Ferbam
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tris(dimethyldithiocarbamato)iron | |
| Other names
Ferric dimethyl dithiocarbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 14484-64-1 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.970 |
| RTECS number | NO8750000 |
| Properties | |
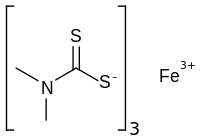
| [(CH3)2NCS2]3Fe | |
| Molar mass | 416.5 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark brown to black, odorless solid[1] |
| Melting point | Decomposes above 356°F[1] |
| Boiling point | Decomposes[1] |
| 0.01% (20°C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Reacts with strong oxidizers, moisture[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
3000 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 2000 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 1130 mg/kg (rat, oral) 3400 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[2] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 15 mg/m3[1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 mg/m3[1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
800 mg/m3[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ferbam is a fungicide.
Safety
People can be exposed to ferbam in the workplace by breathing it in, skin absorption, swallowing it, and eye contact. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit (permissible exposure limit) for ferbam exposure in the workplace as 15 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 1 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday. At levels of 800 mg/m3, ferbam is immediately dangerous to life and health.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0286". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Ferbam". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/28/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.