Direct-controlled municipalities of China
| Municipality[1] 直辖市 Zhíxiáshì | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category |
First-level administration Unitary state |
| Location | People's Republic of China |
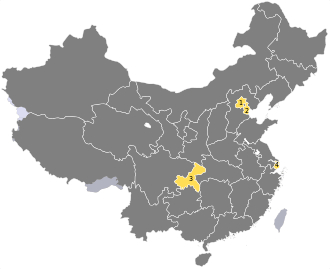
| Number | 4 (#1 Beijing; #2 Tianjin; #3 Chongqing; #4 Shanghai) |
| Populations | 12,938,224 (Tianjin) – 28,846,170 (Chongqing) |
| Areas | 2,448.1 square miles (6,341 km2) (Shanghai) – 31,816 square miles (82,400 km2) (Chongqing) |
| Government | Dual-Party government |
| Subdivisions | District, county, autonomous county |
| This article is part of a series on |
| Administrative divisions of China |
|---|
|
Analogous county level units Management areas Management committee |
|
Townships
Subdistricts County-controlled districts (pilot) |
|
Analogous township level units Management areas Management committee Areas Farms area, Prison area, University towns etc. |
|
|
|
History: before 1912, 1912–49, 1949–present Administrative division codes |
A municipality (simplified Chinese: 直辖市; traditional Chinese: 直轄市; pinyin: zhíxiáshì), also translated as direct-controlled municipality (formally, municipality directly under the central government, or province-level municipality), is the highest level of classification for cities used by the People's Republic of China. These cities have the same rank as provinces, and form part of the first tier of administrative divisions of China.
A municipality is a "city" (Chinese: 市; pinyin: shì) with "provincial" (Chinese: 省级; pinyin: shěngjí) power under a unified jurisdiction. As such it is simultaneously a city and a province of its own right.
A municipality is often not a "city" in the usual sense of the term (i.e., a large continuous urban settlement), but instead an administrative unit comprising, typically, a main central urban area (a city in the usual sense, usually with the same name as the municipality), and its much larger surrounding rural area containing many smaller cities (districts and subdistricts), towns and villages. The larger municipality spans over 100 kilometres (62 mi). To distinguish a "municipality" from its actual urban area (the traditional meaning of the word city), the term Chinese: 市区, or "urban area", is used.
History
The first municipalities were the 11 cities of Nanjing, Shanghai, Beijing, Tianjin, Qingdao, Chongqing, Xi'an, Guangzhou, Hankou (now part of Wuhan), Shenyang, and Harbin when the ROC government ruled China. They were established in 1927 soon after they were designated as "cities" during the 1920s. Nominally, Dalian was a municipality as well, although it was under Japanese control. These cities were first called special municipalities/cities (特别市; 特別市; tébiéshì), but were later renamed Yuan-controlled municipalities (院辖市; 院轄市; yuànxiáshì), then direct-controlled municipalities (直辖市; 直轄市; zhíxiáshì) by the Central Government.
After the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, Anshan, Benxi, and Fushun were also made municipalities, while Qingdao, Dalian, and Harbin were reduced to provincial municipalities.[2] Hankou was merged into Wuhan. Hence, there remained 12 municipalities, until Dalian was elevated in 1950. In November 1952, Nanjing was reduced to a provincial municipality.[3] In July 1953, Harbin was restored to municipality status, along with Changchun.[4] Except Beijing and Tianjin, which were under central control, all other municipalities were governed by the greater administrative areas.
In June 1954, 11 of the 14 municipalities were reduced to sub-provincial cities; many of them became capitals of the provinces they were in. Only Beijing, Shanghai, and Tianjin remained municipalities, until Chongqing was restored as a municipality in 1997 with a much enlarged area. Tianjin was also temporarily reverted to sub-provincial city status around the 1960s.
Position in hierarchy
Municipalities are the highest-ranked cities in the PRC. Some cities of lower levels may also refer to themselves as municipalities in the English language.
Three levels of cities in the People's Republic of China:
- Municipalities (直辖市; 直轄市; zhíxiáshì);
- Prefecture-level cities (地级市; 地級市; dìjíshì), including sub-provincial cities; and,
- County-level cities (县级市; 縣級市; xiànjíshì), including sub-prefecture-level cities.
Administration
In municipalities, the highest ranking government official is the Mayor. The mayor is also a delegate in the National People's Congress (the legislature)[5] and Deputy Secretary of the CPC Municipal Committee. However, the highest administrative authority in the municipality belongs to the Secretary of the CPC Municipal Committee or Party Secretary.
Current PRC Municipalities
| ISO[6] | Division name | Simplified Chinese | Pinyin | Abbr. | Population[7] | Area (km²) | Divisions | City seat | Origin Province (split date) |
Origin Prefecture | Origin County |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN-11 | Beijing | 北京市 | Běijīng Shì | 京 jīng | 19,612,368 | 16,801 | List (16 districts) | Dongcheng Tongzhou |
Hebei (Oct. 1949) |
Shuntian | Daxing |
| CN-12 | Tianjin | 天津市 | Tiānjīn Shì | 津 jīn | 12,938,224 | 11,760 | List (16 districts) | Heping | Hebei (Jan. 1967) |
Tianjin | Tianjin |
| CN-31 | Shanghai | 上海市 | Shànghǎi Shì | 沪 hù | 23,019,148 | 6,340 | List (16 districts) | Huangpu | Jiangsu (Mar. 1927) |
Songjiang | Shanghai |
| CN-50 | Chongqing | 重庆市 | Chóngqìng Shì | 渝 yú | 28,846,170 (City Core 16,240,026) |
82,300 (City Core 6,268) |
List (24 districts, 10 counties, & 4 autonomous counties) (City Core: 19 districts) |
Yuzhong | Sichuan (May 1997) |
Chongqing | Ba |
Former ROC and PRC municipalities
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Pinyin | Abbr. | City seat | Administration period | Original province | Original prefecture | Original county |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jingdu | 京都市 | Jīngdū Shì | 京 jīng | Dongcheng | 1921–1927 | Zhili (present province: Hebei) |
Shuntian | Daxing |
| Jingu | 津沽市 | Jīngū Shì | 津 jīn | Heping | 1921–1927 | Zhili (present province: Hebei) |
Tianjin | Tianjin |
| Songhu | 淞沪市 | Sōnghù Shì | 沪 hù | Huangpu | 1921–1927 | Jiangsu | Songjiang | Shanghai |
| Qingdao | 青岛市 | Qīngdǎo Shì | 青 qīng | Shinan | 1921–1927, 1929–1949 | Shandong | Jiaozhou | Jiao |
| Harbin | 哈尔滨市 | Hāerbīn Shì | 哈 hā | Nangang | 1921–1927, 1947–1949, 1953–1954 | Songjiang (present province: Heilongjiang) |
Binzhou | Bin |
| Hankou | 汉口市 | Hànkǒu Shì | 汉 hàn | Jiang'an | 1921–1927, 1929–1931, 1947–1949 | Hubei | Hanyang | Hanyang |
| Wuxi | 无锡市 | Wúxī Shì | 锡 xī | Binhu | 1921–1927 | Jiangsu | Changzhou | Wuxi |
| Hangzhou | 杭州市 | Hángzhōu Shì | 杭 háng | Gongshu | 1921–1927 | Zhejiang | Hangzhou | Yuhang |
| Ningbo | 宁波市 | Níngbō Shì | 甬 yǒng | Jiangdong | 1921–1927 | Zhejiang | Ningbo | Yin |
| Anqing | 安庆市 | Ānqìng Shì | 安 ān | Daguan | 1921–1927 | Anhui | Anqing | Huaining |
| Nanchang | 南昌市 | Nánchāng Shì | 洪 hóng | Donghu | 1921–1927 | Jiangxi | Nanchang | Nanchang |
| Wuchang | 武昌市 | Wǔchāng Shì | 武 wǔ | Wuchang | 1921–1927 | Hubei | Wuchang | Jiangxia |
| Guangzhou | 广州市 | Guǎngzhōu Shì | 穗 suì | Yuexiu | 1921–1927, 1930, 1947–1954 | Guangdong | Guangzhou | Panyu Nanhai |
| Wuzhou | 梧州市 | Wúzhōu Shì | 梧 wú | Changzhou | 1921–1927 | Guangxi | Wuzhou | Cangwu |
| Nanjing | 南京市 | Nánjīng Shì | 宁 níng | Xuanwu | 1927–1952 | Jiangsu | Jiangning | Jiangning |
| Xi'an | 西安市 | Xī'ān Shì | 京 hào | Weiyang | 1927–1954 | Shaanxi | Xi'an | Chang'an |
| Wuhan | 武汉市 | Wǔhàn Shì | 汉 hàn | Jiang'an | 1927–1929, 1949 | Hubei | Hanyang Wuchang |
Hanyang Jiangxia |
| Beiping | 北平市 | Jīngdū Shì | 平 píng | Dongcheng | 1928–1949 | Zhili (present province: Hebei) |
Shuntian | Daxing |
| Dalian | 大连市 | Dàlián Shì | 连 lián | Xigang | 1947–1949 | Andong/Liaodong (present province: Liaoning) |
Jinzhou | Ninghai |
| Shenyang | 沈阳市 | Shěnyáng Shì | 沈 shěn | Shenhe | 1947–1954 | Liaoxi (present province: Liaoning) |
Fengtian | Fengtian |
| Anshan | 鞍山市 | Ānshān Shì | 鞍 ān | Tiedong | 1949–1954 | Andong/Liaodong (present province: Liaoning) |
Liaoyang | Haicheng Liaoyang |
| Benxi | 本溪市 | Běnxī Shì | 甬 běn | Pingshan | 1949–1954 | Andong/Liaodong (present province: Liaoning) |
Fengtian | Benxi |
| Fushun | 抚顺市 | Fǔshùn Shì | 抚 fǔ | Xinfu | 1949–1954 | Andong/Liaodong (present province: Liaoning) |
Fengtian | Fushun |
| Lüda | 旅大市 | Lǚdà Shì | 旅 lǚ | Xigang | 1950–1954 | Lüda (present province: Liaoning) |
Jinzhou | Ninghai |
| Changchun | 长春市 | Chángchūn Shì | 津 chūn | Nanguan | 1953–1954 | Jilin | Changchun | Changchun |
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Municipalities in China. |
- ↑ "Local Governments". Chinese Government's Official Web Portal. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ↑ Archived March 18, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Archived March 18, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Archived June 19, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Chongqing Mayor: Government Must Place Service Above Anything Else". Xinhua News Agency. March 3, 2003. Archived from the original on November 21, 2008. Retrieved February 21, 2011.
- ↑ ISO 3166-2:CN (ISO 3166-2 codes for the provinces of China)
- ↑ "Communiqué of the National Bureau of Statistics of People's Republic of China on Major Figures of the 2010 Population Census (No. 1)". National Bureau of Statistics of China. April 28, 2011. Retrieved July 19, 2011.