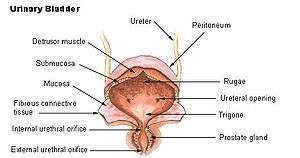
Detrusor urinae muscle
| Detrusor urinae muscle | |
|---|---|
|
Urinary bladder | |
| Details | |
| Origin | posterior surface of the body of the pubis |
| Insertion | prostate (male), vagina (female) |
| Nerve |
Sympathetic - hypogastric n. (T10-L2) Parasympathetic - pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-4) |
| Actions |
Sympathetic relaxes, to store urine Parasympathetic contracts, to urinate |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus detrusor vesicae urinariae |
| TA | A08.3.01.014 |
| FMA | 68018 |
The detrusor urinae muscle, also detrusor muscle, muscularis propria of the urinary bladder and (less precise) muscularis propria, is smooth muscle found in the wall of the bladder. The detrusor muscle remains relaxed to allow the bladder to store urine, and contracts during urination to release urine.[1] Related are the urethral sphincter muscles which envelop the urethra to control the flow of urine when they contract.
Structure
The fibers of the detrusor muscle arise from the posterior surface of the body of the pubis in both sexes (musculi pubovesicales), and in the male from the adjacent part of the prostate and its capsule. These fibers pass, in a more or less longitudinal manner, up the inferior surface of the bladder, over its apex, and then descend along its fundus to become attached to the prostate in the male, and to the front of the vagina in the female. At the sides of the bladder the fibers are arranged obliquely and intersect one another.
The 3 layers of muscles are arranged longitudinal-circular-longitudinal from innermost to outermost.
References
- ↑ Netdoctor.co.uk - The bladder and how it works Reviewed by Dr Hilary McPherson, consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist and Dr Kate Patrick, specialist registrar
External links
- Histology at KUMC urinary/renal18-{{{2}}}
- Detrusor myectomy for detrusor overactivity: 1-year follow-up