Earlandite
| Earlandite | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General | |
| Category | Organic mineral |
| Formula (repeating unit) | [Ca3(C6H5O7)2(H2O)2]·2H2O |
| Strunz classification | 10.AC.15 |
| Crystal system |
Triclinic Unknown space group |
| Unit cell |
a = 5.9466(4), b = 10.2247(8) c = 16.6496(13) [Å]; Z = 2 |
| Identification | |
| Color | White, pale yellow |
| Crystal habit | Nodular |
| Streak | White |
| Diaphaneity | Transparent |
| Specific gravity | 1.80–1.95 (measured), 2.00 (calculated) |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (+) |
| Refractive index |
nα = 1.515 nβ = 1.530 nγ = 1.580 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.065 |
| 2V angle | 60° |
| Solubility | Insoluble |
| References | [1][2][3][4] |
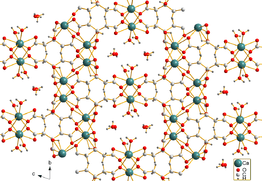
Earlandite [Ca3(C6H5O7)2(H2O)2]·2H2O is the mineral form of calcium citrate tetrahydrate. It was first reported in 1936 and named after the English microscopist Arthur Earland FRSE. Earlandite occurs as warty fine-grained nodules ca. 1 mm in size in bottom sediments of the Weddell Sea, off Antarctica.[3] Its crystal symmetry was first assigned as orthorhombic, then as monoclinic, and finally as triclinic.[1]
References
- 1 2 Herdtweck, Eberhardt; Kornprobst, Tobias; Sieber, Roland; Straver, Leo; Plank, Johann (2011). "Crystal Structure, Synthesis, and Properties of tri-Calcium di-Citrate tetra-Hydrate [Ca3(C6H5O7)2(H2O)2]·2H2O". Z. Anorg. Allgemeine Chemie. 637 (6): 655–659. doi:10.1002/zaac.201100088.
- ↑ Earlandite. Mindat.org
- 1 2 Anthony, John W.; Bideaux, Richard A.; Bladh, Kenneth W.; Nichols, Monte C., eds. (2003). "Earlandite". Handbook of Mineralogy (PDF). V (Borates, Carbonates, Sulfates). Chantilly, VA, US: Mineralogical Society of America. ISBN 0962209740.
- ↑ Earlandite. Webmineral
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.