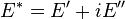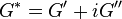Dynamic modulus
Dynamic modulus (sometimes complex modulus[1]) is the ratio of stress to strain under vibratory conditions (calculated from data obtained from either free or forced vibration tests, in shear, compression, or elongation). It is a property of viscoelastic materials.
Viscoelastic stress–strain phase-lag
Viscoelasticity is studied using dynamic mechanical analysis where an oscillatory force (stress) is applied to a material and the resulting displacement (strain) is measured.[2]
- In purely elastic materials the stress and strain occur in phase, so that the response of one occurs simultaneously with the other.
- In purely viscous materials, there is a phase difference between stress and strain, where strain lags stress by a 90 degree (
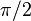 radian) phase lag.
radian) phase lag. - Viscoelastic materials exhibit behavior somewhere in between that of purely viscous and purely elastic materials, exhibiting some phase lag in strain.[3]
Stress and strain in a viscoelastic material can be represented using the following expressions:
- Strain:
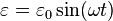
- Stress:
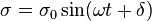 [3]
[3]
where
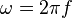 where
where 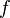 is frequency of strain oscillation,
is frequency of strain oscillation,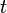 is time,
is time,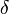 is phase lag between stress and strain.
is phase lag between stress and strain.
Storage and loss modulus
The storage and loss modulus in viscoelastic materials measure the stored energy, representing the elastic portion, and the energy dissipated as heat, representing the viscous portion.[3] The tensile storage and loss moduli are defined as follows:
- Storage:
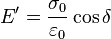
- Loss:
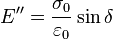 [3]
[3]
Similarly we also define shear storage and shear loss moduli, 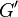 and
and 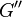 .
.
Complex variables can be used to express the moduli 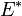 and
and 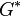 as follows:
as follows:
where 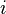 is the imaginary unit.
is the imaginary unit.
See also
References
- ↑ The Open University (UK), 2000. T838 Design and Manufacture with Polymers: Solid properties and design, page 30. Milton Keynes: The Open University.
- ↑ PerkinElmer "Mechanical Properties of Films and Coatings"
- 1 2 3 4 5 Meyers and Chawla (1999): "Mechanical Behavior of Materials," 98-103.