Echos
Echos (Greek: ἦχος [ˈixos] "sound"; pl. echoi ἦχοι [ˈiçi], Old Church Slavonic: гласъ [glasŭ] "voice, sound") is the name in Byzantine music theory for a mode within the eight mode system (oktoechos), each of them ruling several melody types, and it is used in the melodic and rhythmic composition of Byzantine chant ("thesis of the melos"), differentiated according to the chant genre and according to the performance style ("method of the thesis"). It is akin to a Western medieval tonus, an Andalusian tab', an Arab naġam (since 1400 "maqam"), or a Persian parde (since 18th century dastgah).
Overview and semantics
The noun echos in Greek means "sound" in general. It acquired the specialized meaning of mode early on in the development of Byzantine music theory since the Octoechos reform in 692.
In general, the concept of echos denotes a certain octave species, its intervallic structure as well as a set of more or less explicitly formulated melodic rules and formulae that represent a certain category of melodies within the musical genre. As such, echos is the basis for composing or improvising new melodies that belong to it, as well as for properly performing existing pieces that have been written in it. These rules include the distinction of a hierarchy of degrees (tones, notes), where certain degrees figure as cadence notes (ἑστώτες) around which the melody will revolve prominently, or on which the melody will end most of the time. However, only very late stages of the theory (19th-20th century) actually provide systematic descriptions of echoi, while earlier stages use mostly diagrams, indirect descriptions and examples. Explicit detailed descriptions must still be provided based on extensive analysis, as is the case with modal phenomena in numerous other cultures.
History and reconstruction
Early treatises only state the initial or "base" degree (η βασή) which is the tone sung as a burden (ἴσον) by certain singers of the choir called "isokrates" in order to support any melody composed in a certain echos. By this support singers (psaltes) could easily recognise the relative position of each note as it was organised by tetrachords based on the basis note of each echos. This base degree of the mode was communicated by an intonation formula of a foresinger, known as enechema.

There are different forms to notate enechema which are crucial to understand the different chant books and their notation. All these forms were written in red ink. The explicit long form was called by Jørgen Raasted intonation,[1] but only the books of the cathedral rite used such explicit intonations, also between the sections, where these intonations were called medial intonation. This explicit form made sense, since the intonation also communicated the changes between the left and the right choir and their leaders performed these intonations to coordinate these changes. There was a short form as well which was called modal signature. It indicated the echos by the numeral like πλα' for "plagios protos," while the neumes sung with the last syllable of the enechema were written above right to the numeral. This short form was used in two different ways, as main signature it indicated the echos of a whole composition, but especially in sticheraria notators also wrote medial signatures between the neumes above a kolon of the text, in order to indicate that the melos changed here into another echos. The traditional Greek term for these medial signatures was "martyria" (μαρτυρία), since the medial signature also "testified" the phthongos of the cadence made at the kolon.
Echemata of the dialogue treatise
Within the dialogue treatise (erotapokriseis) a catalogue of short formulas memorizes each echos of the Hagiopolitan octoechos and its two phthorai (νενανῶ and νανὰ). These formulas are also called "echemata" (ἠχήματα)—or more often "enechemata" (ἐνηχήματα) or "apechemata" (ἀπηχήματα). The use echemata was also imitated by Carolingian cantors who used similar intonation formulas and collected them in a separate book called tonary.
Περὶ πλαγίωνἈπο τοῦ πλαγίου πρώτου ἤχου πάλιν καταβαίνεις τέσσαρας φωνάς, καὶ εὑρίσκεται πάλιν πλάγιος πρώτου· ὅυτως δὲ / ἄνανε ἄνες ἀνὲ ἄνες·
Ὁμοίως καὶ ὁ β' ἤχος καταβαίνων φωνάς δ', εὑρίσκεις τὸν πλάγιον αὐτοῦ, ἤγουν τὸν πλάγιον τοῦ δευτέρου. πλ Β οὕτως δέ.
Ὁμοίως πάλιν ὁ τρίτος καταβαίνεις φωνὰς τέσσαρας, καὶ εὑρίσκεται ὁ πλάγιος αὐτοῦ, ἤγουν ὁ βαρύς, οὕτως·
Ὁμοίως καὶ ἀπὸ τὸν τέταρτον καταβαίνων φωνὰς τέσσαρας, εὑρίσκεις τὸν πλάγιον αὐτοῦ, ὡς ἐστὶ ὁ πλ δ'οὕτως·[2]
The enechemata of the medieval eight diatonic echoi already present a fundamental difference to the Carolingian octoechos:
- the kyrios and plagios do use the same octave species, but their basis tone with the ison is on the top of the pentachord within the mele of kyrioi echoi, while it is on the bottom within the mele of plagioi echoi;
- the octave species (D—a—d, E—b—e, B flat—F—b flat, and C—G—c) are different as well from the Western octoechos as from the New Method, which had adapted the fret scheme of the tambur keyboard as the common tonal reference for all Ottoman musicians. Traditional protopsaltes at Athos and Istanbul who belong to local schools of the eighteenth century, do indeed not follow the Chrysanthine intonation, they always intone a pentachord on a pure fifth between the bases of echos varys and kyrios tritos.
- there is no absolute or fixed position of the octave species. Sticheraric and papadic chant genres exploit not only the possibility to change between the echoi, but also the characteristic that every note (phthongos "sound, voice") has an echos defined by the octoechos. A register change is usually arranged by a transposition about a fifth, which turns a kyrios into a plagios and vice versa. Also other temporary transpositions are possible (see the five rings of the bigger Koukouzelian wheel), but not frequent.
- the ruling tone system is tetraphonic and based on fifth equivalence which allows the fore mentioned register changes. Heptaphonia (similar to the Western use of systema teleion and solfège with seven syllables) exist only on the level of a melos within a certain echos. Changes to the triphonic system are indicated by the phthora nana.
- except of a pure diatonic octoechos the chromatic and enharmonic genus is not excluded, since even the Hagiopolitan octoechos accepted the use of two phthorai (νενανὼ and νανὰ).

Echemata of the Papadikai and their modern interpretation
More information on the structure of echoi is only indicated in a very rudimentary way through diagrams involving neumes—the Byzantine round notation. The details of the actual intervallic and melodic structure of echoi are virtually impossible to deduce from theoretical treatises prior to the 18th century. In fact, only relatively late systematic comparisons of the echoi with the makamlar of Ottoman court music, such as those by the Kyrillos Marmarinos, Archbishop of Tinos, in his manuscript dated 1747, and the reform of the Byzantine notation by Chrysanthos of Madytos at the first half of the 19th century make it possible to understand the structure of echoi and to attempt reconstructions of melodies from earlier manuscripts.

He already introduced his readers into the diatonic genus and its phthongoi in the 5th chapter of the first book, called "About the parallage of the diatonic genus" (Περὶ Παραλλαγῆς τοῦ Διατονικοῦ Γένους). In the 8th chapter he demonstrates, how the intervals can be found on the keyboard of the tambur.[3]
Hence, the phthongoi of the diatonic genus had been defined according to the proportions, as they were later called the "soft chroa of the diatonic genus" (τὸ γένος μαλακὸν διατονικὸν). For Chrysanthos this was the only diatonic genus, as far as it had been used since the early church musicians, who memorised the phthongoi by the intonation formulas (enechemata) of the Papadic Octoechos. In fact, he did not use the historical intonations, he rather translated them in the Koukouzelian wheel in the 9th chapter (Περὶ τοῦ Τροχοῦ) according to a current practice of parallage, which was common to 18th-century versions of Papadike:
Τὸ δὲ Πεντάχορδον, τὸ ὁποῖον λέγεται καὶ Τροχὸς, περιέχει διαστήματα τέσσαρα, τὰ ὁποῖα καθ᾽ ἡμᾶς μὲν εἶναι τόνοι. Περιορίζονται δὲ τὰ τέσσαρα διαστήματα ταῦτα ἀπὸ φθόγγους πέντε.
- πα βου γα δι Πα[4]
The pentachord which was also called wheel (τροχὸς), contains four intervals which we regard as certain tones [ἐλάσσων τόνος, ἐλάχιστος τόνος, and 2 μείζονες τόνοι]. The four intervals spanned five phthongoi:
πα βου γα δι Πα ["Πα" means here the fifth-equivalent for the protos: α']
These five stations of the pentachord could be memorised by the echemata of the kyrioi echoi in ascending direction or by those of the plagioi echoi in descending direction (see Chrysanthos' explanation of the trochos parallage). Each of these echemata had the potential to develop an own melos within its melody types:

Each echema is followed by the incipit of a sticheron ideomelon which illustrates a certain melos of the echos. The following book Kekragarion illustrates, how the hesperinos psalm κύριε ἐκέκραξα has to be sung according to the sticheraric melos of each echos. The Kekragarion was later included in the printed editions of the Anastasimatarion or Voskresnik.
Chrysanthos' exegesis of the papadic enechemata
In the chapter "On the apechemata" (Περὶ Ἀπηχημάτων) of his "Great Theoretikon",[5] Chrysanthos translated the Byzantine octoechos and its intonation formulas (apechemata, or enechemata), as they could be found in the Papadikai, by offering an exegesis of the papadic apechemata in comparison to the simpler forms used by Orthodox chanters today. They served as kind of model for the composition within a certain melos, similar to the seyirler of an Ottoman makam.
Protos echoi
For the diatonic echos protos, the medieval enechema had the finalis on the top of the protos pentachord, while the enechema passes through it:
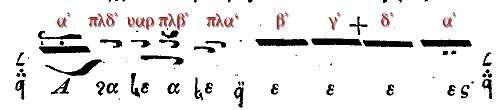
Chrysanthos made this exegesis to explain the melos of the whole echos:

In the first descending half he made the usual cadence on D (πα, phthongos πλα') which corresponds to the finalis of the modern melos, while it was once the finalis and the basis of the plagios protos. The second half, when the melos raises again, but within the papadic melos (used with a cherubikon or koinonikon) it prepared a change to another base tone on the upper tetrachord like a (κε, phthongos α').[6]
Hence, according to the current practice of Orthodox chant the protos mele were rather based on the lower tetrachord, but the formula could be used a fifth higher likewise. The step between the phthongoi of tetartos (δ') and protos (α') could be C—D (νη—πα) or G—a (δι—κε).

Concerning the enechema of the plagios protos, it had not changed during the centuries.

Unlike the tradition which always used register changes, the modern interpretation did not fix the base degree of echos plagios protos to the bottom of the pentachord, it could appear regularly at the top like in the troparic and heirmologic melos: a (κε)—c (νη')—b (ζω')—a (κε) or D (πα)—F (γα)—E (βου)—D (πα).[7]
Chrysanthos' exegesis just passed the protos pentachord D (πα)—a (κε) in an ascending movement, before using the cadence pattern to the base degree of the mode.

Devteros echoi
Chrysanthos' bridges between the diatonic echos devteros of the Byzantine past and the chromatic melos of the present Orthodox traditions. The latter is characterised by the constant use of the mesos form, which is not on the phthongoi of devteros—b natural (ζω', phthongos β') and E (βου, phthongos πλβ'), but between them on G (βου, phthongos πλδ').
The usual diatonic kyrios form was this enechema, but only the descending part would lead to the base tone of the mesos devteros.

As a consequence, Chrysanthos' exegesis starts and ends on this mesos, but it follows the Hagiopolitan convention to pass through the former devteros pentachord, but he even passes through the tetartos pentachord C (νη, phthongos πλδ')—G (δι, phthongos δ'), as it used by the current melos of echos devteros.

Concerning the chromatic melos of the devteros echoi in the current octoechos, the papadic devteros mele had become "soft chromatic" under the influence of the phthora nenano.

Nevertheless, according to the very particular interpretation of Chrysanthos the melos and scale of echos devteros is ruled by a diphonic organisation based on just two diatonic intervals: the major and minor tone. As a result, the octave C—c between νη and νη' becomes slightly diminished. Chrysanthos' concept of diphonia was so radical that it found no commonplace in current chant manuals, instead a lot alternative interpretations proposed various divisions of the chromatic tetrachords between νη—γα (C—F) and δι—νη' (G—c).

At the end of his chapter "on the apechemata" Chrysanthos offers a separate exegesis of phthora nenano as a modern deduction of the plagios devteros enechema, whose medieval form was this. But it had moved now with the phthora nenano to the phthongos of plagios protos.[8]

Tritos echoi
Chrysanthos did not offer any exegesis for the apechema of the diatonic echos tritos. He only mentions the intonation of phthora nana instead, which is still used as the echos tritos intonation formula in current Orthodox traditions.

Hence, his exegesis of this enharmonic phthora is within the enharmonic genus and the triphonic tone system of the phthora nana.[9]
The same enharmonic interpretation was done with the plagios called "echos varys" (grave mode), obviously in certain cases, when the plagios tetartos was expected of fourth under the base tone. Hence, the enharmonic tritos echoi are not separated by a pentachord, but usually both set on F (γα, phthongos γ' as well as υαρ), in troparic, sticheraric and heirmologic mele:


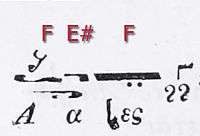
Within the papadic chant genre (cherubika, koinonika), but also during the composed recitation of Polyeleos psalms and kalophonic heirmoi (Ἄξιον ἐστίν), the diatonic melos of echos varys was chosen. Its base tone was one phthongos below the plagios tetartos. According to Chrysanthos it diminished the tritos pentachord to a kind of tritone, at least when it was set on fret arak of the Ottoman tambur, but there are also more traditional ways of intonation depending on the local school of a chanter.[10]

Tetartos echoi
The tetartos echoi have changed between the Byzantine and the Orthodox octoechos today.
The original tetartos pentachord between plagios and kyrios—C (νη) and G (δι) or likewise G (δι) and d (πα')—does still exist in the papadic melos of echos tetartos, which is known as the "papadic Agia" (Ἅγια παπαδικῆς).[11]

Chrysanthos made for the papadic melos this exegesis.

A commonly used form of Ἅγια παπαδικῆς might be the one which Chyrsanthos mentions as the one used by Petros Peloponnesios.

The diatonic plagios of tetartos according to the enechema known from the treatises called Papadikai[12]

which was interpreted by Chrysanthos, as follows.

Since the plagios devteros has moved to the phthongos of plagios protos (πλα'), the original phthongos of the diatonic plagios devteros was vacant. In fact, as a diatonic phthora it was represented by a medial signature of the so-called "echos legetos" (ἦχος λέγετος) which had preserved the diatonic intonation of plagios devteros.[13]

The signature was used within the heirmologion kalophonikon, since heirmoi of devteros echoi were still treated as a diatonic melos unlike the school of Petros Peloponnesios and his follower Petros Byzantios. According to their school the echos legetos was part of the tetartos echoi, as a mesos tetartos it was used for the heirmologic melos, where the base and final degree was a low intoned E (βου), and for the sticheraric melos, which had the base degree of the mode and closing cadences on D (πα), but the concluding finalis E (βου).
Chrysanthos interpreted also echos legetos as a diatonic mesos tetartos.

He also mentioned a common enechema as it was used by Iakovos the Protopsaltes.

In this last paragraph of the chapter about the apechemata Chrysanthos referred to ten echoi within the tradition of Hagiopolites.
Ἦχοι μὲν εἶναι ὀκτὼ τῆς ψαλμῳδίας· ἀπηχήματα δὲ σῴζονται δέκα. Διότι ὁ Τέταρτος ἦχος, καὶ ὁ Πλάγιος τοῦ δευτέρου, ἔχουσιν ἀνὰ δύο ἀπηχήματα.[14]
The echoi of the psalmody are eight. The apechemata preserved though are ten, because the echos tetartos, and the plagios of the devteros, have two apechemata each.
But unlike the Hagiopolites, where the phthora nana was mentioned as a "mesos tetartos" and the nenano phthora as "mesos devteros", echos legetos seemed to have slipped into the mesos tetartos role, but it was a diatonic mesos, not an enharmonic like phthora nana. In fact, Chrysanthos could not longer mention nana and nenano as additional echoi, since their melos had already replaced the diatonic mele of the devteros and tritos echoi.
Echos vs. maqam in eponymous compositional practice
In other Ottoman music traditions like the list of composed Mevlevi dance suites as models of well-known and new makamlar created by eponymous masters resulted in a proliferation of modes (makamlar, maqamat),[15] echoi are not attributed to specific composers, but are rather regarded as belonging to the collective and anonymous heritage of liturgical chant. Eponymous compositions do exist throughout most of the history of Byzantine chant, but their echos is always classified from within the system of existing echoi. Due to an interest for makamlar compositions Phanariotes like Georgios the Protopsaltes, one of the great teachers of Orthodox chant, also became a student of the dervish composer Dede Efendi, after he had learnt Turkish. Byzantine notation developed as a universal notation system during the 19th century which includes even attempts to integrate makamlar within the mele of the Octoechos, while ornamental details became part of an oral tradition.[16]
Cultural "relations"
The system of echoi is rich and diverse. Closer study and comparison with modal systems of neighboring cultures reveals a complex network of cultural and ethnic influences throughout the centuries—a vivid exchange between musicians across the borders of ethnic and religious identity (Phanariotes).[17] The basic theory of echoi is formalized in a system of eight modes called the Octoechos. See the article Neobyzantine Octoechos for a discussion of its origins and a critique of this concept vis-a-vis actual practice.
See also
- Mode
- Centonization
- Ottoman makam, Arab maqām, and Central Asian Shashmaqam
- Persian dastgah
Sources
- ↑ Jørgen Raasted (1966).
- ↑ Christian Hannick & Gerda Wolfram (1997, pp. 84f) quoted according to Mount Athos, S. Dionysios Monastery, Ms. 570, fol. 26-26'.
- ↑ Chrysanthos' chapter "About the diapason system" (Μερ. Α', Βιβ. α', κεφ. η' Περὶ τοῦ Διαπασῶν συστήματος, p. 28) introduced into the chord lengths and recognised in a schematic representation of the tetrachord (12+9+7=28).
- ↑ Chrysanthos (1832, Μερ. Α', Βιβ. α', κεφ. θ' Περὶ τοῦ Τροχοῦ, 28—§66).
- ↑ Chrysanthos of Madytos (1832, 135-42—§§307–317).
- ↑ As an example listen to the papadic protos melos at the beginning of Petros Bereketis' kalophonic composition about Θεοτόκε παρθένε (Demosthenis Païkopoulos). After three minutes the base tone changes to the higher tetrachord.
- ↑ In the papadic melos of echos plagios protos it is rather in the lower register, but this melos is nearly the same with respect to the one of kyrios protos. Listen to the fifth section of Bereketis' Θεοτόκε παρθένε, where Demosthenis Païkopoulos uses a free monosyllabic enechema which seems closer to the kyrios formula. The difference is a stronger emphasise of the mesos or diphonos F (γα) which sometimes attracts G (δι), especially among Phanariotes (17'50").
- ↑ For the proper intonation of the enharmonic diesis which is augmented in descending direction, listen to Demosthenis Païkopoulos' interpretation of the echos plagios devteros section in Petros Bereketis' didactic chant (mathema) (24'02").
- ↑ Listen the tritos section of Bereketis' kalophonic composition (9'15").
- ↑ The Chrysanthine intonation is commonly used in all Orthodox monodic traditions of the Balkans, but there are traditionalists at Istanbul and Athos who prefer another diatonic varys intonation according to the trochos system (Gerlach 2006, 889-890). Demosthenis Païkopoulos for example uses the trochos intonation of the Patriarchal school, when he sings the varys section of Petros Bereketis' kalophonic composition about Θεοτόκε παρθένε (29'16").
- ↑ Listen to the section echos tetartos in Petros' kalophonic theotokion which he composed in this melos (12'58").
- ↑ Hence, it also still in use within the papadic melos of the current echos plagios tetartos, listen to the eighth section of Petros' kalophonic composition passing through all the eight echoi (34'51").
- ↑ It was used by Petros Bereketis in the echos devteros section of his composition (4'58"), although as the kyrios devteros.
- ↑ Chrysanthos of Madytos (1832, 141—§317).
- ↑ About an exact situation of makamlar as a melodic model between improvisation and composition, see Habib Hassan Touma (1971).
- ↑ For a rather systematic approach, see the treatises by Keïvelis (1856) and Keltzanides (1881).
- ↑ Rudolf M. Brandl (1989).
Papadikai
- Hannick, Christian; Wolfram, Gerda, eds. (1997), Die Erotapokriseis des Pseudo-Johannes Damaskenos zum Kirchengesang, Monumenta Musicae Byzantinae - Corpus Scriptorum de Re Musica, 5, Vienna: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, ISBN 3-7001-2520-8.
- Conomos, Dimitri, ed. (1985), The Treatise of Manuel Chrysaphes, the Lampadarios: [Περὶ τῶν ἐνθεωρουμένων τῇ ψαλτικῇ τέχνῃ καὶ ὧν φρουνοῦσι κακῶς τινες περὶ αὐτῶν] On the Theory of the Art of Chanting and on Certain Erroneous Views that some hold about it (Mount Athos, Iviron Monastery MS 1120, July 1458), Monumenta Musicae Byzantinae - Corpus Scriptorum de Re Musica, 2, Vienna: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, ISBN 978-3-7001-0732-3.
- Hannick, Christian; Wolfram, Gerda, eds. (1985), Gabriel Hieromonachus: [Περὶ τῶν ἐν τῇ ψαλτικῇ σημαδίων καὶ τῆς τούτων ἐτυμολογίας] Abhandlung über den Kirchengesang, Monumenta Musicae Byzantinae - Corpus Scriptorum de Re Musica, 1, Vienna: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, ISBN 3-7001-0729-3.
- Panagiotes the New Chrysaphes. "London, British Library, Harley Ms. 5544". Papadike and the Anastasimatarion of Chrysaphes the New, and an incomplete Anthology for the Divine Liturgies (17th century). British Library. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
Treatises of the New Method (since 19th century)
- Chrysanthos of Madytos (1832). Pelopides, Panagiotes G., ed. Θεωρητικόν μέγα της μουσικής συνταχθέν μεν παρά Χρυσάνθου αρχιεπισκόπου Διρραχίου του εκ Μαδύτων εκδοθέν δε υπό Παναγιώτου Γ. Πελοπίδου Πελοποννησίου διά φιλοτίμου συνδρομής των ομογενών. Triest: Michele Weis.
- Anastasiou, Spiridon; Keïvelis, Ioannis G. (1856). Απάνθισμα ή Μεδζμουαϊ μακαμάτ περιέχον μεν διάφορα τουρκικά άσματα. Istanbul: Taddaios Tividesian.
- Keltzanides, Panagiotes (1881). Μεθοδική διδασκαλία θεωρητική τὲ καὶ πρακτική πρὸς ἐκμάθησιν καὶ διάδοσιν τοῦ γνησίου ἐξωτερικοῦ μέλους τῆς καθ᾿ ἡμᾶς Ἑλληνικῆς Μουσικῆς κατ᾿ ἀντιπαράθεσιν πρὸς τὴν Ἀραβοπερσικήν. Istanbul: A. Koromela & Sons.
- Kosmas Metropolit of Madyta (1897). Ποιμενικός αυλός περιέχων μουσικά έργα εκδιδόμενα αδεία του Υπουργείου της Δημοσίας Εκπαιδεύσεως υπό ημερομηνίαν 25 Ραμαζάν 313 και 15 Φεβρουαρίου 312 (1897) και υπ΄ αριθμόν 552. Διηρημένα εις τρία τεύχη Κοσμά του εκ Μαδύτων μητροπολίτου Πελαγωνίας. 1. Athens: Spyridones Kousoulinos.
Anthologies of Makam Music
- Georgiadis, Panagiotis, ed. (1859). Καλλίφωνος Σειρήν ήτοι Συλλογή Διαφόρων Ασμάτων, Τουρκικών, Ευρωπαϊκών και Ελληνικών Μελοποιηθέντων υπό Χ. Παναγιώτου Γεωργιάδου του Προυσαέως. Istanbul: Igniatidis.
- Keïvelis, Ioannis G.; Anastasiou, Spyridon, eds. (1856). Απάνθισμα ή Μεδζμουαϊ μακαμάτ περιέχον μεν διάφορα τουρκικά άσματα. Istanbul: Taddaios Tividesian.
- Keïvelis, Ioannis G., ed. (1872). Μουσικόν Απάνθισμα (Μεδζμουάϊ Μακαμάτ) διαφόρων ασμάτων μελοποιηθέντων παρά διαφόρων μελοποιών, τονισθέντων μεν παρά Ιωάννου Γ. Ζωγράφου Κεϊβέλη και παρ' άλλων μουσικοδιδασκάλων Εκδοθέντων δε υπ' αυτού, περιέχον προσέτι την οδηγίαν των ρυθμών της Ασιατικής Μουσικής. Istanbul: Evangelinos Misaelidos.
- Phokaeos, Theodoros; Chourmouzios Chartophylakos (1830). Βίβλος καλουμένη Ευτέρπη : Περιέχουσα συλλογήν εκ των νεωτέρων και ηδυτέρων εξωτερικών μελών, με προσθήκην εν τω τέλει και τινών ρωμαϊκών τραγωδίων εις μέλος οθωμανικόν και ευρωπαϊκόν εξηγηθέντων εις το νέον της μουσικής σύστημα παρά Θεοδώρου Φωκέως, και Σταυράκη Βυζαντίου των μουσικολογιωτάτων. Galata: Kastoros.
- Phokaeos, Theodoros; Chourmouzios Chartophylakos (1843–1846). Η Πανδώρα ήτοι συλλογή εκ των νεωτέρωνκαι ηδυτέρων εξωτερικών μελών εις τόμους 2 όπου και προσετέθησαν και τα ελληνικά τραγούδια της προεκδοθείσης Η Πανδώρα ήτοι συλλογή εκ των νεωτέρωνκαι ηδυτέρων εξωτερικών μελών εις τόμους 2 όπου και προσετέθησαν και τα ελληνικά τραγούδια της προεκδοθείσης (1830) Ευτέρπης του Χουρμουζίου Χαρτοφύλακος Θεοδώρου Παράσχου Φωκαέως. 1–2. Istanbul: Publisher of the Patriarchate.
- Vlachopoulos, Soterios I. (1848). Αρμονία ήτοι ελληνικά και τουρκικά άσματα ποιηθέντα και τονισθέντα υπό Σ. Ι. Βλαχοπούλου. Istanbul: E. Kayol.
- Vlahakis, Nikolaos D. (1870). Η Λεσβία Σαπφώ ήτοι ασματολόγιον περιέχον εξωτερικά άσματα, εις ύφος Ελληνικόν, Ευρωπαϊκόν και Τουρκικόν. Athens: Stavrakis Anagnostou.
Studies
- Brandl, Rudolf Maria (1989). Elsner, Jürgen, ed. "Konstantinopolitanische Makamen des 19. Jahrhunderts in Neumen: die Musik der Fanarioten". Maqam - Raga - Zeilenmelodik: Konzeptionen und Prinzipien der Musikproduktion. 1. Arbeitstagung der Study Group "maqām" beim International Council for Traditional Music vom 28. Juni bis 2. Juli 1988 in Berlin. Berlin: 156–169.
- Erol, Merıh (25 May 2008). "'External' music in Constantinople". Encyclopaedia of the Hellenic World, Constantinople. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
- Gerlach, Oliver (2011). "Religious Chant in the late Ottoman Empire – Between Petros Bereketēs and Hamamîzade İsmail Dede Efendi". Studies of the Dark Continent in European Music History: Collected Essays on Traditions of Religious Chant in the Balkans. Rome: Aracne. pp. 81–110. ISBN 9788854838406.
- Gerlach, Oliver (2006). "The older the singer the better! On the role of creativity in passing down liturgical music from the 19th and 20th centuries". In László Dobszay (ed.). Papers read at the 12th Meeting of the IMS Study Group “Cantus Planus” Lillafüred/Hungary, 2004. Aug. 23–28. Budapest: Institute for Musicology of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. pp. 883–891.
- Joubran, Romanos Rabih (2009). The Use of Eastern Musical Modes in Byzantine Compositions during the 19th and 20th Century (PDF). Pittsburgh. pp. 530–553. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
- Popescu-Judeţ, Eugenia; Şırlı, Adriana Ababi (2000). Sources of 18th-century music : Panayiotes Chalathzoglou and Kyrillos Marmarinos' comparative treatises on secular music. Istanbul: Pan Yayıncılık. ISBN 975-843405-5.
- Raasted, Jørgen (1966). Intonation Formulas and Modal Signatures in Byzantine Musical Manuscripts. Monumenta Musicae Byzantinae, Subsidia. 7. Copenhagen: E. Munksgaard.
- Touma, Habib Hassan (1971). "The Maqam Phenomenon: An Improvisation Technique in the Music of the Middle East". Ethnomusicology. 15: 38–48. doi:10.2307/850386. JSTOR 850386.
- Zannos, Ioannis (1994). Vogel, Martin, ed. Ichos und Makam - Vergleichende Untersuchungen zum Tonsystem der griechisch-orthodoxen Kirchenmusik und der türkischen Kunstmusik. Orpheus-Schriftenreihe zu Grundfragen der Musik. 74. Bonn: Verlag für systematische Musikwissenschaft. ISBN 9783922626749.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Enechemata. |
- Jeffery, Peter (4 December 2010). "At the Origins of the Byzantine Musical Tradition: The Eight Modes (with demonstration of the old echemata)". White Plains: Axion Estin Foundation.
- Galanes, Demetrios. "Modern apechemata of the echoi".
- Païkopoulos, Demosthenis. "Petros Bereketes: Θεοτόκε παρθένε".
- Stanitsas, Thrasyvoulos (1978). "Amanes".
- Karaca, Kani. "Zaharya Efendi Mir Cemil (Ζαχαρίας ο χανεντές): Murabbâ Beste "Çeşm-i meygûnun ki bezm-i meyde cânân döndürür" in makam segâh (echos legetos)".
- "Archon cantors of the Great Church of Christ (about the different Patriarchal schools with historical recordings)". Association of Constantinopolitan Friends of Music (Athens).
!["You descend 4 steps [φοναὶ] from the echos protos [kyrios protos/authentic protus: a—G—F—E—DD] and you will find again the plagios protos , this way [D—F—E—DD]."](../I/m/Enechemata_(%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%80%CF%81%E1%BF%B6%CF%84%CE%BF%CF%82%2C_%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%80%CE%BB%CE%B1%CE%B3%CE%B9%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%84%CE%BF%E1%BF%A6_%CF%80%CF%81%CF%8E%CF%84%CE%BF%CF%85).jpg)
![You do the same way in echos devteros. If you descend 4 steps [b—a—G—F—EE] to find its plagios, i.e. πλ β', thus [E—F—G—F—EE].](../I/m/Enechemata_(%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CE%B4%CE%B5%CF%8D%CF%84%CE%B5%CF%81%CE%BF%CF%82%2C_%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%80%CE%BB%CE%AC%CE%B3%CE%B9%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%84%CE%BF%E1%BF%A6_%CE%B4%CE%B5%CF%85%CF%84%CE%AD%CF%81%CE%BF%CF%85).jpg)
![Hence, you descend four steps from echos tritos 4 steps [c—c—b—c—G—a—G—a—G—F—E—FF] and you will find its plagios which is called 'grave' (βαρύς), this way [F—G—E#—FF].](../I/m/Enechemata_(%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%84%CF%81%CE%AF%CF%84%CE%BF%CF%82%2C_%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CE%B2%CE%B1%CF%81%CF%8D%CF%82).jpg)
![Also from echos tetartos you descend 4 steps [φοναὶ: G—F—E—D—CC] and you will find its plagios, which is πλ δ', like this way [C—D—C—CC].](../I/m/Enechemata_(%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%84%CE%AD%CF%84%CE%B1%CF%81%CF%84%CE%BF%CF%82%2C_%E1%BC%A6%CF%87%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%80%CE%BB%CE%AC%CE%B3%CE%B9%CE%BF%CF%82_%CF%84%CE%BF%E1%BF%A6_%CF%84%CE%B5%CF%84%CE%AC%CF%81%CF%84%CE%BF%CF%85).jpg)