Eastern United States
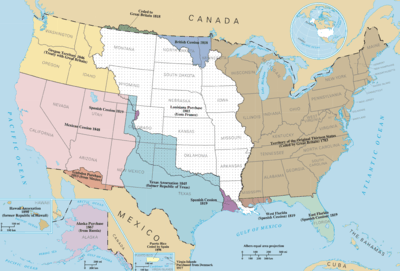

The Eastern United States, commonly referred to as the American East or simply the East, is a region roughly coinciding with the boundaries of the United States established in the 1783 Treaty of Paris, which bounded the new country to the west along the Mississippi River. It is geographically diverse, spanning the Northeast and Southeast as well as the eastern part of the Central United States.
In 2011 the 26 states east of the Mississippi (including Washington, D.C. but not the small portions of Minnesota and Louisiana east of the river) had an estimated population of 179,948,346 or 58.28% of the total U.S. population of 308,745,358 (excluding Puerto Rico).
Southern United States
The Southern United States constitutes a large region in the south-eastern and south-central United States. Because of the region's unique cultural and historic heritage, including Native Americans; early European settlements of English, Scots-Irish, Scottish and German heritage ; importation of hundreds of thousands of enslaved Africans; growth of a large proportion of African Americans in the population, reliance on slave labor, and legacy of the Confederacy after the American Civil War, the South developed its own customs, literature, musical styles, and varied cuisines, that have profoundly shaped traditional American culture.The South's culture is deeply rooted in the American Civil War.
In the last few decades, the Southern US has been attracting internal and international migrants. The American South is among the fastest-growing areas in the United States.
Kentucky, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Arkansas, Alabama, Mississippi, Florida, and Louisiana are parts of the Eastern United States which make up the area often known as the Southern United States.
New England
New England is a region of the United States located in the northeastern corner of the country, bounded by the Atlantic Ocean, Canada and the state of New York, consisting of the modern states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.
In one of the earliest English settlements in the New World, English Pilgrims from Europe first settled in New England in 1620, in the colony of Plymouth. In the late 18th century, the New England colonies would be among the first North American British colonies to demonstrate ambitions of independence from the British Crown, although they would later threaten secession over the War of 1812 between the United States and Britain.
New England produced the first examples of American literature and philosophy and was home to the beginnings of free public education. In the 19th century, it played a prominent role in the movement to abolish slavery in the United States. It was the first region of the United States to be transformed by the Industrial Revolution.
It is a region with one of the highest levels of support for the Democratic Party in the United States, with the majority of voters in every state voting for the Democrats in the 1992, 1996, 2004, 2008 and 2012 Presidential elections, and every state but New Hampshire voting for Al Gore in 2000.
The Midwest
The Midwestern United States (in the U.S. generally referred to as the Midwest) is one of the four geographic regions within the United States that are recognized by the United States Census Bureau.
The region consists of seven states in the central and inland northeastern US: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin. A 2006 Census Bureau estimate put the population at 66,217,736. Both the geographic center of the contiguous U.S. and the population center of the U.S. are in the Midwest. The United States Census Bureau divides this region into the East North Central States (essentially the Great Lakes States) and the West North Central States.
Chicago is the largest city in the region, followed by Indianapolis and Columbus. Chicago has the largest metropolitan statistical area, followed by Detroit, and Minneapolis – Saint Paul. Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan is the oldest city in the region, having been founded by French missionaries and explorers in 1668.
The term Midwest has been in common use for over 100 years. Another term sometimes applied to the same general region is "the heartland". Other designations for the region have fallen into disuse, such as the "Northwest" or "Old Northwest" (from "Northwest Territory") and "Mid-America". Since the book Middletown appeared in 1929, sociologists have often used Midwestern cities (and the Midwest generally) as "typical" of the entire nation. The region has a higher employment-to-population ratio (the percentage of employed people at least 16 years old) than the Northeast, the West, the South, or the Sun Belt states.
Four of the states associated with the Midwestern United States (Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota) are traditionally referred to as belonging to the Great Plains region. However, in recent years they are often included in the Midwestern region.
Major population centers
The following is a list of the 24 largest cities in the East by population:
 New York City
New York City
population: 8,175,133 Chicago
Chicago
population: 2,695,598 Philadelphia
Philadelphia
population: 1,526,006 Jacksonville
Jacksonville
population: 821,784- Indianapolis
population: 820,445  Columbus
Columbus
population: 787,033.jpg) Charlotte
Charlotte
population: 731,424 Detroit
Detroit
population: 713,777 Memphis
Memphis
population: 646,889 Baltimore
Baltimore
population: 620,961 Boston
Boston
population: 617,594 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
population: 601,723 Nashville
Nashville
population: 601,222 Louisville, Kentucky
Louisville, Kentucky
population: 597,337 Milwaukee
Milwaukee
population: 594,833 Virginia Beach, Virginia
Virginia Beach, Virginia
population: 437,994 Atlanta
Atlanta
population: 420,003 Raleigh
Raleigh
population: 403,892 Miami
Miami
population: 399,457- Cleveland
population: 396,815  Tampa
Tampa
population: 335,709 Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh
population: 305,704 Cincinnati
Cincinnati
population: 296,943- Lexington, Kentucky
population: 295,803
See also
References
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eastern United States. |
Coordinates: 38°N 82°W / 38°N 82°W