Dettingen unter Teck
| Dettingen unter Teck | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
 Dettingen unter Teck | ||
Location of Dettingen unter Teck within Esslingen district 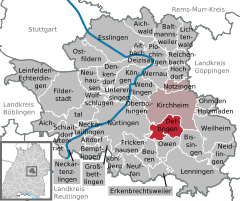
 | ||
| Coordinates: 48°36′58″N 9°27′6″E / 48.61611°N 9.45167°ECoordinates: 48°36′58″N 9°27′6″E / 48.61611°N 9.45167°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Admin. region | Stuttgart | |
| District | Esslingen | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Rainer Haußmann | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 15.13 km2 (5.84 sq mi) | |
| Population (2015-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 6,010 | |
| • Density | 400/km2 (1,000/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 73265 | |
| Dialling codes | 07021 | |
| Vehicle registration | ES | |
| Website | www.dettingen-teck.de | |
Dettingen (Swabian: Deddenge) is a municipality in the district of Esslingen in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany.
Geography
It is located 40 km southeast of Stuttgart and 4 km south of Kirchheim unter Teck.
On the right Guckenrain, district of Dettingen, on the left Dettingen, in the background Kirchheim unter Teck
History
Dettingen 1683/1685 in Kieserschen forest stock book Already from antiquity in Lautertal were found settlement traces. Right through the valley and the village leads the Lautertal Limes, a Roman border fortification that the vernacular as Sybillenspur knows. South of today's city lies fort Dettingen unter Teck. Dettingen was first mentioned around 1100. Exceptional is the high number of six castles and noble seats that you could find on Dettinger denunciation. None of the castles is more received, they are all gone off in the early Middle Ages. The Companies based noble families had to Dettinger Markung the main part of the manorial rights. The high authority was already since 1381 the House of Württemberg, in 1415 brought the Württemberger the rights as local lords in. On the German Peasants' War 1525 also Dettinger tenants were actively involved. In the Thirty Years War the city was heavily damaged, the population decreased by war and plague to around one third. At the beginning of the 17th century the city had around 1300 inhabitants, 1654 there were only 511 people in the village. The site was slow to recover, the Napoleonic wars in the 17th century brought another setback. Yet in 1715 were 160 court yards not inhabited and 300 acres of fields and vineyards lay fallow. In 1803 Dettingen had then about 1800 inhabitants. In 1939 the airfield of Wolf Hirth GmbH was expelled from the Air Force as airfield. The court, however, was relatively small and was therefore not covered by the air force. At the end of the Second World War Dettingen was hit hard on April 20, 1945, the fateful day. Days before had sought and found refuge on their march to retreat to the Swabian Alb in Dettingen German troops. The barns and cellars were full of German soldiers, began as Allied fighter-bombers to 16 clock with a systematic bombardment of the town. Explosive and incendiary bombs were dropped, quickly burned 69 houses and 39 barns ablaze. The church, the town hall, the Schlössle, the old school, the kindergarten and the fire station were destroyed by fire, the cattle burnt in the stables. Ten local residents and 13 soldiers died. One day later, the Americans invaded and occupied the village. Dettingen belonged until 1938 to Oberamt Kirchheim, then to district Nürtingen and from 1973 to Esslingen district.
Demographics
The number of inhabitants are estimates, census results (¹) or official extrapolations of statistica office Stuttgart. Jahr Einwohnerzahl
- 1654: ca. 511
- 1700: ca. 1.000
- 3. december 1834: ¹ 2.192
- 1. december 1871: ¹ 1.907
- 1. december 1900: ¹ 2.048
- 17. may 1939: ¹ 2.366
- 13. september 1950: ¹ 3.131
- 6. june 1961: ¹ 3.616
- 27. may 1970: ¹ 4.047
- 25. may 1987: ¹ 5.055
- 31. december 1995: 5.355
- 31. december 2000: 5.438
- 31. december 2005: 5.642
- 31. december 2010: 5.698
Local council
The local council in Dettingen has 14 members. Communal elections in Baden-Württemberg 25 May 2014 had the following official results.[2] The local council are the elected voluntary members and the mayor as president. The mayor has one vote.
| Political parties and community voters | % 2014 |
Sitze 2014 |
% 2009 |
Sitze 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDU/FWV | Christian Democratic Union of Germany/Free voters | 32,90 | 4 | 30,20 | 4 |
| FWG | Free voters Baden-Württemberg | 28,58 | 4 | 42,60 | 6 |
| SPD | Social Democratic Party of Germany | 19,35 | 3 | 27,20 | 4 |
| DBL | Dettinger citizen list | 19,17 | 3 | 0,0 | 0 |
| total | 100,0 | 14 | 100,0 | 14 | |
| poll | 51,98 % | 57,50 % | |||
Mayor
- 1932–1945 Wilhelm Faßnacht
- 1945–1948 Gottlieb Lauxmann
- 1948–1957 Julius Mahle
- 1957–1972 Richard Käser
- 1972–1996 Günter Fischer
- since 1996: Rainer Haußmann
On the 4. march 2012 Rainer Haußmann was re-elected for a third period. [3]
Traffic
The Teck Railway runs since 1899 from Wendlingen, Kirchheim, Dettingen, Owen to Oberlenningen (about 20 kilometers). The Royal Württemberg State Railways built the - now restored and used elsewhere - station building as a unit station type IIa. The station can be found in 1:87 as a model on many model railroads, including name, incidentally, also at the largest model railway in the world in miniature wonderland in Hamburg. [6] 2009, Teck Railway was electrified to Kirchheim and has since been on the S-Bahn Stuttgart traveled, the more distance over Dettingen after Oberlenningen is per direction per hour from a regional train operates. Dettingen belongs to the district of Esslingen the Transport and Tariff Association Stuttgart and is the Tarifwabe Kirchheim / Teck.

Former Dettingen station (2007)
Notable people from Dettingen
- Albert Pflüger (1879–1965), Politician (SPD), Member of Landtag
Literatur
(in German)
- Hans Schwenkel: Heimatbuch des Kreises Nürtingen (Band 2). Würzburg 1953, S. 177–206.
- Der Landkreis Esslingen. Herausgegeben vom Landesarchiv Baden-Württemberg i. V. mit dem Landkreis Esslingen, Jan Thorbecke Verlag, Ostfildern 2009, ISBN 978-3-7995-0842-1, Band 1, Seite 403.
- Albert Schüle: Heimatbuch der Gemeinde Dettingen unter Teck. Herausgegeben von der Gemeinde Dettingen unter Teck, Gottlieb & Osswald, Kirchheim 1981.
- Karl Buck: Luftfahrt an der Teck – Geschichte und Geschichten zur Fliegerei im Land an der Teck 1928–1958; Gleit-, Segel- und Motorflug. Fluggelände und Privatlandeplatz, Segelflugschule, Flugzeugbau. Buck, Ulm 2008, ISBN 978-3-00-023757-7.
