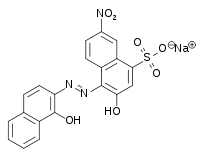
Eriochrome Black T
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Sodium 1-[1-Hydroxynaphthylazo]-6-nitro-2-naphthol-4-sulfonate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Sodium 4-[2-(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)hydrazin-1-ylidene]-7-nitro-3-oxo-3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1-sulfonate | |
| Other names
Sodium 4-[2-(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)hydrazin-1-ylidene]-7-nitro-3-oxonaphthalene-1-sulfonate; Solochrome Black T; ET-00 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1787-61-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | EBT |
| 4121162 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.683 |
| EC Number | 217-250-3 |
| MeSH | Eriochrome+black+T |
| PubChem | 6808871 5359641 (4E) 5351620 |
| RTECS number | QK2197000 |
| UN number | 2923 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H12N3O7SNa | |
| Molar mass | 461.381 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark red/brown powder |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.2, 11.55 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Eriochrome Black T is a complexometric indicator that is used in complexometric titrations, e.g. in the water hardness determination process. It is an azo dye. Eriochrome is a trademark of Huntsman Petrochemical, LLC.[1]
In its protonated form, Eriochrome Black T is blue. It turns red when it forms a complex with calcium, magnesium, or other metal ions.

EBT is blue in a buffered solution at pH 10. It turns red when Ca2+ ions are added.
Applications
When used as an indicator in an EDTA titration, the characteristic blue end-point is reached when sufficient EDTA is added and the metal ions bound to the indicator are chelated by EDTA, leaving the free indicator molecule.
Eriochrome Black T has also been used to detect the presence of rare earth metals.[2]
References
- ↑ http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/858390?lang=en®ion=US
- ↑ Dubenskaya, L. O.; Levitskaya, G. D. (1999). "Use of eriochrome black T for the polarographic determination of rare-earth metals". Journal of Analytical Chemistry. 54 (7): 655–657. ISSN 1061-9348.
External links
- J.T. Baker MSDS
- Describes a procedure for determining the hardness of water using EDTA with Eriochrome indicator
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.