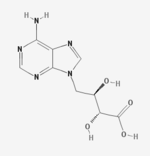
Eritadenine
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 140628 |
| PubChem | 159961 |
| |
| |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Eritadenine is an isolate of Shiitake. Eritadenine is an inhibitor of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase (SAHH) and has hypocholesterolemic activity.
Synthesis
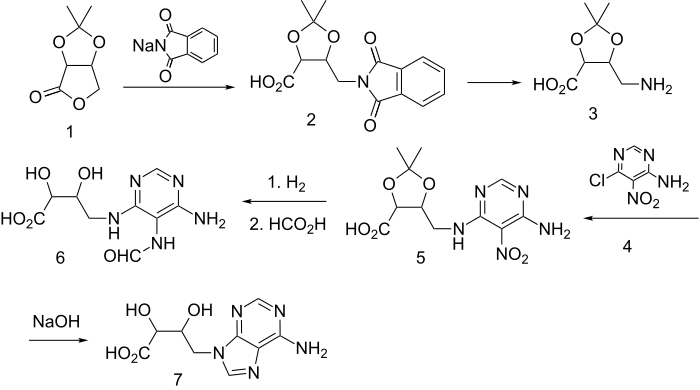
The structure is a purine alkylated with an oxidized sugar fragment.
Ring opening of the protected lactone (1), derived from erythrose with sodium phthalimide gives the acid 2; hydrazinolysis (cf Gabriel synthesis) then leads to the amino acid 3. Displacement of chlorine in pyrimidine 4 by the amine function on 3 serves to attach the future imidazole nitrogen and the sugar-derived sidechain (5). The nitro group is then reduced by catalytic hydrogenation, the resulting primary amine is the most basic and is selectively formylated with formic acid. These strongly acidic conditions serve to remove the acetonide protecting group as well (6). Treatment with NaOH then serves to close the imidazole ring, forming eritadenine (7)
References
- ↑ Kamiya, T.; Saito, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Seki, H. (1969). "Structure and synthesis of lentysine, a new hypocholesterolemic substance". Tetrahedron Letters. 10 (53): 4729. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)88795-5.
- ↑ Kamiya, T.; Saito, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Seki, H. (1972). "Hypocholesterolemic alkaloids of lentinus edodes (berk.) sing. II. A novel synthesis of eritadenine". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 9 (2): 359. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570090230.