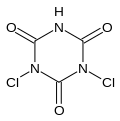
Dichloroisocyanuric acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,3-dichloro-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4,6-trione | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 2782-57-2 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 15857 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.625 | ||
| KEGG | D08650 | ||
| PubChem | 16726 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3HCl2N3O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 197.96 g/mol | ||
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Dichloroisocyanuric acid, also known as dichlor or dichloro-s-triazinetrione and is marketed under many names (e.g. troclosene), is a chemical compound with the formula (C(O)NCl)2(C(O)NH). This colourless solid is the active ingredient in many commercial bacteriocides, algicides, and cleaning agents. It is an oxidizer that reacts with water to form hypochlorous acid, the sodium salt of which is the active ingredient in bleach.
The sodium salt of dichloroisocyanuric acid, sodium dichloroisocyanurate, is the active ingredient in the powderized cleanser Comet and is also used as a pool disinfectant.
Synthesis
It is manufactured by chlorination of cyanuric acid:[1]
- (C(O)NH)3 + 2 Cl2 → (C(O)NCl)2(C(O)NH) + 2 HCl
See also
- Trichloroisocyanuric acid (trichlor)
- Sodium dichloroisocyanurate the corresponding sodium salt
References
- ↑ Huthmacher, K.; Most, D. (2005), "Cyanuric Acid and Cyanuric Chloride", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_191
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/30/2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.