EBC-46
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | injected |
| Identifiers | |
| PubChem (CID) | 23627739 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H42O10 |
| Molar mass | 562.647 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| (verify) | |
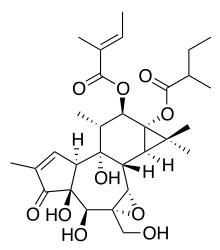
EBC-46 is an experimental drug candidate being studied pre-clinically[1] by the Australian company Ecobiotics (specifically its drug discovery subsidiary Qbiotics). It was discovered through an automated screening process of natural products by selecting increasingly purified fractions of plant extracts, based on their ability to produce the desired activity profile. This is then followed by artificial synthesis of the isolated compound to confirm its chemical structure. EBC-46 is a phorbol ester which, along with other related compounds, acts as a protein kinase C regulator.[2]
The initial lead came from observation that marsupials found the seed of Fontainea picrosperma unpalatable due to an inflammatory chemical present in reasonably high concentrations. This was identified as 12-tigloyl-13-(2-methylbutanoyl)-6,7-epoxy-4,5,9,12,13,20-hexahydroxy-1-tiglian-3-one.[3]
ECB-46 is an extract from the blushwood berries of Queensland, Australia.
See also
References
- ↑ Boyle, G. M.; d'Souza, M. M. A.; Pierce, C. J.; Adams, R. A.; Cantor, A. S.; Johns, J. P.; Maslovskaya, L.; Gordon, V. A.; Reddell, P. W.; Parsons, P. G. (2014). "Intra-Lesional Injection of the Novel PKC Activator EBC-46 Rapidly Ablates Tumors in Mouse Models". PLoS ONE. 9 (10): e108887. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0108887.
- ↑ Aitken, A. (1987). "The activation of protein kinase G by daphnane, ingenane and tigliane diterpenoid esters". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 94: 247. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.1987.tb01049.x.
- ↑ Tiglian-3-one derivatives. Patent WO 2007/070985