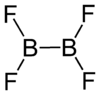
Diboron tetrafluoride
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diboron tetrafluoride | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Tetrafluorodiborane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 13965-73-6 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 123165 | ||
| PubChem | 139653 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| B2F4 | |||
| Molar mass | 97.616 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 4.3 kg/m3 (gas) | ||
| Melting point | −56 °C (−69 °F; 217 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −34 °C (−29 °F; 239 K) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 79.1 J/mol K | |||
| Std molar entropy (S |
317.3 J/mol K | ||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
-1440.1 kJ/mol | ||
| Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚) |
-1410.4 kJ/mol | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Diboron tetrafluoride is a colorless gas. It can be formed by reacting boron monofluoride with boron trifluoride at low temperatures, taking care not to form higher polymers.[1]
References
- ↑ P. L. Timms (1972). Low Temperature Condensation. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry. p. 143. ISBN 0-12-023614-1.
- Louis Trefonas and William N. Lipscomb (1958). "Crystal and Molecular Structure of Diboron Tetrafluoride, B2F4". J. Chem. Phys. 28 (1): 54. doi:10.1063/1.1744079.
- Gayles, J. N.; Self, J. (1964). "Infrared Spectrum of Diboron Tetrafluoride in the Gaseous and Solid States". Journal of Chemical Physics. 40 (12): 3530–3539. doi:10.1063/1.1725048.
- Arthur Finch and Hermann Irving Schlesinger (1958). "Diboron Tetrafluoride". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80 (14): 3573–3574. doi:10.1021/ja01547a020.
- A. K. Holliday; F. B. Taylor (1964). "Diboron tetrafluoride. Part II. Reactions with some oxides and organometallic compounds". J. Chem. Soc.: 2731–2734. doi:10.1039/JR9640002731.
- Vernon H. Dibeler; Susan K. Liston (1968). "Mass-spectrometric study of photoionization. XII. Boron trifluoride and diboron tetrafluoride". J. Chem. Soc. 7 (9): 1742–1746. doi:10.1021/ic50067a010.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.