Enceladus Life Finder
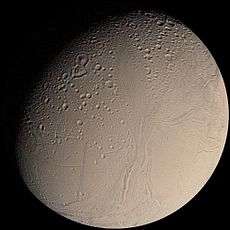
Enceladus Life Finder (ELF) is a proposed astrobiology mission concept for a NASA spaceprobe intended to assess the habitability of the internal aquatic ocean of Enceladus, which is Saturn's sixth-largest moon[1][2] and seemingly similar in chemical makeup to comets.[3] The spaceprobe would orbit Saturn and fly through Enceladus's geyser-like plumes multiple times. It would be powered by energy supplied from solar panels on the spacecraft.
Overview

The Enceladus Life Finder mission has been proposed in 2015 for Discovery Mission 13 funding.[2] If selected, a launch readiness date of December 31, 2021 may be possible.[4]
The ELF mission would search for biosignature and biomolecules in the geysers of Enceladus. The south polar jets loft water, salts and organic molecules dozens of miles over the moon's surface from an underground regional ocean. The theory is that the water is warmed by thermal vents similar to features found deep in Earth's oceans. ELF's instruments would measure amino acids — the building blocks of proteins — analyze fatty acids, and determine whether methane (CH4) found in the plumes could have been produced by living organisms.[2]
In 2008, the Cassini orbiter was flown through a plume and analyzed the material with its neutral mass spectrometer. The orbiter detected simple organics, including methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2) nitrogen, and complex organic compounds.[5] Cassini also detected sodium and potassium at a concentration implying a salty liquid ocean.[5] However, Cassini does not have the equipment with the sensitivity required for direct analyses.[1][5]
Mission concept

The Enceladus Life Finder (ELF) mission would pursue the implications of Cassini orbiter's 2005 discoveries of active jetting from, and existence of an ocean within, Enceladus. The current mission concept would have the ELF orbiter fly 8 to 10 times over a period of 3 years through plumes of water launched above the south pole of Enceladus.[2] The geysers could provide easy access for sampling the moon's subsurface ocean, and if there is microbial life in it, ice particles from the sea could contain the evidence astrobiologists need to identify them.[6]
Objectives
The goals of the mission are derived directly from the most recent decadal survey: first, to determine primordial sources of organics and the sites of organic synthesis today; and second, to determine if there are current habitats in Enceladus where the conditions for life could exist today, and if life exists there now.[1] To achieve these goals, the ELF mission has three objectives:[1]
- To measure abundances of a carefully selected set of neutral species, some of which were detected by Cassini, to ascertain whether the organics and volatiles coming from Enceladus have been thermally altered over time.
- To determine the details of the interior marine environment — pH, oxidation state, available chemical energy, and temperature — that permit characterization of the life-carrying capacity of the interior.
- To look for indications that organics are the result of biological processes through three independent types of chemical measurements that are widely recognized as diagnostic of life.
Proposed scientific payload

The ELF spacecraft would use two mass spectrometers to assess habitability of the interior oceanic environment. The two proposed scientific instruments are:[1][5]
- Mass Spectrometer for Planetary Exploration (MASPEX), optimized to analyze the gas expelled from the vents.
- Enceladus Icy Jet Analyzer (ENIJA), optimized to analyze solid particles expelled from the vents.
The Cassini spacecraft has measured small silica particles, normally formed at 90 °C or higher, streaming from Enceladus.[7] The size and composition of the particles suggest that they come from current hydrothermal activity,[8][9][10][11] where the moon's ocean meets the underlying rock, a prime habitat for life.[7][12]
ELF's instruments would conduct three kinds of tests in order to minimize the ambiguity involved in life detection.[1][5] The first would look for a characteristic distribution of amino acids (the building blocks of proteins). The second test would determine whether the carbon number distribution in fatty acids or isoprenoids is biased toward a particular rule (even, odd, or divisible by a small integer). The third would measure carbon and hydrogen isotopic ratios, together with the abundance of methane relative to other alkanes, to assess whether the values fall in the range for biological processes.[5]
See also
- Abiogenesis
- Astrobiology
- Discovery Program
- Enceladus Explorer
- Europa Clipper
- Journey to Enceladus and Titan (JET)
- Life Investigation For Enceladus (LIFE)
- THEO
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Lunine, J.I.; Waite, J.H.; Postberg, F.; Spilker, L. (2015). Enceladus Life Finder: The search for life in a habitable moon (PDF). 46th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2015). Houston, Texas.: Lunar and Planetary Institute.
- 1 2 3 4 Clark, Stephen (April 6, 2015). "Diverse destinations considered for new interplanetary probe". Space Flight Now. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ↑ Battersby, Stephen (March 26, 2008). "Saturn's moon Enceladus surprisingly comet-like". New Scientist. Retrieved April 16, 2015.
- ↑ "NASA Discovery Program Draft Announcement of Opportunity". NASA Science Mission Directorate. SpaceRef. February 19, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Lunine, Jonathan. "Searching for Life in the Saturn System: Enceladus Life Finder" (PDF). ELF Team. Lunar And Planetary Institute. Retrieved 2015-04-07.
- ↑ Gronstal, Aaron (July 30, 2014). "Enceladus in 101 Geysers". NASA Astrobiology Institute. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- 1 2 Witze, Alexandra (March 11, 2015). "Hints of hot springs found on Saturnian moon". Nature News. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ↑ Ocean Within Enceladus May Harbor Hydrothermal Activity. March 11, 2015.
- ↑ Platt, Jane; Bell, Brian (April 3, 2014). "NASA Space Assets Detect Ocean inside Saturn Moon". NASA. Retrieved April 3, 2014.
- ↑ Iess, L.; Stevenson, D.J.; et al. (April 4, 2014). "The Gravity Field and Interior Structure of Enceladus". Science. 344 (6179): 78–80. Bibcode:2014Sci...344...78I. doi:10.1126/science.1250551. Retrieved April 3, 2014.
- ↑ Amos, Jonathan (April 3, 2014). "Saturn's Enceladus moon hides 'great lake' of water". BBC News. Retrieved April 7, 2014.
- ↑ Anderson, Paul Scott (March 13, 2015). "Cassini Finds Evidence for Hydrothermal Activity on Saturn's Moon Enceladus". AmericaSpace. Retrieved April 7, 2015.


.jpg)