.[30] Non-gambling dice games, such as Yatzy, Poker dice, or Yahtzee became popular in the mid-20th century.
The line between dice and board games is not clear-cut, as dice are often used as randomization devices in board games, such as Monopoly or Risk, while serving as the central drivers of play in games such as Backgammon or Pachisi.
Casino games

Casino game design can entail the creation of an entirely new casino game, the creation of a variation on an existing casino game, or the creation of a new side bet on an existing casino game.[32] Casino game mathematician, Michael Shackleford has noted that it is much more common for casino game designers today to make successful variations than entirely new casino games.[33] Gambling columnist John Grochowski points to the emergence of community-style slot machines in the mid-1990s, for example, as a successful variation on an existing casino game type.[34] Unlike the majority of other games which are designed primarily in the interest of the player, one of the central aims of casino game design is to optimise the house advantage and maximise revenue from gamblers. Successful casino game design works to provide entertainment for the player and revenue for the gambling house. To maximise player entertainment, casino games are designed with simple easy-to-learn rules that emphasize winning (i.e. whose rules enumerate many victory conditions and few loss conditions[33]), and that provide players with a variety of different gameplay postures (e.g. card hands).[32] Player entertainment value is also enhanced by providing gamblers with familiar gaming elements (e.g. dice and cards) in new casino games.[32][33] To maximise success for the gambling house, casino games are designed to be easy for croupiers to operate and for pit managers to oversee.[32][33] The two most fundamental rules of casino game design is that the games must be non-fraudable[32] (including being as nearly as possible immune from advantage gambling[33]), and that they must mathematically favor the house winning. Shackleford suggests that the optimum casino game design should give the house an edge of smaller than 5%.[33]
Role-playing games
The design of role-playing games requires the establishment of setting, characters, and basic gameplay rules or mechanics. After a role-playing game is produced, additional design elements are often devised by the players themselves. In many instances, for example, character creation is left to the players. Likewise, the progression of a role-playing game is determined in large part by the gamemaster whose individual campaign design may be directed by one of several role-playing game theories.
There is no central core for tabletop role-playing game theory because different people want such different things out of the games. Probably the most famous category of RPG theory, GNS Theory assumes that people want one of three things out of the game – a better, more interestingly challenging game, to create a more interesting story, or a better simulation – in other words better rules to support worldbuilding. GNS Theory has been abandoned by its creator, partly because it neglects emotional investment, and partly because it just didn't work properly. There are techniques that people use (such as dice pools) to better create the game they want – but with no consistent goal or agreement for what makes for a good game there's no overarching theory generally agreed on.
Sports
Sports games are made with the same rules as the sport the game portrays.[35][36][37]
Video games
Video game design is a process that takes place in the pre-production phase of video game development. In the video game industry, game design describes the creation of the content and rules of a video game.[38] The goal of this process for the game designer is to provide players with the opportunity to make meaningful decisions in relation to playing the game.[38] Elements of video game design such as the establishment of fundamental gameplay rules provide a framework within which players will operate, while the addition of narrative structures provide players with a reason to care about playing the game.[39] To establish the rules and narrative, an internally consistent game world is created, requiring visual, audio, and programming development for world, character, and level design. The amount of work that is required to accomplish this often demands the use of a design team which may be divided into smaller game design disciplines.[40] In order to maintain internal consistency between the teams, a specialized software design document known as a "game design document" (and sometimes an even broader scope "game bible" document) provides overall contextual guidance on ambient mood, appropriate tone, and other less tangible aspects of the game world.[41]
An important aspect of video game design is human-computer interaction[42] and game feel.
War games
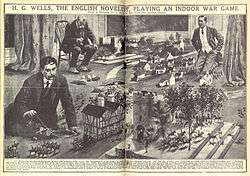
The first military war games, or Kriegsspiel, were designed in Prussia in the 19th century to train staff officers.[43] They are also played as a hobby for entertainment.
Modern war games are designed to test doctrines, strategies and tactics in full scale exercises with opposing forces at venues like the NTC, JRTC and the JMRC, involving NATO countries.
See also
Notes
- ↑ a term used in education and psychology to describe how a child can learn to make sense of the world around them
References
- ↑ Konzack, Lars (2007). "Rhetorics of Computer and Video Game Research" in Williams & Smith (ed.) The Players' Realm: Studies on the Culture of Video Games and gaming. McFarland.
- ↑ Crawford, G. (2012). Video Gamers. London: Routledge.
- ↑ Consalvo, 2007
- ↑ Griffiths, M. (1999). "Violent video games and aggression: A review of the literature" (PDF). Aggression and violent behavior. 4 (2): 203–212. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 November 2013.
- ↑ Rollings and Morris, 2000; Rouse III, 2001
- ↑ Fabricatore et al., 2002; Falstein, 2004
- ↑ Roger B. Myerson (1991). Game Theory: Analysis of Conflict, Harvard University Press, p. 1. Chapter-preview links, pp. vii–xi.
- ↑ R. J. Aumann ([1987] 2008). "game theory," Introduction, The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd Edition. Abstract.
- ↑ Leonard, Robert (2010), Von Neumann, Morgenstern, and the Creation of Game Theory, New York: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 9780521562669
- ↑ • Eric Rasmusen (2007). Games and Information, 4th ed. Description and chapter-preview.
• David M. Kreps (1990). Game Theory and Economic Modelling. Description.
• R. Aumann and S. Hart, ed. (1992, 2002). Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications v. 1, ch. 3–6 and v. 3, ch. 43. - ↑ Crawford, Chris (2003). Chris Crawford on Game Design. New Riders. ISBN 0-88134-117-7.
- ↑ Human growth and the development of personality, Jack Kahn, Susan Elinor Wright, Pergamon Press, ISBN 978-1-59486-068-3
- ↑ Learning, playing and interacting. Good practice in early years foundation stage. Page 9
- ↑ Wood, E. and J. Attfield. (2005). Play, learning and the early childhood curriculum. 2nd ed. London: Paul Chapman
- 1 2 Martlew, J., Stephen, C. & Ellis, J. (2011). Play in the primary school classroom? The experience of teachers supporting children's learning through a new pedagogy. Early Years, 31(1), 71–83.
- ↑ Whitebread, D., Coltman, P., Jameson, H. & Lander, R. (2009). Play, cognition and self regulation: What exactly are children learning when they learn through play? Educational & Child Psychology, 26(2), 40–52.
- ↑ Gamespot UK – So You Want To Be An: Artist – Accessed 17 November 2012.
- ↑ Exhibitions: The Art of Video Games – Accessed 17 November 2012.
- ↑ Bates 2004, pp. 176–180
- ↑ Moore, Novak 2010, p. 95
- ↑ Oxland 2004, p. 301-302
- ↑ Bates 2004, pp. 178, 180
- ↑ Oxland 2004, p. 301
- ↑ "The Tough Life of a Games Tester" from IGN
- 1 2 3 4 5 Neyfakh, Leon. "Quest for fun; Sometimes the most addictive new technology comes in a simple cardboard box". Boston Globe. 11 March 2012
- 1 2 3 Wadley, Carma. "Rules of the game: Do you have what it takes to invent the next 'Monopoly'?" Deseret News. 18 November 2008.
- 1 2 Johnson, Bruce E. "Board games: affordable and abundant, boxed amusements from the 1930s and '40s recall the cultural climate of an era." Country Living. 1 December 1997.
- ↑ Whigfield, Nick. "Video Hasn't Killed Interest in Board Games ; New Technologies Have Contributed to Revival of Tabletop Entertainment". The Irish Times. 12 May 2014.
- ↑ Hesse, Monica. "Rolling the dice on a jolly good pastime". The Washington Post. 29 August 2011.
- ↑ "PressTV – Burnt City, key to lost civilization". PressTV. Retrieved 5 March 2015.
- ↑ Shackleford, Michael. "House Edge of casino games compared". Wizardofodds.com. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lubin, Dan. "Casino Game Design: From Cocktail Napkin Sketch to Casino Floor". Available: . Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Shackleford, Michael. "Ten Commandments for Game Inventors". Wizardofodds.com. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- ↑ Grochowski, John. "Gaming Guru: Tracing Back the Roots of Some Popular Gaming Machines at Casinos". The Press of Atlantic City. 28 August 2013.
- ↑ "The Designer's Notebook: Designing and Developing Sports Games". Gamasutra. Retrieved on 15 December 2014.
- ↑ "Game Design: Sports Games". stevevincent.info. Retrieved on 14 December 2014
- ↑ "Fundamentals of Sports Game Design" (PDF). Retrieved on 15 December 2014.
- 1 2 Brathwaite, Brenda; Schreiber, Ian (2009). Challenges for Game Designers. Charles River Media. pp. 2–5. ISBN 158450580X.
- ↑ Lecky-Thompson, Guy W. (2008). Video Game Design Revealed. Cengage Learning. pp. 43–45. ISBN 1584506075.
- ↑ Dille, Flint; Platten, John Zuur (2007). The Ultimate Guide to Video Game Writing and Design. Lone Eagle. pp. 137–149. ISBN 158065066X.
- ↑ Rogers, Scott (2010). Level Up!: The Guide to Great Video Game Design. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 57–81. ISBN 0470970928.
- ↑ Barr, Pippin. "Video Game Values – Play as Human-Computer Interaction" (PDF). Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Lischka, Konrad (22 June 2009). "Wie preußische Militärs den Rollenspiel-Ahnen erfanden". Der Spiegel (in German). Retrieved 15 February 2010.
Further reading
- Baur, Wolfgang. Complete Kobold Guide to Game Design. Open Design LLC 2012. ISBN 978-1936781065
- Burgun, Keith. Game Design Theory: A New Philosophy for Understanding Games. Publisher: A K Peters/CRC Press 2012. ISBN 978-1466554207
- Costikyan, Greg. Uncertainty in Games. MIT Press 2013. ISBN 978-0262018968
- Elias, George Skaff. Characteristics of Games. MIT Press 2012. ISBN 978-0262017138
- Hofer, Margaret. The Games We Played: The Golden Age of Board & Table Games. Princeton Architectural Press 2003. ISBN 978-1568983974
- Huizinga, Johan. Homo Ludens: A Study of the Play-Element in Culture. Beacon Press 1971. ISBN 978-0807046814
- Kankaanranta, Marja Helena. Design and Use of Serious Games (Intelligent Systems, Control and Automation: Science and Engineering). Springer 2009. ISBN 978-9048181414.
- Norman, Donald A. The Design of Everyday Things. Basic Books 2002. ISBN 978-0465067107.
- Peek, Steven. The Game Inventor's Handbook. Betterway Books 1993. ISBN 978-1558703155
- Peterson, Jon. Playing at the World. Unreason Press 2012. ISBN 978-0615642048.
- Schell, Jesse. The Art of Game Design: A book of lenses. CRC Press 2008. ISBN 978-0123694966
- Salen Tekinbad, Katie. Rules of Play: Game Design Fundamentals. The MIT Press 2003. ISBN 978-0262240451.
- Tinsman, Brian. The Game Inventor's Guidebook: How to Invent and Sell Board Games, Card Games, Role-Playing Games, & Everything in Between! Morgan James Publishing 2008. ISBN 978-1600374470
- Woods, Stewart. Eurogames: The Design, Culture and Play of Modern European Board Games. McFarland 2012. 978-0786467976
- Bates, Bob (2004). Game Design (2nd ed.). Thomson Course Technology. ISBN 1-59200-493-8.
- Moore, Michael E.; Novak, Jeannie (2010). Game Industry Career Guide. Delmar: Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-4283-7647-2.
- Oxland, Kevin (2004). Gameplay and design. Addison Wesley. ISBN 0-321-20467-0.