Latin America
.svg.png) | |
| Area | 19,197,000 km2 (7,412,000 sq mi)[1] |
|---|---|
| Population | 626,741,000 (2015 est.)[2][lower-alpha 2] |
| Pop. density | 31/km2 (80/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Latin American |
| Countries | 20[lower-alpha 3] |
| Dependencies | 13 |
| Languages |
Mainly: Quechua, Mayan languages, Guaraní, French, Aymara, Nahuatl, Italian, English, Dutch, Welsh |
| Time zones | UTC-2 to UTC-8 |
| Largest cities |
(Metro areas)[3][4] 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. |
Latin America[lower-alpha 1] is the group of countries and dependencies in the Americas where Romance languages are predominant. The term originated in 19th century France to consider French-speaking territories in the Americas along with the larger group of countries where Spanish and Portuguese languages prevailed. It is therefore broader than the terms Ibero-America or Hispanic America—though it usually excludes French Canada.
Latin America consists of nineteen sovereign states and several territories and dependencies which cover an area that stretches from the northern border of Mexico to the southern tip of South America, including the Caribbean. It has an area of approximately 19,197,000 km2 (7,412,000 sq mi),[1] almost 13% of the Earth's land surface area. As of 2015, its population was estimated at more than 626 million[2][lower-alpha 2] and in 2014, Latin America had a combined nominal GDP of 5,573,397 million USD[5] and a GDP PPP of 7,531,585 million USD.[5][6] The term "Latin America" was first used in 1861 in La revue des races Latines, a magazine "dedicated to the cause of Pan-Latinism".[7]
Etymology and definitions
Origin
The idea that a part of the Americas has a linguistic affinity with the Romance cultures as a whole can be traced back to the 1830s, in the writing of the French Saint-Simonian Michel Chevalier, who postulated that this part of the Americas was inhabited by people of a "Latin race", and that it could, therefore, ally itself with "Latin Europe" in a struggle with "Teutonic Europe", "Anglo-Saxon America" and "Slavic Europe".[8] A further investigation of the concept of Latin America is by Michel Gobat in the American Historical Review.[9]
The idea was later taken up by Latin American intellectuals and political leaders of the mid- and late-nineteenth century, who no longer looked to Spain or Portugal as cultural models, but rather to France.[10] The term was first used in Paris in an 1856 conference by the Chilean politician Francisco Bilbao[11] and the same year by the Colombian writer José María Torres Caicedo in his poem "Two Americas".[12]
The term Latin America was supported by the French Empire of Napoleon III during the French invasion of Mexico as a way to include France among countries with influence in the Americas and to exclude Anglophone countries. It played a role in his campaign to imply cultural kinship of the region with France, transform France into a cultural and political leader of the area, and install Maximilian of Habsburg as emperor of the Second Mexican Empire.[13] This term was also used in 1861 by French scholars in La revue des races Latines, a magazine dedicated to the Pan-Latinism movement.[14]
Contemporary definitions


- In one sense, Latin America refers to territories in the Americas where the Spanish or Portuguese languages prevail: Mexico, most of Central and South America, and in the Caribbean, Cuba, the Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico. Latin America is, therefore, defined as all those parts of the Americas that were once part of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires.[15] By this definition, Latin America is coterminous with Ibero-America ("Iberian America").[16]
- Particularly in the United States, the term more broadly refers to all of the Americas south of the United States, thus including the Guianas, the Anglophone Caribbean (and Belize); the Francophone Caribbean; and the Dutch-speaking Caribbean. (In Curaçao and Aruba, Papiamento – a predominantly Iberian-derived creole language – is spoken by the majority of the population.) This definition emphasizes a similar socioeconomic history of the region, which was characterized by formal or informal colonialism, rather than cultural aspects (see, for example, dependency theory).[17] As such, some sources avoid this oversimplification by using the phrase "Latin America and the Caribbean" instead, as in the United Nations geoscheme for the Americas.[18][19][20]
- In a more literal definition, which remains faithful to the semantic origin, Latin America designates countries in the Americas south of the United States where a Romance language (a language derived from Latin) predominates: Spanish, Portuguese, and French and the creole languages based upon these.[21] Cf. Languages of South America and Languages of North America.
- If entities at the sub-national level are included, Quebec would also be considered part of Latin America, while conversely Anglophone Colombia would be excluded, as would the many regions where Amerindian languages predominate. By the same logic, parts of the United States where Spanish and French are official languages (such as New Mexico and Louisiana) would be considered Latin American. However, in practice, Quebec is rarely considered part of Latin America due to the fact that its history, distinctive culture, economy, geographical location, and British-inspired political institutions are generally deemed too closely intertwined with the rest of Canada.[22]
The distinction between Latin America and Anglo-America is a convention based on the predominant languages in the Americas by which Romance-language and English-speaking cultures are distinguished. Neither area is culturally or linguistically homogeneous; in substantial portions of Latin America (e.g., highland Peru, Bolivia, Guatemala, and Paraguay), Native American cultures and, to a lesser extent, Amerindian languages, are predominant, and in other areas, the influence of African cultures is strong (e.g., the Caribbean basin – including parts of Colombia and Venezuela).
Subregions and countries
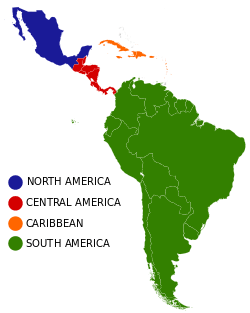
Latin America can be subdivided into several subregions based on geography, politics, demographics and culture. If defined as all of the Americas south of the United States, the basic geographical subregions are North America, Central America, the Caribbean and South America;[23] the latter contains further politico-geographical subdivisions such as the Southern Cone, the Guianas and the Andean states. It may be subdivided on linguistic grounds into Hispanic America, Portuguese America and French America. One exception is the commonwealth of Puerto Rico. The commonwealth is part of the United States of America and its population are all legal US citizens thanks to the Jones-Shafroth Act , signed by President Woodrow Wilson on March 2, 1917. For this reason, all Puerto Ricans are actually Americans and known as US citizens. After the law was signed and passed Puerto Rico, although being in the Latin America region, became a territory of North America, and is no longer part of Latin America regardless of its location.
*: Not a sovereign state
Criticism
The concept of Latin America has been criticized by a number of intellectuals. Historian Jaime Eyzaguirre criticizes the term Latin America for "disguising" and "diluting" the Spanish character of a region (e.g. Hispanic America) with the inclusion of nations that according to him do not share the same pattern of conquest and colonization.[25]
History
Pre-Columbian history


The earliest known settlement was identified at Monte Verde, near Puerto Montt in Southern Chile. Its occupation dates to some 14,000 years ago and there is some disputed evidence of even earlier occupation. Over the course of millennia, people spread to all parts of the continents. By the first millennium CE, South America's vast rainforests, mountains, plains and coasts were the home of tens of millions of people. The earliest settlements in the Americas are of the Las Vegas Culture[26] from about 8000 BCE and 4600 BCE, a sedentary group from the coast of Ecuador, the forefathers of the more known Valdivia culture, of the same era. Some groups formed more permanent settlements such as the Chibcha (or "Muisca" or "Muysca") and the Tairona groups. These groups are in the circum Caribbean region. The Chibchas of Colombia, the Quechuas and Aymaras of Bolivia and Perú were the three indigenous groups that settled most permanently.
The region was home to many indigenous peoples and advanced civilizations, including the Aztecs, Toltecs, Maya, and Inca. The golden age of the Maya began about 250, with the last two great civilizations, the Aztecs and Incas, emerging into prominence later on in the early fourteenth century and mid-fifteenth centuries, respectively. The Aztec empire was ultimately the most powerful civilization known throughout the Americas, until its downfall in part by the Spanish invasion.
European colonization

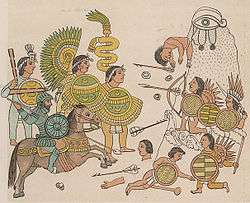
With the arrival of the Europeans following Christopher Columbus' voyages, the indigenous elites, such as the Incas and Aztecs, lost power to the heavy European invasion. Hernándo Cortés seized the Aztec elite's power with the help of local groups who had favored the Aztec elite, and Francisco Pizarro eliminated the Incan rule in Western South America. The European powers of Spain and Portugal colonized the region, which along with the rest of the uncolonized world, was divided into areas of Spanish and Portuguese control by the line of demarcation in 1494, which gave Spain all areas to the west, and Portugal all areas to the east (the Portuguese lands in South America subsequently becoming Brazil). By the end of the sixteenth century Spain and Portugal had been joined by others, including France, in occupying large areas of North, Central and South America, ultimately extending from Alaska to the southern tips of the Patagonia. European culture, customs and government were introduced, with the Roman Catholic Church becoming the major economic and political power to overrule the traditional ways of the region, eventually becoming the only official religion of the Americas during this period.
Epidemics of diseases brought by the Europeans, such as smallpox and measles, wiped out a large portion of the indigenous population. Historians cannot determine the number of natives who died due to European diseases, but some put the figures as high as 85% and as low as 25%. Due to the lack of written records, specific numbers are hard to verify. Many of the survivors were forced to work in European plantations and mines. Intermixing between the indigenous peoples and the European colonists was very common, and, by the end of the colonial period, people of mixed ancestry (mestizos) formed majorities in several colonies.
Slavery and forced labor in colonial Latin America
Indigenous peoples of the Americas in various European colonies were forced to work in European plantations and mines; along with African slaves who were also introduced in the proceeding centuries.
Independence (1804–25)

.jpg)
In 1804, Haiti became the first Latin American nation to gain independence, following a violent slave revolt led by Toussaint L'ouverture on the French colony of Saint-Domingue. The victors abolished slavery. Haitian independence inspired independence movements in Spanish America.
By the end of the eighteenth century, Spanish and Portuguese power waned on the global scene as other European powers took their place, notably Britain and France. Resentment grew among the majority of the population in Latin America over the restrictions imposed by the Spanish government, as well as the dominance of native Spaniards (Iberian-born Peninsulares) in the major social and political institutions. Napoleon's invasion of Spain in 1808 marked a turning point, compelling Criollo elites to form juntas that advocated independence. Also, the newly independent Haiti, the second oldest nation in the New World after the United States, further fueled the independence movement by inspiring the leaders of the movement, such as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla of Mexico, Simón Bolívar of Venezuela and José de San Martín of Argentina, and by providing them with considerable munitions and troops.
Fighting soon broke out between juntas and the Spanish colonial authorities, with initial victories for the advocates of independence. Eventually these early movements were crushed by the royalist troops by 1810, including those of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla in Mexico in the year 1810. Later on Francisco de Miranda in Venezuela by 1812. Under the leadership of a new generation of leaders, such as Simón Bolívar "The Liberator", José de San Martín of Argentina, and other Libertadores in South America, the independence movement regained strength, and by 1825, all Spanish America, except for Puerto Rico and Cuba, had gained independence from Spain. In the same year in Mexico, a military officer, Agustín de Iturbide, led a coalition of conservatives and liberals who created a constitutional monarchy, with Iturbide as emperor. This First Mexican Empire was short-lived, and was followed by the creation of a republic in 1823.

Independent Empire of Brazil

During the invasion of Portugal (1807), the Portuguese royal family fled to Brazil, establishing Rio de Janeiro as the de facto capital of Portugal. This had the side effect of creating within Brazil many of the institutions required to exist as an independent state; most importantly, it freed Brazil to trade with other nations at will. After Napoleon's army was finally defeated in 1815, in order to maintain the capital in Brazil and allay Brazilian fears of being returned to colonial status, King John VI of Portugal raised the de jure status of Brazil to an equal, integral part of a United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil, and the Algarves, rather than a mere colony, a status which it enjoyed for the next seven years.
Tensions between Portuguese and Brazilians increased, and the Portuguese Cortes, guided by the new political regime imposed by the 1820 Liberal Revolution, tried to re-establish Brazil as a colony.[27] The Brazilians refused to yield, and Prince Pedro decided to stand with them, declaring the country's independence from Portugal on 7 September 1822.[28] A month later, Prince Pedro was declared the first Emperor of Brazil, with the regnal title of Dom Pedro I, resulting in the foundation of the Empire of Brazil.[29]
The Brazilian War of Independence, which had already begun along this process, spread through northern, northeastern regions and in Cisplatina province.[30] With the last Portuguese soldiers surrendering on 8 March 1824,[31] Portugal officially recognized Brazil on 29 August 1825.[32]
On 7 April 1831, worn down by years of administrative turmoil and political dissensions with both liberal and conservative sides of politics, including an attempt of republican secession,[33] as well as unreconciled with the way that absolutists in Portugal had given to the succession of King John VI, Pedro I went to Portugal to reclaim his daughter's crown, abdicating the Brazilian throne in favor of his five-year-old son and heir (who thus became the Empire's second monarch, with the regnal title of Dom Pedro II).[34]

As the new Emperor could not exert his constitutional powers until he became of age, a regency was set up by the National Assembly.[35] In the absence of a charismatic figure who could represent a moderate face of power, during this period a series of localized rebellions took place, as the Cabanagem, the Malê Revolt, the Balaiada, the Sabinada, and the Ragamuffin War, which emerged from the dissatisfaction of the provinces with the central power, coupled with old and latent social tensions peculiar of a vast, slaveholding and newly independent nation state.[36] This period of internal political and social upheaval, which included the Praieira revolt, was overcome only at the end of the 1840s, years after the end of the regency, which occurred with the premature coronation of Pedro II in 1841.[37]
During the last phase of the monarchy, internal political debate was centered on the issue of slavery. The Atlantic slave trade was abandoned in 1850,[38] as a result of the British' Aberdeen Act, but only in May 1888 after a long process of internal mobilization and debate for an ethical and legal dismantling of slavery in the country, was the institution formally abolished.[39]
The foreign affairs in the monarchy were basically related issues with the countries of the Southern Cone with which Brazil has borders. Long after the Cisplatine War that resulted in independence for Uruguay,[40] Brazil won three international wars during the 58-year reign of Pedro II. These were the Platine War, the Uruguayan War and the devastating Paraguayan War, the largest war effort in Brazilian history.[41][42]
On 15 November 1889, worn out by years of economic stagnation, in attrition with the majority of Army officers, as well as with rural and financial elites (for different reasons), the monarchy was overthrown by a military coup.[43]
Conservative-liberal conflicts in the 19th Century

Development of Spanish American Independence
After the independence of many Latin American countries, there was conflict between the people and the government, much of which can be reduced to the contrasting ideologies between liberalism and conservatism.[44] Conservatism was the dominant system of government prior to the revolutions and it was founded on having social classes, including governing by kings. Liberalists wanted to see a change in the ruling systems, and to move away from monarchs and social classes in order to promote equality.
When liberal Guadalupe Victoria became the first president of Mexico in 1824, conservatists relied on their belief that the state had been better off before the new government came into power, so, by comparison, the old government was better in the eyes of the Conservatives. Following this sentiment, the conservatives pushed to take control of the government, and they succeeded. General Santa Anna was elected president in 1833. The following decade, the Mexican–American War (1846–48) caused Mexico to lose a significant amount of territory to the United States. This loss led to a rebellion by the enraged liberal forces against the conservative government.
In 1837, conservative Rafael Carrera conquered Guatemala and separated from the Central American Union. The instability that followed the disintegration of the union led to the independence of the other Central American countries.
In Brazil, rural aristocrats were in conflict with the urban conservatives. Portuguese control over Brazilian ports continued after Brazil's independence. Following the conservative idea that the old government was better, urbanites tended to support conservatism because more opportunities were available to them as a result of the Portuguese presence.
Simón Bolívar became president of Gran Colombia in 1819 after the region gained independence from Spain. He led a military-controlled state. Citizens did not like the government's position under Bolívar: The people in the military were unhappy with their roles, and the civilians were of the opinion that the military had too much power. After the dissolution of Gran Colombia, New Grenada continued to have conflicts between conservatives and liberals. These conflicts were each concentrated in particular regions, with conservatives particularly in the southern mountains and the Valley of Cauca. In the mid-1840s some leaders in Caracas organized a liberal opposition. Antonio Leocadio Guzman was an active participant and journalist in this movement and gained much popularity among the people of Caracas.[45]
In Argentina, the conflict manifested itself as a prolongued civil war between unitarianas (i.e. centralists) and federalists, which were in some aspects respectively analogous to liberals and conservatives in other countries. Between 1832 and 1852, the country existed as a confederation, without a head of state, although the federalist governor of Buenos Aires province, Juan Manuel de Rosas, was given the powers of debt payment and international relations and exerted a growing hegemony over the country. A national constitution was only enacted in 1853, reformed in 1860, and the country reorganized as a federal republic led by a liberal-conservative elite.[46] After Uruguay achieved its independence, in 1828, a similar polarization cristallized between blancos and colorados, where the agrarian conservative interests were pitted against the liberal commercial interests based in Montevideo, and which eventually resulted in the Guerra Grande civil war (1839–1851).[47]
British influence in Latin America during 19th century

Losing the North American colonies at the end of the 18th century left Great Britain in need of new markets to supply resources in the early 19th century.[48] In order to solve this problem, Great Britain turned to the Spanish colonies in South America for resources and markets. In 1806 a small British force surprise attacked the capitol of the viceroyalty in Río de la Plata.[49] As a result, the local garrison protecting the capitol was destroyed in an attempt to defend against the British conquest. The British were able to capture numerous amounts of precious metals, before a French naval force intervened on behalf of the Spanish King and took down the invading force. However, this caused much turmoil in the area as militia took control of the area from the viceroy. The next year the British attacked once again with a much larger force attempting to reach and conquer Montevideo.[50] They failed to reach Montevideo but succeeded in establishing an alliance with the locals. As a result, the British were able to take control of the Indian markets.
This newly gained British dominance hindered the development of Latin American industries and strengthened the dependence on the world trade network.[51] Britain now replaced Spain as the region's largest trading partner.[52] Great Britain invested significant capital in Latin America in order to develop the area as a market for processed goods.[53] From the early 1820s to 1850, the post-independence economies of Latin American countries were lagging and stagnant.[48] Eventually, enhanced trade among Britain and Latin America led to state development such as infrastructure improvements. These improvements included roads and railroads which grew the trades between countries and outside nations such as Great Britain.[54] By 1870, exports dramatically increased, attracting capital from abroad (including Europe and USA).[55]
French involvement in Latin America during the 19th century

Between 1821 and 1910, Mexico battled through various civil wars between the established Conservative government and the Liberal reformists ("Mexico Timeline- Page 2)". On May 8, 1827 Baron Damas, the French Minister of Foreign Affairs, and Sebastián Camacho, a Mexican diplomat, signed an agreement called "The Declarations" which contained provisions regarding commerce and navigation between France and Mexico. At this time the French government did not recognise Mexico as an independent entity.[56] It was not until 1861 that the liberalist rebels, led by Benito Juárez, took control of Mexico City, consolidating liberal rule. However, the constant state of warfare left Mexico with a tremendous amount of debt owed to Spain, England, and France, all of whom funded the Mexican war effort (Neeno). As newly appointed president, Benito Juárez suspended payment of debts for next two years, to focus on a rebuilding and stabilization initiative in Mexico under the new government. On December 8, 1861, Spain, England and France landed in Veracruz in order to seize unpaid debts from Mexico. However, Napoleon III, with intentions of establishing a French client state to further push his economic interests, pressured the other two powers to withdraw in 1862 (Greenspan; "French Intervention in Mexico…").

France under Napoleon III remained and established Maximilian of Habsburg, Archduke of Austria, as Emperor of Mexico.[57] The march by the French to Mexico City enticed heavy resistance by the Mexican government, it resulted in open war-fare. The Battle of Puebla in 1862 in particular presented an important turning point in which Ignacio Zaragoza led the Mexican army to victory as they pushed back the French offensive ("Timeline of the Mexican Revolution"). The victory came to symbolize Mexico's power and national resolve against foreign occupancy and as a result delayed France's later attack on Mexico City for an entire year (Cinco de Mayo (Mexican History)). With heavy resistance by Mexican rebels and the fear of United States intervention against France, forced Napoleon III to withdraw from Mexico, leaving Maximilian to surrender, where he would be later executed by Mexican troops under the rule of Porfirio Díaz.[58] Napoleon III's desire to expand France's economic empire influenced the decision to seize territorial domain over the Central American region. The port city of Veracruz, Mexico and France's desire to construct a new canal were of particular interest. Bridging both New World and East Asian trade routes to the Atlantic were key to Napoleon III's economic goals to the mining of precious rocks and the expansion of France's textile industry. Napoleon's fear of the United States' economic influence over the Pacific trade region, and in turn all New World economic activity, pushed France to intervene in Mexico under the pretense of collecting on Mexico's debt. Eventually France began plans to build the Panama Canal in 1881 until 1904 when the United States took over and proceeded with its construction and implementation ("Read Our Story").
United States involvement in Latin America during the 19th Century
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was included in President James Monroe's 1823 annual message to Congress. The doctrine warns European nations that the United States will no longer tolerate any new colonization of Latin American countries. It was originally drafted to meet the present major concerns, but eventually became the precept of U.S. foreign policy in the Western Hemisphere. The doctrine was put into effect in 1865 when the U.S. government supported Mexican president, Benito Juárez, diplomatically and militarily. Some Latin American countries viewed the U.S. interventions, allowed by the Monroe Doctrine when the U.S. deems necessary, with suspicion.[59]
Another important aspect of United States involvement in Latin America is the case of the filibuster William Walker. In 1855, he traveled to Nicaragua hoping to overthrow the government and take the land for the United States. With only the aid of 56 followers, he was able to take over the city of Granada, declaring himself commander of the army and installing Patricio Rivas as a puppet president. However, Rivas's presidency ended when he fled Nicaragua; Walker rigged the following election to ensure that he became the next president. His presidency did not last long, however, as he was met with much opposition from political groups in Nicaragua and neighbouring countries. On May 1, 1857, Walker was forced by a coalition of Central American armies to surrender himself to a United States Navy officer who repatriated him and his followers. When Walker subsequently returned to Central America in 1860, he was apprehended by the Honduran authorities and executed.
Mexican–American War (1846–48)

The Mexican–American War, another instance of U.S. involvement in Latin America, was a war between the United States and Mexico that started in April 1846 and lasted until February 1848. The main cause of the war was the United States' annexation of Texas in 1845 and a dispute afterwards about whether the border between Mexico and the United States ended where Mexico claimed, at the Nueces River, or ended where the United States claimed, at the Rio Grande. Peace was negotiated between the United States and Mexico with the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo, which stated that Mexico was to cede land which would later become part of California and New Mexico as well as give up all claims to Texas, for which the United States would pay $15,000,000. However, tensions between the two countries were still high and over the next six years things only got worse with raids along the border and attacks by Native Americans against Mexican citizens. To defuse the situation, the United States agreed to purchase 29,670 squares miles of land from Mexico for $10,000,000 so a southern railroad could be built to connect the Pacific and Atlantic coasts. This would become known as the Gadsden Purchase. A critical component of U.S. intervention in Latin American affairs took form in the Spanish–American War, which drastically affected the futures of Cuba and Puerto Rico in the Americas, as well as Guam and the Philippines, by dismantling some of the last remaining Spanish colonial possessions throughout the world.
World wars (1914–45)
World War I and the Zimmermann Telegram

The Zimmermann Telegram was a 1917 diplomatic proposal from the German Empire for Mexico to join an alliance with Germany in the event of the United States entering World War I against Germany. The proposal was intercepted and decoded by British intelligence. Revelation of the contents outraged the American public and swayed public opinion. President Woodrow Wilson moved to arm American merchant ships in order to defend themselves against German submarines, which had started to attack them. The news helped generate support for the United States declaration of war on Germany in April of that year.[60]
The message came as a coded telegram dispatched by the Foreign Secretary of the German Empire, Arthur Zimmermann, on January 16, 1917. The message was sent to the German ambassador of Mexico, Heinrich von Eckardt. Zimmermann sent the telegram in anticipation of the resumption of unrestricted submarine warfare by Germany on 1 February, an act which Germany presumed would lead to war. The telegram instructed Ambassador Eckardt that if the U.S. appeared certain to enter the war, he was to approach the Mexican Government with a proposal for military alliance, with funding from Germany. As part of the alliance, Germany would assist Mexico in reconquering Texas and the Southwest. Eckardt was instructed to urge Mexico to help broker an alliance between Germany and Japan. Mexico, in the middle of the Mexican Revolution, far weaker militarily, economically and politically than the U.S., ignored the proposal; after the U.S. entered the war, it officially rejected it.
Brazil's participation in World War II
After World War I, in which Brazil was an ally of the United States, Great Britain, and France, the country realized it needed a more capable army but didn't have the technology to create it. In 1919, the French Military Mission was established by the French Commission in Brazil. Their main goal was to contain the inner rebellions in Brazil. They tried to assist the army by bringing them up to the European military standard but constant civil missions did not prepare them for World War II.
Brazil President, Getúlio Vargas, wanted to industrialize Brazil, allowing it to be more competitive with other countries. He reached out to Germany, Italy, France, and the United States to act as trade allies. Many Italian and German people immigrated to Brazil many years before World War II began thus creating a Nazi influence. The immigrants held high positions in government and the armed forces. It was recently found that 9,000 war criminals escaped to South America, including Croats, Ukrainians, Russians and other western Europeans who aided the Nazi war machine. Most, perhaps as many as 5,000, went to Argentina; between 1,500 and 2,000 are thought to have made it to Brazil; around 500 to 1,000 to Chile; and the rest to Paraguay and Uruguay.[61] It was not a secret that Vargas had an admiration for Hitler's Nazi Germany and its Führer. He even let German Luftwaffe build secret air forces around Brazil, but he knew that he could never favor the Nazis because of their racism towards the large black population in Brazil. This alliance with Germany became Brazil's second best trade alliance behind the United States.

Brazil continued to try to remain neutral to the United States and Germany because it was trying to make sure it could continue to be a place of interest for both opposing countries. Brazil attended continental meetings in Buenos Aires, Argentina (1936); Lima, Peru (1938); and Havana, Cuba (1940) that obligated them to agree to defend any part of the Americas if they were to be attacked. Eventually Brazil decided to stop trading with Germany once Germany started attacking offshore trading ships resulting in Germany declaring a blockade against the Americas in the Atlantic Ocean. Furthermore, Germany also ensured that they would be attacking the Americas soon.
Once the German submarines attacked unarmed Brazilian trading ships, President Vargas met with United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt to discuss how they could retaliate. On January 22, 1942, Brazil officially ended all relations with Germany, Japan, and Italy, becoming a part of the Allies.
The Brazilian Expeditionary Force was sent to Naples, Italy to fight for democracy. Brazil was the only Latin American country to send troops to Europe. Initially, Brazil wanted to only provide resources and shelter for the war to have a chance of gaining a high postwar status but ended up sending 25,000 men to fight.[62]
After World War II, the United States and Latin America continued to have a close relationship. For example, USAID created family planning programs in Latin America combining the NGOs already in place, providing the women in largely Catholic areas access to contraception.[63]
Involvement in World War II
There was Nazi influence in certain parts of the region, but Jewish migration from Europe during the war continued. Only a few people recognized or knew about the Holocaust.[64] Furthermore, numerous military bases were built during the war by the United States, but some also by the Germans. Even now, unexploded bombs from the second world war that need to be made safe still remain.[65]
Cold War (1946–90)
Economy

The Great Depression caused Latin America to grow at a slow rate, separating it from leading industrial democracies. The two world wars and U.S. Depression also made Latin American countries favor internal economic development, leading Latin America to adopt the policy of import substitution industrialization.[67] Countries also renewed emphasis on exports. Brazil began selling automobiles to other countries, and some Latin American countries set up plants to assemble imported parts, letting other countries take advantage of Latin America's low labor costs. Colombia began to export flowers, emeralds and coffee grains and gold, becoming the world's second leading flower exporter.
Economic integration was called for, to attain economies that could compete with the economies of the United States or Europe. Starting in the 1960s with the Latin American Free Trade Association and Central American Common Market, Latin American countries worked toward economic integration.
In efforts to help regain global economic strength the U.S. began to heavily assist countries involved in World War II at the expense of Latin America. Markets that were previously unopposed as a result of the war in Latin America grew stagnant as the rest of the world no longer needed their goods.
Reforms
Large countries like Argentina called for reforms to lessen the disparity of wealth between the rich and the poor, which has been a long problem in Latin America that stunted economic growth.[68]
Advances in public health caused an explosion of population growth, making it difficult to provide social services. Education expanded, and social security systems introduced, but benefits usually went to the middle class, not the poor. As a result, disparity of wealth increased. Increasing inflation and other factors caused countries to be unwilling to fund social development programs to help the poor.
Bureaucratic authoritarianism
Bureaucratic authoritarianism was practiced in Brazil after 1964, in Argentina, and in Chile under Augusto Pinochet, in a response to harsh economic conditions. It rested on the conviction that no democracy could take the harsh measures to curb inflation, reassure investors, and quicken economic growth quickly and effectively. Though inflation fell sharply, industrial production dropped with the decline of official protection.[68]
US relations
After World War II and the beginning of a Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union, US diplomats became interested in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, and frequently waged proxy wars against the Soviet Union in these countries. The US sought to stop the spread of communism. Latin American countries generally sided with the US in the Cold War period, even though they were neglected since the US's concern with communism were focused in Europe and Asia, not Latin America. Between 1946 and 1959 Latin America received only 2% of the United States foreign aid despite having poor conditions similar to the main recipients of The Marshall Plan.[69] Some Latin American governments also complained of the US support in the overthrow of some nationalist governments, and intervention through the CIA. In 1947, the US Congress passed the National Security Act, which created the National Security Council in response to the United States's growing obsession with anti-communism.[70]
In 1954, when Jacobo Arbenz of Guatemala accepted the support of communists and attacked holdings of the United Fruit Company, the US decided to assist Guatemalan counter-revolutionaries in overthrowing Arbenz.[71] These interventionist tactics featured use of the CIA rather than the military, which was used in Latin America for the majority of the Cold War in events including the overthrow of Salvador Allende. Latin America was more concerned with issues of economic development, while the United States focused on fighting communism, even though the presence of communism was small in Latin America.[70]
Cuban Revolution
By 1959, Cuba was afflicted with a corrupt dictatorship under Batista, and Fidel Castro ousted Batista that year and set up the first communist state in the hemisphere. The United States imposed a trade embargo on Cuba, and combined with Castro's expropriation of private enterprises, this was detrimental to the Cuban economy.[67] Around Latin America, rural guerrilla conflict and urban terrorism increased, inspired by the Cuban example. The United States put down these rebellions by supporting Latin American countries in their counter guerrilla operations through the Alliance for Progress launched by President John F. Kennedy. This thrust appeared to be successful. A Marxist, Salvador Allende, became president of Chile in 1970, but was overthrown three years later in a military coup backed by the United States. Despite civil war, high crime and political instability, most Latin American countries eventually adopted bourgeois liberal democracies while Cuba maintained its socialist system.
Bay of Pigs Invasion

Encouraged by the success of Guatemala in the 1954 Guatemalan coup d'état,[72] in 1960, the U.S. decided to support an attack on Cuba by anti-Castro rebels. The Bay of Pigs invasion was an unsuccessful invasion of Cuba in 1961, financed by the U.S. through the CIA, to overthrow Fidel Castro. The incident proved to be very embarrassing for the new Kennedy administration.[73]
Alliance for Progress
President John F. Kennedy initiated the Alliance for Progress in 1961, to establish economic cooperation between the U.S. and Latin America. The Alliance would provide $20 billion for reform in Latin America, and counterinsurgency measures. Instead, the reform failed because of the simplistic theory that guided it and the lack of experienced American experts who could understand Latin American customs.
Nicaraguan Revolution
Following the American occupation of Nicaragua in 1912, as part of the Banana Wars, the Somoza family political dynasty came to power, and would rule Nicaragua until their ouster in 1979 during the Nicaraguan Revolution. The era of Somoza family rule was characterized by strong U.S. support for the government and its military[15] as well as a heavy reliance on U.S. based multi-national corporations. The Nicaraguan Revolution (Spanish: Revolución Nicaragüense or Revolución Popular Sandinista) encompassed the rising opposition to the Somoza dictatorship in the 1960s and 1970s, the campaign led by the Sandinista National Liberation Front (FSLN) to violently oust the dictatorship in 1978–79, the subsequent efforts of the FSLN to govern Nicaragua from 1979 until 1990 and the Contra War which was waged between the FSLN and the Contras from 1981–1990.
The Revolution marked a significant period in Nicaraguan history and revealed the country as one of the major proxy war battlegrounds of the Cold War with the events in the country rising to international attention. Although the initial overthrow of the Somoza regime in 1978–79 was a bloody affair, the Contra War of the 1980s took the lives of tens of thousands of Nicaraguans and was the subject of fierce international debate.[74] During the 1980s both the FSLN (a Leftist collection of political parties) and the Contras (a rightist collection of counter-revolutionary groups) received large amounts of aid from the Cold War super-powers (respectively, the Soviet Union and the United States).
Washington Consensus

The set of specific economic policy prescriptions that were considered the "standard" reform package were promoted for crisis-wracked developing countries by Washington, D.C.-based institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and the US Department of the Treasury during the 1980s and 1990s.
In recent years, several Latin American countries led by socialist or other left wing governments – including Argentina and Venezuela – have campaigned for (and to some degree adopted) policies contrary to the Washington Consensus set of policies. (Other Latin countries with governments of the left, including Brazil, Chile and Peru, have in practice adopted the bulk of the policies.) Also critical of the policies as actually promoted by the International Monetary Fund have been some US economists, such as Joseph Stiglitz and Dani Rodrik, who have challenged what are sometimes described as the "fundamentalist" policies of the International Monetary Fund and the US Treasury for what Stiglitz calls a "one size fits all" treatment of individual economies.
The term has become associated with neoliberal policies in general and drawn into the broader debate over the expanding role of the free market, constraints upon the state, and US influence on other countries' national sovereignty.
This politico-economical initiative was institutionalized in North America by the 1994 NAFTA, and elsewhere in the Americas through a series of like agreements. The comprehensive Free Trade Area of the Americas project, however, was rejected by most South American countries at the 2005 4th Summit of the Americas.
Turn to the left

In most countries, since the 2000s left-wing political parties have risen to power. The presidencies of Hugo Chávez in Venezuela, Ricardo Lagos and Michelle Bachelet in Chile, Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff in Brazil, Néstor Kirchner and his wife Cristina Fernández in Argentina, Tabaré Vázquez and José Mujica in Uruguay, Evo Morales in Bolivia, Daniel Ortega in Nicaragua, Rafael Correa in Ecuador, Fernando Lugo in Paraguay, Manuel Zelaya in Honduras (removed from power by a coup d'état), Mauricio Funes and Salvador Sánchez Cerén in El Salvador are all part of this wave of left-wing politicians who often declare themselves socialists, Latin Americanists, or anti-imperialists (often implying opposition to US policies towards the region). A development of this has been the creation of the eight-member ALBA alliance, or "The Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America" (Spanish: Alianza Bolivariana para los Pueblos de Nuestra América) by some of the countries already mentioned. By June 2014, Honduras (Juan Orlando Hernández), Guatemala (Otto Pérez Molina), Colombia (Juan Manuel Santos) and Panama (Ricardo Martinelli) had right-wing governments.
Return of social movements
In 1982, Mexico announced that it could not meet its foreign debt payment obligations, inaugurating a debt crisis that would "discredit" Latin American economies throughout the decade.[75] This debt crisis would lead to neoliberal reforms that would instigate many social movements in the region. A "reversal of development" reigned over Latin America, seen through negative economic growth, declines in industrial production, and thus, falling living standards for the middle and lower classes.[76] Governments made financial security their primary policy goal over social security, enacting new neoliberal economic policies that implemented privatization of previously national industries and informalization of labor.[75] In an effort to bring more investors to these industries, these governments also embraced globalization through more open interactions with the international economy.
Significantly, as democracy spread across much of Latin America, the realm of government more inclusive (a trend that proved conductive to social movements), the economic ventures remained exclusive to a few elite groups within society. Neoliberal restructuring consistently redistributed income upward while denying political responsibility to provide social welfare rights, and though development projects took place throughout the region, both inequality and poverty increased.[75] Feeling excluded from these new projects, the lower classes took ownership of their own democracy through a revitalization of social movements in Latin America.
Both urban and rural populations had serious grievances as a result of the above economic and global trends and have voiced them in mass demonstrations. Some of the largest and most violent of these have been protests against cuts in urban services, such as the Caracazo in Venezuela and the Argentinazo in Argentina.[77]

Rural movements have made diverse demands related to unequal land distribution, displacement at the hands of development projects and dams, environmental and indigenous concerns, neoliberal agricultural restructuring, and insufficient means of livelihood. These movements have benefited considerably from transnational support from conservationists and INGOs. The Movement of Rural Landless Workers (MST) is perhaps the largest contemporary Latin American social movement.[77] As indigenous populations are primarily rural, indigenous movements account for a large portion of rural social movements, including the Zapatista rebellion in Mexico, the Confederation of Indigenous Nationalities of Ecuador (CONAIE), indigenous organizations in the Amazon region of Ecuador and Bolivia, pan-Mayan communities in Guatemala, and mobilization by the indigenous groups of Yanomami peoples in the Amazon, Kuna peoples in Panama, and Altiplano Aymara and Quechua peoples in Bolivia.[77] Other significant types of social movements include labor struggles and strikes, such as recovered factories in Argentina, as well as gender-based movements such as the Mothers of the Plaza de Mayo in Argentina and protests against maquila production, which is largely a women's issue because of how it draws on women for cheap labor.[77]
Commodity boom and increasing relations with China
The 2000s commodities boom caused positive effects for many Latin American economies. Another trend is the rapidly increasing importance of the relations with China.[78]
Demographics
| Historical populations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1750 | 16,000,000 | — |
| 1800 | 24,000,000 | +50.0% |
| 1850 | 38,000,000 | +58.3% |
| 1900 | 74,000,000 | +94.7% |
| 1950 | 167,000,000 | +125.7% |
| 1999 | 511,000,000 | +206.0% |
| 2013 | 603,191,486 | +18.0% |
| Source: "UN report 2004 data" (PDF). | ||
Largest cities
The following is a list of the ten largest metropolitan areas in Latin America.[3]
| City | Country | Metropolitan population (2015) | Gross Domestic Product (USD, 2015) | GDP per capita (USD, 2015) | Global economic ranking by GDP (2015) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mexico City | | 22,976,700 | $490.6 billion | $16,239 | 12th |
| 2. | São Paulo | | 20,847,500 | $530.9 billion | $25,650 | 10th |
| 3. | Buenos Aires | | 15,481,800 | $482.9 billion | $35,906 | 13th |
| 4. | Rio de Janeiro | | 12,460,200 | $356.6 billion | $23,176 | 28th |
| 5. | Lima | | 10,674,116 | $206.4 billion | $15,530 | 48th |
| 6. | Bogotá | | 9,135,800 | $195.9 billion | $21,497 | 51st |
| 7. | Santiago | | 7,164,400 | $191.4 billion | $28,929 | 53rd |
| 8. | Belo Horizonte | | 5,595,800 | $120.7 billion | $20,134 | 81st |
| 9. | Caracas | | 3,260,200 | $85.8 billion | $15,890 | 161st |
| 10. | Guadalajara | | 4,687,700 | $80.7 billion | $14,206 | 162nd |
Ethnic groups
The inhabitants of Latin America are of a variety of ancestries, ethnic groups, and races, making the region one of the most diverse in the world. The specific composition varies from country to country: many have a predominance of European-Amerindian or more commonly referred to as Mestizo or Castizo depending on the admixture, population; in others, Amerindians are a majority; some are dominated by inhabitants of European ancestry; and some countries' populations are primarily Mulatto. Asian and Afro-Amerindian (historically sometimes called Zambo) minorities are also identified regularly. People with European ancestry are the largest single group, and along with people of part-European ancestry, they combine to make up approximately 80% of the population,[80] or even more.[81]
Language
Spanish and Portuguese are the predominant languages of Latin America. Spanish is spoken as first language by about 60% of the population, Portuguese is spoken by about 34% of the population and about 6% of the population speak other languages such as Quechua, Mayan languages, Guaraní, Aymara, Nahuatl, English, French, Dutch and Italian. Portuguese is spoken only in Brazil (Brazilian Portuguese), the biggest and most populous country in the region. Spanish is the official language of most of the rest of the countries on the Latin American mainland (Spanish language in the Americas), as well as in Cuba, Puerto Rico (where it is co-official with English), and the Dominican Republic. French is spoken in Haiti and in the French overseas departments of Guadeloupe, Martinique and Guiana, and the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon; it is also spoken by some Panamanians of Afro-Antillean descent. Dutch is the official language in Suriname, Aruba, and the Netherlands Antilles. (As Dutch is a Germanic language, these territories are not necessarily considered part of Latin America.)

Native American languages are widely spoken in Peru, Guatemala, Bolivia, Paraguay and Mexico, and to a lesser degree, in Panama, Ecuador, Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, Argentina, and Chile amongst other countries. In Latin American countries not named above, the population of speakers of indigenous languages tend to be very small or even non-existent (e.g. Uruguay). Mexico is possibly the only country that contains a wider variety of indigenous languages than any Latin American country, but the most spoken language is Nahuatl.
In Peru, Quechua is an official language, alongside Spanish and any other indigenous language in the areas where they predominate. In Ecuador, while holding no official status, the closely related Quichua is a recognized language of the indigenous people under the country's constitution; however, it is only spoken by a few groups in the country's highlands. In Bolivia, Aymara, Quechua and Guaraní hold official status alongside Spanish. Guaraní, along with Spanish, is an official language of Paraguay, and is spoken by a majority of the population (who are, for the most part, bilingual), and it is co-official with Spanish in the Argentine province of Corrientes. In Nicaragua, Spanish is the official language, but on the country's Caribbean coast English and indigenous languages such as Miskito, Sumo, and Rama also hold official status. Colombia recognizes all indigenous languages spoken within its territory as official, though fewer than 1% of its population are native speakers of these languages. Nahuatl is one of the 62 native languages spoken by indigenous people in Mexico, which are officially recognized by the government as "national languages" along with Spanish.
Other European languages spoken in Latin America include: English, by some groups in Puerto Rico, as well as in nearby countries that may or may not be considered Latin American, like Belize and Guyana; German, in southern Brazil, southern Chile, portions of Argentina, Venezuela and Paraguay; Italian, in Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela, and Uruguay; Ukrainian, Polish and Russian in southern Brazil, and Welsh, in southern Argentina.[82][83][84][85][86][87] Yiddish and Hebrew are possible to be heard around Buenos Aires and São Paulo especially.[88] Non-European or Asian languages include Japanese in Brazil and Peru, Korean in Brazil, Arabic in Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela and Chile and Chinese throughout South America.
In several nations, especially in the Caribbean region, creole languages are spoken. The most widely spoken creole language in Latin America and the Caribbean is Haitian Creole, the predominant language of Haiti; it is derived primarily from French and certain West African tongues with Amerindian, English, Portuguese and Spanish influences as well. Creole languages of mainland Latin America, similarly, are derived from European languages and various African tongues.
The Garifuna language is spoken along the Caribbean coast in Honduras, Guatemala, Nicaragua and Belize mostly by the Garifuna people a mixed race Zambo people who were the result of mixing between Indigenous Caribbeans and escaped Black slaves. Primarily an Arawakan language, it has influences from Caribbean and European languages.
Religion

The vast majority of Latin Americans are Christians (90%),[89] mostly Roman Catholics belonging to the Latin Church.[90] About 70% of the Latin American population consider themselves Catholic.[91]
Migration
Due to economic, social and security developments that are affecting the region in recent decades, the focus is now the change from net immigration to net emigration. About 10 million Mexicans live in the United States.[92] 31.7 million Americans listed their ancestry as Mexican as of 2010, or roughly 10% of the population.[93] According to the 2005 Colombian census or DANE, about 3,331,107 Colombians currently live abroad.[94] The number of Brazilians living overseas is estimated at about 2 million people.[95] An estimated 1.5 to two million Salvadorans reside in the United States.[96] At least 1.5 million Ecuadorians have gone abroad, mainly to the United States and Spain.[97] Approximately 1.5 million Dominicans live abroad, mostly in the United States.[98] More than 1.3 million Cubans live abroad, most of them in the United States.[99] It is estimated that over 800,000 Chileans live abroad, mainly in Argentina, the United States, Canada, Australia and Sweden.[100] An estimated 700,000 Bolivians were living in Argentina as of 2006 and another 33,000 in the United States.[101] Central Americans living abroad in 2005 were 3,314,300,[102] of which 1,128,701 were Salvadorans,[103] 685,713 were Guatemalans,[104] 683,520 were Nicaraguans,[105] 414,955 were Hondurans,[106] 215,240 were Panamanians,[107] 127,061 were Costa Ricans[108] and 59,110 were Belizeans.
For the period 2000–2005, Chile, Costa Rica, Panama, and Venezuela were the only countries with global positive migration rates, in terms of their yearly averages.[109]
Education
Despite significant progress, education access and school completion remains unequal in Latin America. The region has made great progress in educational coverage; almost all children attend primary school and access to secondary education has increased considerably. Quality issues such as poor teaching methods, lack of appropriate equipment and overcrowding exist throughout the region. These issues lead to adolescents dropping out of the educational system early.[110] Most educational systems in the region have implemented various types of administrative and institutional reforms that have enabled reach for places and communities that had no access to education services in the early 1990s. Compared to prior generations, Latin American youth have seen an increase in their levels of education. On average, they have completed two years schooling more than their parents.[110]
However, there are still 23 million children in the region between the ages of 4 and 17 outside of the formal education system. Estimates indicate that 30% of preschool age children (ages 4–5) do not attend school, and for the most vulnerable populations, the poor and rural, this calculation exceeds 40 percent. Among primary school age children (ages 6 to 12), coverage is almost universal; however there is still a need to incorporate 5 million children in the primary education system. These children live mostly in remote areas, are indigenous or Afro-descendants and live in extreme poverty.[111]
Among people between the ages of 13 and 17 years, only 80% are full-time students in the education system; among them only 66% advance to secondary school. These percentages are lower among vulnerable population groups: only 75% of the poorest youth between the ages of 13 and 17 years attend school. Tertiary education has the lowest coverage, with only 70% of people between the ages of 18 and 25 years outside of the education system. Currently, more than half of low income children or living in rural areas fail to complete nine years of education.[111]
Crime and violence
Latin America and the Caribbean have been cited by numerous sources to be the most dangerous regions in the world.[112][113] Studies have shown that Latin America contains the majority of the world's most dangerous cities. Many analysts attribute the reason to why the region has such an alarming crime rate and criminal culture is largely due to social and income inequality within the region, they say that growing social inequality is fueling crime in the region.[114] Many agree that the prison crisis will not be resolved until the gap between the rich and the poor is addressed.

Crime and violence prevention and public security are now important issues for governments and citizens in Latin America and the Caribbean region. Homicide rates in Latin America are the highest in the world. From the early 1980s through the mid-1990s, homicide rates increased by 50 percent. The major victims of such homicides are young men, 69 percent of whom are between the ages of 15 and 19 years old. Countries with the highest homicide rate per year per 100,000 inhabitants as of 2014 were: Honduras 95.2, Venezuela 57.2, Belize 43.8, El Salvador 42.6, Guatemala 38.5, Colombia 31.4, Puerto Rico 27.2, Brazil 26.1, Dominican Republic 23.4 and Mexico 22.3.[115] Compared to the world average homicide rating of 6.9, the country with the highest rating in Latin America is more than 13x's the world average. The top 10 highest homicide rates per 100,000 inhabitants ever recorded since 1995 were entirely made up of countries from Latin America and they were El Salvador, Honduras, and Colombia with El Salvador scoring the highest homicide rate ever recorded at 139.1 back in 1995.[116]
Brazil has more overall homicides than any country in the world, at 50,108, accounting for one in 10 globally.[115] In Colombia alone, one person was murdered every 10 minutes in 2005.[117] Amnesty International has even named Latin America as the most dangerous region in the world for journalists to work.[118] Crime-related violence in Latin America represents the most threat to public health, striking more victims than HIV/AIDS or other infectious diseases.[119] Countries with low crime rates in Latin America are Argentina, Chile, Cuba, Costa Rica, Panama and Uruguay.[120]
Economy
Size
According to Goldman Sachs' BRICS review of emerging economies, by 2050 the largest economies in the world will be as follows: China, United States, India, Japan, Germany, United Kingdom, Brazil and Mexico.[121]
| Country | Population[122] (2010) Millions |
2015 GDP (Nominal)[123] In Billions US$ |
2015 GDP (PPP) In Billions US$ |
|---|---|---|---|
| |
43.5 | 601.7 | 972.3 |
| |
9.9 | 33.5 | 73.9 |
| |
201 | 1,799.6 | 3,207.9 |
| |
17.1 | 240.0 | 424.3 |
| |
45 | 274.0 | 665.0 |
| |
4.7 | 51.6 | 74.1 |
| |
11.3 | N/A | N/A |
| |
10.5 | 66.6 | 147.6 |
| |
14.5 | 98.9 | 181.8 |
| |
6.2 | 25.7 | 52.9 |
| |
15.5 | 63.2 | 125.6 |
| |
10.0 | 8.8 | 19.0 |
| |
7.6 | 19.9 | 41.0 |
| |
113.4 | 1,161.0 | 2,220.1 |
| |
5.8 | 12.3 | 31.2 |
| |
3.5 | 47.5 | 82.2 |
| |
6.5 | 29.1 | 60.8 |
| |
29.1 | 179.9 | 385.4 |
| |
3.4 | 55.0 | 74.2 |
| |
29.0 | 131.9 | 491.6 |
| Total | 577.8 | N/A | N/A |
Development
Over the past two centuries, Latin America’s GDP per capita has fluctuated around world average. However, there is a substantial gap between Latin America and the western economies. Between 1820 and 2008, this gap widened from 0.8 to 2.7 times.[124] Since 1980, Latin America also lost growth versus the world average. Many nations such as Asia joined others on a rapid economic growth path, but Latin America has grown at slower pace and its share of world output declined from 9.5 % in 1980 to 7.8% in 2008.[125]
Standard of living
Latin America is the region with the highest levels of income inequality in the world.[126] The following table lists all the countries in Latin America indicating a valuation of the country's Human Development Index, GDP at purchasing power parity per capita, measurement of inequality through the Gini index, measurement of poverty through the Human Poverty Index, measurement of extreme poverty based on people living under 1.25 dollars a day, life expectancy, murder rates and a measurement of safety through the Global Peace Index. Green cells indicate the best performance in each category while red indicates the lowest.
| Country | HDI 2015 Estimates |
GDP (PPP) 2015 Per Capita In US$ [127] |
Real GDP 2015 Growth % |
Income inequality[128] (2011) Gini |
Extreme Poverty[129] (2011) <1.25 US$ % |
Youth Literacy[130] 2015% |
2016 Life Expectancy[131] |
Murder[132] (2012) Rate per 100,000 |
Peace[133] (2014) GPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
0.836 | 20,170 | 5.4 | 45.8 | 0.9 | 99.2 | 81 | 2.4 | 1.789 |
| |
0.662 | 6,421 | 4.1 | 57.3 | 14.0 | 99.4 | 69 | 8.9 | 1.969 |
| |
0.755 | 15,690 | −3.0 | 53.9 | 0.3 | 97.5 | 74 | 26.1[115] | 2.073 |
| |
0.832 | 23,564 | 2.3 | 52.1 | 0.8 | 98.9 | 79 | 3.2 | 1.591 |
| |
0.720 | 13,794 | 2.5 | 53.9[134] | 8.2 | 98.2 | 76 | 31[135] | 2.701 |
| |
0.766 | 15,318 | 3.0 | 50.3 | 0.7 | 98.3 | 79 | 11.3 | 1.781 |
| |
0.769 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 100.0 | 79 | 5.0 | 1.986 |
| |
0.702 | 15,777 | 5.5 | 48.4 | 4.3 | 97.0 | 78 | 25.0 | 2.093 |
| |
0.732 | 11,168 | −0.6 | 49.0 | 5.1 | 98.7 | 77 | 15.2 | 2.042 |
| |
0.666 | 8,293 | 2.3 | 46.9 | 15.1 | 96.0 | 75 | 42.6[115] | 2.280 |
| |
0.627 | 7,721 | 3.8 | 53.7 | 16.9 | 87.4 | 72 | 38.5 | 2.248 |
| |
0.483 | 1,794 | 2.5 | 59.5 | 54.9 | 72.3 | 64 | 6.9 | 2.127 |
| |
0.606 | 4,861 | 3.5 | 57.7 | 23.3 | 95.9 | 71 | 95.2[115] | 2.281 |
| |
0.756 | 18,335 | 2.3 | 51.7 | 8.4 | 98.5 | 77 | 22.7 | 2.500 |
| |
0.631 | 4,972 | 4.0 | 52.3 | 15.8 | 87.0 | 73 | 13.6 | 1.882 |
| |
0.780 | 20,512 | 6.0 | 52.3 | 9.5 | 97.6 | 79 | 21.6 | 1.877 |
| |
0.679 | 8,671 | 3.0 | 52.0 | 5.1 | 98.6 | 77 | 11.5 | 1.976 |
| |
0.734 | 12,077 | 2.4 | 48.0 | 5.9 | 97.4 | 74 | 10.3 | 2.304 |
| |
0.793 | 21,719 | 2.5 | 42.4 | 0.0 | 98.8 | 77 | 5.9 | 1.565 |
| |
0.762 | 15,892 | −10.0 | 43.5 | 3.5 | 98.5 | 75 | 57.2[115] | 2.410 |
Environment
 |
 |
 | ||


| Country | Environmental performance[137] (2012) EPI |
CO2 emissions[138] (2009) (tons of CO2 per capita) |
|---|---|---|
| |
56.48 | 4.14 |
| |
54.57 | 1.31 |
| |
60.90 | 1.74 |
| |
55.34 | 3.84 |
| |
62.33 | 1.33 |
| |
69.03 | 1.37 |
| |
56.48 | 2.40 |
| |
52.44 | 1.79 |
| |
60.55 | 2.09 |
| |
52.08 | 1.10 |
| |
51.88 | 1.03 |
| |
41.15 | 0.24 |
| |
52.54 | 0.96 |
| |
49.11 | 3.72 |
| |
59.23 | 0.73 |
| |
57.94 | 2.10 |
| |
52.40 | 0.64 |
| |
50.29 | 1.32 |
| |
57.06 | 2.31 |
| |
55.62 | 5.45 |
Inequality
_02.jpg)

Poverty continues to be one of the region's main challenges; according to the ECLAC, Latin America is the most unequal region in the world.[139] Inequality is undermining the region's economic potential and the well-being of its population, since it increases poverty and reduces the impact of economic development on poverty reduction.[140] Children in Latin America are often forced to seek work on the streets when their families can no longer afford to support them, leading to a substantial population of street children in Latin America.[141] According to some estimates, there are 40 million street children in Latin America.[142] Inequality in Latin America has deep historical roots in the Latin European racially based Casta system[143][144][145][146][147][148][149] instituted in Latin America in colonial times that have been difficult to eradicate since the differences between initial endowments and opportunities among social groups have constrained the poorest's social mobility, thus making poverty to be transmitted from generation to generation, becoming a vicious cycle. High inequality is rooted in the deepest exclusionary institutions of the Casta system[150][151][152] that have been perpetuated ever since colonial times and that have survived different political and economic regimes. Inequality has been reproduced and transmitted through generations because Latin American political systems allow a differentiated access on the influence that social groups have in the decision making process, and it responds in different ways to the least favored groups that have less political representation and capacity of pressure.[153] Recent economic liberalisation also plays a role as not everyone is equally capable of taking advantage of its benefits.[154] Differences in opportunities and endowments tend to be based on race, ethnicity, rurality and gender. Because inequality in gender and location are near universal, race and ethnicity play a larger, more integral role in the unequal discriminatory practices in Latin America. These differences have a strong impact on the distribution of income, capital and political standing.
In 2008, According to UNICEF, Latin America and the Caribbean region had the highest combined income inequality in the world with a measured net Gini coefficient of 48.3, an unweighted average which is considerably higher than the world's Gini coefficient average of 39.7. Gini is the statistical measurement used to measure income distribution across entire nations and their populations and their income inequality. The other regional averages were: sub-Saharan Africa (44.2), Asia (40.4), Middle East and North Africa (39.2), Eastern Europe and Central Asia (35.4), and high-income nations (30.9).[155]
According to a study by the World Bank,the richest decile of the population of Latin America earn[156] 48% of the total income, while the poorest 10% of the population earn only 1.6% of the income. In contrast, in developed countries, the top decile receives 29% of the total income, while the bottom decile earns 2.5%. The countries with the highest inequality in the region (as measured with the Gini index in the UN Development Report[157]) in 2007 were Haiti (59.5), Colombia (58.5), Bolivia (58.2), Honduras (55.3), Brazil (55.0), and Panama (54.9), while the countries with the lowest inequality in the region were Venezuela (43.4), Uruguay (46.4) and Costa Rica (47.2).

According to the World Bank, the poorest countries in the region were (as of 2008):[158] Haiti, Nicaragua, Bolivia and Honduras. Undernourishment affects to 47% of Haitians, 27% of Nicaraguans, 23% of Bolivians and 22% of Hondurans.
Many countries in Latin America have responded to high levels of poverty by implementing new, or altering old, social assistance programs such as conditional cash transfers. These include Mexico's Progresa Oportunidades, Brazil's Bolsa Escola and Bolsa Familia, Panama's Red de Oportunidades and Chile's Chile Solidario.[159] In general, these programs provide money to poor families under the condition that those transfers are used as an investment on their children's human capital, such as regular school attendance and basic preventive health care. The purpose of these programs is to address the inter-generational transmission of poverty and to foster social inclusion by explicitly targeting the poor, focusing on children, delivering transfers to women, and changing social accountability relationships between beneficiaries, service providers and governments.[160] These programs have helped to increase school enrollment and attendance and they also have shown improvements in children's health conditions.[161] Most of these transfer schemes are now benefiting around 110 million people in the region and are considered relatively cheap, costing around 0.5% of their GDP.[162] In some countries e.g. in Peru decentralisation is hoped to help address social justice and poverty better. NGOs which addressed those problems on the local level before could help with that.[163]
Trade blocs

The major trade blocs (or agreements) in the region are the Pacific Alliance and Mercosur. Minor blocs or trade agreements are the G3 Free Trade Agreement, the Dominican Republic – Central America Free Trade Agreement (DR-CAFTA), the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Andean Community of Nations (CAN). However, major reconfigurations are taking place along opposing approaches to integration and trade; Venezuela has officially withdrawn from both the CAN and G3 and it has been formally admitted into the Mercosur (pending ratification from the Paraguayan legislature). The president-elect of Ecuador has manifested his intentions of following the same path. This bloc nominally opposes any Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the United States, although Uruguay has manifested its intention otherwise. Chile, Peru, Colombia and Mexico are the only four Latin American nations that have an FTA with the United States and Canada, both members of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
Tourism

Income from tourism is key to the economy of several Latin American countries.[164] Mexico is the only Latin American country to be ranked in the top 10 worldwide in the number of tourist visits. It received by far the largest number of international tourists, with 29.1 million visitors in 2014, followed by Brazil, with 6.4 million; Argentina, with 5.9 million; Dominican Republic, with 5.1 million, Chile, with 3.6 million, Puerto Rico with 3.2 million, Peru with 3.2 million; Cuba with 2.9 million; Uruguay,with 2.6 million; and Colombia, with 2.5 million.[165] Places such as Cancún, Galápagos Islands, Machu Picchu, Chichen Itza, Cartagena de Indias, Cabo San Lucas, Acapulco, Rio de Janeiro, Salvador, Margarita Island, San Ignacio Miní, Buenos Aires, São Paulo, Salar de Uyuni, Punta del Este, Santo Domingo, Labadee, San Juan, La Habana, Panama City, Iguazú Falls, Puerto Vallarta, Poás Volcano National Park, Punta Cana, Viña del Mar, Mexico City, Quito, Bogotá, Santa Marta, San Andrés, Lima, Maceió, Fortaleza, Florianópolis, Cuzco, Ponce, Perito Moreno Glacier and Patagonia are popular among international visitors in the region.
| Country | International tourist arrivals[165] (2014) (1000s) |
Tourism receipts[166] (2011) (Millions of US$) |
Tourism receipts (2011) (US$ per arrival) |
Tourism receipts (2011) (US$ per capita) |
Tourism receipts[167] (2003) (as % of GDP) |
Tourism receipts[168] (2003) (as % of exports) |
Direct and indirect employment[169] in tourism (2005) (%) |
Tourism competitiveness[170] (2011) (TTCI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
5,935 | 5,353 | 945 | 133 | 7.4 | 1.8 | 9.1 | 4.20 |
| |
798 2013 arrivals | 310 | 384 | 31 | 9.4 | 2.2 | 7.6 | 3.35 |
| |
5,813 2013 arrivals | 6,555 | 1,207 | 34 | 3.2 | 0.5 | 7.0 | 4.36 |
| |
3,673 | 1,831 | 596 | 107 | 5.3 | 1.9 | 6.8 | 4.27 |
| |
2,565 | 4,061 | 873 | 45 | 6.6 | 1.4 | 5.9 | 3.94 |
| |
2,527 | 2,156 | 982 | 459 | 17.5 | 8.1 | 13.3 | 4.43 |
| |
2,970 | 2,187 | 872 | 194 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| |
5,141 | 4,353 | 1,011 | 440 | 36.2 | 18.8 | 19.8 | 3.99 |
| |
1,557 | 837 | 734 | 58 | 6.3 | 1.5 | 7.4 | 3.79 |
| |
1,345 | 415 | 351 | 67 | 12.9 | 3.4 | 6.8 | 3.68 |
| |
1,455 | 1,350 | 1,102 | 94 | 16.0 | 2.6 | 6.0 | 3.82 |
| |
465 | 167 | 655 | 17 | 19.4 | 3.2 | 4.7 | N/A |
| |
868 | 701 | 753 | 92 | 13.5 | 5.0 | 8.5 | 3.79 |
| |
29,091 | 11,869 | 507 | 105 | 5.7 | 1.6 | 14.2 | 4.43 |
| |
1,330 | 377 | 356 | 65 | 15.5 | 3.7 | 5.6 | 3.56 |
| |
1,745 | 1,926 | 1,308 | 550 | 10.6 | 6.3 | 12.9 | 4.30 |
| |
649 | 241 | 460 | 37 | 4.2 | 1.3 | 6.4 | 3.26 |
| |
3,215 | 2,360 | 908 | 81 | 9.0 | 1.6 | 7.6 | 4.04 |
| |
2,682 | 2,187 | 765 | 643 | 14.2 | 3.6 | 10.7 | 4.24 |
| |
986 2013 arrivals | 739 | 1,449 | 25 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 8.1 | 3.46 |
Culture
.jpg)

Latin American culture is a mixture of many cultural expressions worldwide. It is the product of many diverse influences:
- Indigenous cultures of the people who inhabited the continent prior to European Colonization. Ancient and very advanced civilizations developed their own political, social and religious systems. The Mayas, the Aztecs and the Incas are examples of these. Indigenous legacies in music, dance, foods, arts and crafts, clothing, folk culture and traditions are very strong in Latin America. Linguistic effects on Spanish and Portuguese are also marked, such as in terms like pampa, taco, tamale, cacique.
- Western civilization, in particular the culture of Europe, was brought mainly by the colonial powers – the Spanish, Portuguese and French – between the 16th and 19th centuries. The most enduring European colonial influence is language and Roman Catholicism. More recently, additional cultural influences came from the United States and Europe during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, due to the growing influence of the former on the world stage and immigration from the latter. The influence of the United States is particularly strong in northern Latin America, especially Puerto Rico, which is an American territory. Prior to 1959, Cuba, who fought for its independence along American soldiers in the Spanish–American War, was also known to have a close socioeconomic relation with the United States. In addition, the United States also helped Panama become an independent state from Colombia and built the twenty-mile-long Panama Canal Zone in Panama which held from 1903 (the Panama Canal opened to transoceanic freight traffic in 1914) to 1999, when the Torrijos-Carter Treaties restored Panamanian control of the Canal Zone. South America experienced waves of immigration of Europeans, especially Italians, Spaniards, Portuguese, Germans, Austrians, Poles, Ukrainians, French, Dutch, Russians, Croatians, Lithuanians and Ashkenazi Jews. With the end of colonialism, French culture was also able to exert a direct influence in Latin America, especially in the realms of high culture, science and medicine.[172] This can be seen in any expression of the region's artistic traditions, including painting, literature and music, and in the realms of science and politics.
Due to the impact of Enlightenment ideals after the French revolution, a certain number of Iberian-American countries decriminalized homosexuality after France and French territories in the Americas in 1791. Some of the countries that abolished sodomy laws or banned any reference to state interference in consensual adult sexuality in the 19th century were Dominican Republic (1822), Brazil (1824), Peru (1836), Mexico (1871), Paraguay (1880), Argentina (1887), Honduras (1899), Guatemala and El Salvador. Today gay marriage is legal in Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, and French overseas departments, as well as in some states of Mexico. Civil unions can be held in Colombia, Ecuador, Chile and one administrative region of Venezuela.
- African cultures, whose presence derives from a long history of New World slavery. Peoples of African descent have influenced the ethno-scapes of Latin America and the Caribbean. This is manifested for instance in music, dance and religion, especially in countries like Belize, Brazil, Uruguay, Honduras, Puerto Rico, Venezuela, Colombia, Panama, Haiti, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, and Cuba.
- Asian cultures, whose part of the presence derives from the long history of the Coolie trade mostly arriving during the 19th and 20th centuries, and most commonly Chinese workers in Peru and Venezuela. But also from Japanese and Korean immigration especially headed to Brazil. This has largely effected the cuisine, traditions including literature, art and lifestyles and politics. The effects of Asian influences have especially and mostly effected the nations of Belize, Brazil, Cuba, Panama and Peru.
Art

Beyond the rich tradition of indigenous art, the development of Latin American visual art owed much to the influence of Spanish, Portuguese and French Baroque painting, which in turn often followed the trends of the Italian Masters. In general, this artistic Eurocentrism began to fade in the early twentieth century, as Latin Americans began to acknowledge the uniqueness of their condition and started to follow their own path.

From the early twentieth century, the art of Latin America was greatly inspired by the Constructivist Movement. The Movement quickly spread from Russia to Europe and then into Latin America. Joaquín Torres García and Manuel Rendón have been credited with bringing the Constructivist Movement into Latin America from Europe.
An important artistic movement generated in Latin America is muralism represented by Diego Rivera, David Alfaro Siqueiros, José Clemente Orozco and Rufino Tamayo in Mexico, Santiago Martinez Delgado and Pedro Nel Gómez in Colombia and Antonio Berni in Argentina. Some of the most impressive Muralista works can be found in Mexico, Colombia, New York City, San Francisco, Los Angeles and Philadelphia.
Painter Frida Kahlo, one of the most famous Mexican artists, painted about her own life and the Mexican culture in a style combining Realism, Symbolism and Surrealism. Kahlo's work commands the highest selling price of all Latin American paintings.[173]
Colombian sculptor and painter Fernando Botero is also widely known[174][175][176] by his works which, on first examination, are noted for their exaggerated proportions and the corpulence of the human and animal figures.
Film


Latin American film is both rich and diverse. Historically, the main centers of production have been Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, and Cuba. Latin American film flourished after sound was introduced in cinema, which added a linguistic barrier to the export of Hollywood film south of the border.[177]
Mexican cinema started out in the silent era from 1896 to 1929 and flourished in the Golden Era of the 1940s. It boasted a huge industry comparable to Hollywood at the time with stars such as María Félix, Dolores del Río, and Pedro Infante. In the 1970s, Mexico was the location for many cult horror and action movies. More recently, films such as Amores Perros (2000) and Y tu mamá también (2001) enjoyed box office and critical acclaim and propelled Alfonso Cuarón and Alejandro González Iñarritu to the front rank of Hollywood directors. Alejandro González Iñárritu directed in 2010 Biutiful and Birdman (2014), Alfonso Cuarón directed Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban in 2004 and Gravity (2013). Close friend of both, Guillermo del Toro, a top rank Hollywood director in Hollywood and Spain, directed Pan's Labyrinth (2006) and produced El Orfanato (2007). Carlos Carrera (The Crime of Father Amaro), and screenwriter Guillermo Arriaga are also some of the most known present-day Mexican film makers. Rudo y Cursi released in December (2008) in Mexico was directed by Carlos Cuarón.

Argentine cinema has also been prominenent since the first half of the 20th century and today averages over 60 full-length titles yearly. The industry suffered during the 1976–1983 military dictatorship; but re-emerged to produce the Academy Award winner The Official Story in 1985. A wave of imported U.S. films again damaged the industry in the early 1990s, though it soon recovered, thriving even during the Argentine economic crisis around 2001. Many Argentine movies produced during recent years have been internationally acclaimed, including Nueve reinas (2000), Son of the Bride (2001), El abrazo partido (2004), El otro (2007), the 2010 Foreign Language Academy Award winner El secreto de sus ojos and Wild Tales (2014).

In Brazil, the Cinema Novo movement created a particular way of making movies with critical and intellectual screenplays, a clearer photography related to the light of the outdoors in a tropical landscape, and a political message. The modern Brazilian film industry has become more profitable inside the country, and some of its productions have received prizes and recognition in Europe and the United States, with movies such as Central do Brasil (1999), Cidade de Deus (2002) and Tropa de Elite (2007).
Puerto Rican cinema has produced some notable films, such as Una Aventura Llamada Menudo, Los Diaz de Doris and Casi Casi. An influx of Hollywood films affected the local film industry in Puerto Rico during the 1980s and 1990s, but several Puerto Rican films have been produced since and it has been recovering.
Cuban cinema has enjoyed much official support since the Cuban revolution and important film-makers include Tomás Gutiérrez Alea.
Literature
.jpg)
Pre-Columbian cultures were primarily oral, though the Aztecs and Mayans, for instance, produced elaborate codices. Oral accounts of mythological and religious beliefs were also sometimes recorded after the arrival of European colonizers, as was the case with the Popol Vuh. Moreover, a tradition of oral narrative survives to this day, for instance among the Quechua-speaking population of Peru and the Quiché (K'iche') of Guatemala.
From the very moment of Europe's discovery of the continents, early explorers and conquistadores produced written accounts and crónicas of their experience – such as Columbus's letters or Bernal Díaz del Castillo's description of the conquest of Mexico. During the colonial period, written culture was often in the hands of the church, within which context Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz wrote memorable poetry and philosophical essays. Towards the end of the 18th Century and the beginning of the 19th, a distinctive criollo literary tradition emerged, including the first novels such as Lizardi's El Periquillo Sarniento (1816).
The 19th century was a period of "foundational fictions" (in critic Doris Sommer's words), novels in the Romantic or Naturalist traditions that attempted to establish a sense of national identity, and which often focussed on the indigenous question or the dichotomy of "civilization or barbarism" (for which see, say, Domingo Sarmiento's Facundo (1845), Juan León Mera's Cumandá (1879), or Euclides da Cunha's Os Sertões (1902)). The 19th century also witnessed the realist work of Machado de Assis, who made use of surreal devices of metaphor and playful narrative construction, much admired by critic Harold Bloom.
At the turn of the 20th century, modernismo emerged, a poetic movement whose founding text was Nicaraguan poet Rubén Darío's Azul (1888). This was the first Latin American literary movement to influence literary culture outside of the region, and was also the first truly Latin American literature, in that national differences were no longer so much at issue. José Martí, for instance, though a Cuban patriot, also lived in Mexico and the United States and wrote for journals in Argentina and elsewhere.


However, what really put Latin American literature on the global map was no doubt the literary boom of the 1960s and 1970s, distinguished by daring and experimental novels (such as Julio Cortázar's Rayuela (1963)) that were frequently published in Spain and quickly translated into English. The Boom's defining novel was Gabriel García Márquez's Cien años de soledad (1967), which led to the association of Latin American literature with magic realism, though other important writers of the period such as the Peruvian Mario Vargas Llosa and Carlos Fuentes do not fit so easily within this framework. Arguably, the Boom's culmination was Augusto Roa Bastos's monumental Yo, el supremo (1974). In the wake of the Boom, influential precursors such as Juan Rulfo, Alejo Carpentier, and above all Jorge Luis Borges were also rediscovered.
Contemporary literature in the region is vibrant and varied, ranging from the best-selling Paulo Coelho and Isabel Allende to the more avant-garde and critically acclaimed work of writers such as Diamela Eltit, Giannina Braschi, Ricardo Piglia, or Roberto Bolaño. There has also been considerable attention paid to the genre of testimonio, texts produced in collaboration with subaltern subjects such as Rigoberta Menchú. Finally, a new breed of chroniclers is represented by the more journalistic Carlos Monsiváis and Pedro Lemebel.
The region boasts six Nobel Prize winners: in addition to the two Chilean poets Gabriela Mistral (1945) and Pablo Neruda (1971), there is also the Guatemalan novelist Miguel Angel Asturias (1967), the Colombian writer Gabriel García Márquez (1982), the Mexican poet and essayist Octavio Paz (1990), and the Peruvian novelist Mario Vargas Llosa (2010).
Music and dance
Latin America has produced many successful worldwide artists in terms of recorded global music sales. Among the most successful have been Gloria Estefan (Cuba), Mercedes Sosa (Argentina), Roberto Carlos (Brazil), Carlos Santana (Mexico) of whom have sold over 90 million records, Luis Miguel (Mexico), Shakira (Colombia) and Vicente Fernández (Mexico) with over 50 million records sold worldwide. Enrique Iglesias, although not a Latin American, has also contributed for the success of Latin music.
Other notable successful mainstream acts through the years, include Soda Stereo, Celia Cruz, Thalía, Ricky Martin, Marc Anthony, Selena, Lynda Thomas and Menudo.
Caribbean Hispanic music, such as merengue, bachata, salsa, and more recently reggaeton, from such countries as the Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, Trinidad and Tobago, Cuba, and Panama, has been strongly influenced by African rhythms and melodies. Haiti's compas is a genre of music that is influenced by its Caribbean Hispanic counterparts, along with elements of jazz and modern sounds.[178][179]

Another well-known Latin American musical genre includes the Argentine and Uruguayan tango (with Carlos Gardel as the greatest exponent), as well as the distinct nuevo tango, a fusion of tango, acoustic and electronic music popularized by bandoneón virtuoso Ástor Piazzolla. Samba, North American jazz, European classical music and choro combined to form bossa nova in Brazil, popularized by guitarist João Gilberto with singer Astrud Gilberto and pianist Antonio Carlos Jobim.
Other influential Latin American sounds include the Antillean soca and calypso, the Honduras (Garifuna) punta, the Colombian cumbia and vallenato, the Chilean cueca, the Ecuadorian boleros, and rockoleras, the Mexican ranchera and the mariachi which is the epitome of Mexican soul, the Nicaraguan palo de Mayo, the Peruvian marinera and tondero, the Uruguayan candombe, the French Antillean zouk (derived from Haitian compas) and the various styles of music from pre-Columbian traditions that are widespread in the Andean region.

The classical composer Heitor Villa-Lobos (1887–1959) worked on the recording of native musical traditions within his homeland of Brazil. The traditions of his homeland heavily influenced his classical works.[180] Also notable is the recent work of the Cuban Leo Brouwer and guitar work of the Venezuelan Antonio Lauro and the Paraguayan Agustín Barrios. Latin America has also produced world-class classical performers such as the Chilean pianist Claudio Arrau, Brazilian pianist Nelson Freire and the Argentine pianist and conductor Daniel Barenboim. Brazilian opera soprano Bidu Sayão, one of Brazil's most famous musicians, was a leading artist of the Metropolitan Opera in New York City from 1937 to 1952.

Arguably, the main contribution to music entered through folklore, where the true soul of the Latin American and Caribbean countries is expressed. Musicians such as Yma Súmac, Chabuca Granda, Atahualpa Yupanqui, Violeta Parra, Víctor Jara, Jorge Cafrune, Facundo Cabral, Mercedes Sosa, Jorge Negrete, Luiz Gonzaga, Caetano Veloso, Susana Baca, Chavela Vargas, Simon Diaz, Julio Jaramillo, Toto la Momposina, Gilberto Gil, Maria Bethânia, Nana Caymmi, Nara Leão, Gal Costa, Ney Matogrosso as well as musical ensembles such as Inti Illimani and Los Kjarkas are magnificent examples of the heights that this soul can reach.
Latin pop, including many forms of rock, is popular in Latin America today (see Spanish language rock and roll).[181] A few examples are Café Tacuba, Soda Stereo, Maná, Rita Lee, Mutantes, Secos e Molhados Legião Urbana, Titãs, Paralamas do Sucesso, Cazuza, Barão Vermelho, Skank, Miranda!, Cansei de Ser Sexy or CSS, and Bajo Fondo.
More recently, Reggaeton, which blends Jamaican reggae and dancehall with Latin America genres such as bomba and plena, as well as that of hip hop, is becoming more popular, in spite of the controversy surrounding its lyrics, dance steps (Perreo) and music videos. It has become very popular among populations with a "migrant culture" influence – both Latino populations in the United States, such as southern Florida and New York City, and parts of Latin America where migration to the United States is common, such as Puerto Rico, Trinidad and Tobago, Dominican Republic, Colombia, Ecuador, El Salvador, and Mexico.[182]
See also
Notes
- 1 2 In the main Latin American languages:
- Spanish: América Latina or Latinoamérica
- Portuguese: América Latina
- French: Amérique latine
- 1 2 Includes the population estimates for South American and Central American countries excluding Belize, Guyana, the United States, and Spanish and French speaking Caribbean countries and territories, as listed under "Sub-regions and countries"
- ↑ Not including Anglophone, Francophone or Dutch-speaking countries, such as Belize, Guyana, Suriname and Jamaica; see Contemporary Definitions section
References
- 1 2 "World Development Indicators: Rural environment and land use". World Development Indicators, The World Bank. World Bank. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- 1 2 3 "World Population Prospects, The 2015 Revision: Key Findings and Advance Tables" (PDF). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. July 29, 2015. pp. 13–17. Retrieved January 1, 2016.
- 1 2 "Global Metroml Monitor". The Brookings Institution.
- ↑ Geography Department at Loughborough University, The World According to GaWC 2012, Table 4
- 1 2 "GDP Current and PPP estimates for 2014". Imf.org. 2014. Retrieved 2014-08-14.
- ↑ "GDP Current and PPP estimates for 2014". Imf.org. 2014. Retrieved 2014-08-14.
- ↑ Phelan (1968), p. 296.
- ↑ Mignolo, Walter (2005). The Idea of Latin America. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 77–80. ISBN 978-1-4051-0086-1.
- ↑ Michel Gobat, "The Invention of Latin America: A Transnational History of Anti-Imperialism, Democracy, and Race," American Historical Review Vol. 118, no. 3 (December 2013), pp. 1345-1375.
- ↑ McGuiness, Aims (2003). "Searching for 'Latin America': Race and Sovereignty in the Americas in the 1850s" in Appelbaum, Nancy P. et al. (eds.). Race and Nation in Modern Latin America. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 87–107. ISBN 978-0-8078-5441-9
- ↑ "''América latina o Sudamérica?'', por Luiz Alberto Moniz Bandeira, Clarín, 16 de mayo de 2005". Clarin.com. 2005-05-16. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ "Torres Caicedo, José María (1856). ''Las dos Américas'' (poema)". Filosofia.org. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ Chasteen, John Charles (2001). "6. Progress". Born in Blood and Fire: A Concise History of Latin America. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 156. ISBN 978-0-393-97613-7. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ↑ Phelan, J.L. (1968). Pan-latinisms, French Intervention in Mexico (1861–1867) and the Genesis of the Idea of Latin America. Unversidad Nacional Autonónoma de México, Mexico City.
- ↑ Rangel, Carlos (1977). The Latin Americans: Their Love-Hate Relationship with the United States. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. pp. 3–5. ISBN 978-0-15-148795-0. Skidmore, Thomas E.; Peter H. Smith (2005). Modern Latin America (6 ed.). Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-0-19-517013-9.
- ↑ RAE (2005). Diccionario Panhispánico de Dudas. Madrid: Santillana Educación. ISBN 8429406239.
- ↑ Butland, Gilbert J. (1960). Latin America: A Regional Geography. New York: John Wiley and Sons. pp. 115–188. ISBN 978-0-470-12658-5. Dozer, Donald Marquand (1962). Latin America: An Interpretive History. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1–15. ISBN 0-87918-049-8. Szulc, Tad (1965). Latin America. New York Times Company. pp. 13–17. ISBN 0-689-10266-6. Olien, Michael D. (1973). Latin Americans: Contemporary Peoples and Their Cultural Traditions. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston. pp. 1–5. ISBN 978-0-03-086251-9. Black, Jan Knippers (ed.) (1984). Latin America: Its Problems and Its Promise: A Multidisciplinary Introduction. Boulder: Westview Press. pp. 362–378. ISBN 978-0-86531-213-5. Bruns, E. Bradford (1986). Latin America: A Concise Interpretive History (4 ed.). New York: Prentice-Hall. pp. 224–227. ISBN 978-0-13-524356-5. Skidmore, Thomas E.; Peter H. Smith (2005). Modern Latin America (6 ed.). Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 351–355. ISBN 978-0-19-517013-9.
- ↑ Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings, UN Statistics Division. Accessed on line 23 May 2009. (French)
- ↑ Latin America and the Caribbean. The World Bank. Retrieved on 17 July 2009.
- ↑ "Country Directory. Latin American Network Information Center-University of Texas at Austin". Lanic.utexas.edu. Retrieved 2013-12-09.
- ↑ Torres, George (2013). Encyclopedia of Latin American Popular Music. ABC-CLIO. p. xvii. ISBN 9780313087943.
- ↑ Bethell, Leslie (ed.) (1984). The Cambridge History of Latin America. 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. xiv. ISBN 978-0-521-23223-4.
- ↑ María Alejandra Acosta García; Sheridan González, Ma. de Lourdes Romero, Luis Reza, Araceli Salinas (June 2011). "Three". In CONALITEG. Geografía, Quinto Grado (Geography, Fifth Grade) (Second ed.). Mexico City: Secretaría de Educación Pública (Secretariat of Public Education). pp. 75–83.
- ↑ "Insee – Populations légales 2011 – Populations légales 2011 des départements et des collectivités d'outre-mer". www.insee.fr. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ Gongóra, Alvaro; de la Taille, Alexandrine; Vial, Gonzalo. Jaime Eyzaguirre en su tiempo (in Spanish). Zig-Zag. p. 223.
- ↑ The preceramic Las Vegas culture of coastal Ecuador http://www.jstor.org/pss/280325
- ↑ Lustosa, pp. 117–119
- ↑ Lustosa, pp. 150–153
- ↑ Vianna, p. 418
- ↑ Diégues 2004, pp. 168, 164, 178
- ↑ Diégues 2004, pp. 179–180
- ↑ Lustosa, p. 208
- ↑ Ibidem Fausto 1999, pages 82–83
- ↑ Lyra (v.1), p. 17
- ↑ Carvalho 2007, p. 21
- ↑ Ibidem Fausto 1999, Chapter 2, 2.1 to 2.3
- ↑ Ibidem Fausto 1999
- ↑ Bethell, Leslie "The Abolition of the Brazilian Slave Trade: Britain, Brazil and the Slave Trade" Cambridge University Press 1970, "Cambridge Latin American Studides", Chapters 9 to 12. View on Google Books
- ↑ Scott, Rebecca and others, The Abolition of Slavery and the Aftermath of Emancipation in Brazil, Duke University Press 1988 ISBN 0822308886 Seymour Drescher, Chap. 2: "Brazilian Abolition in Comparative Perspective"
- ↑ Levine, Robert M. "The history of Brazil" Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc. 1999, page 62, last paragraph View on Google Books
- ↑ Lyra (v.1), pp. 164, 225, 272
- ↑ Ibidem Fausto 1999, Chapter 2, page 83, and 2.6 "The Paraguayan War"
- ↑ Smallman; Shall C. Fear an Memory in the Brazilian Army and Society, University of North Carolina Press 2002 ISBN 0-8078-5359-3 Chapter 1, "The Overthrow of the Empire," pp. 16–18
- ↑ Pozas, Mario A. El liberalismo hispanoamericano en el siglo XIX. pg2
- ↑ Halperín Donghi, T. (2013). Historia contemporánea de América latina. Madrid: Alianza.
- ↑ Galasso, N. (2011). Historia de la Argentina (Vol. 1).
- ↑ Hudson, R., & Meditz, S. (1990). Uruguay: A Country Study.
- 1 2 Donghi, T. (1970). Historia contemporánea de América Latina (2. ed.). Madrid: Alianza Editorial. 148–149
- ↑ Donghi, 88
- ↑ Donghi, 89
- ↑ Engerman, Stanley L., and Kenneth L. Sokoloff. "History Lessons: Institutions, Factors Endowments, and Paths of Development in the New World." The Journal of Economic Perspectives Vol. 14(3) pp. 217–232 (2000): pp. 217–232. Print. 219
- ↑ "Latin American History from 1800 to 1914." Woodville. Colegio Woodville, n.d. Web. 24 Oct. 2013. . 1–3
- ↑ "Latin American History from 1800 to 1914." Woodville. Colegio Woodville, n.d. Web. 24 Oct. 2013. . 1
- ↑ Racine, K. (Aug2010). "This England and This Now: British Cultural and Intellectual Influence in the Spanish American Independence Era." Hispanic American Historical Review, Vol. 90(Issue 3), p423–454.
- ↑ "Latin American History from 1800 to 1914." Woodville. Colegio Woodville, n.d. Web. 24 Oct. 2013. . 2
- ↑ Robertson, William Spence (1944). French Intervention in Mexico in 1838. Duke University Press. pp. 222–223. JSTOR 2507834.
- ↑ "French Intervention in Mexico and the American Civil War, 1862–1867". U.S Department of State Office of the Historian.
- ↑ Ridge Jr., Michael Allen. "A country in need of American instruction : The U.S. mission to shape and transform Mexico, 1848–1911". Iowa Research Online. University of Iowa.
- ↑ Bakewell, Peter. A History of Latin America. pg 491
- ↑ Andrew, p. 42.
- ↑ Hall, Allan (2012-03-19). "Secret Files Reveal 9,000 Nazi War Criminals Fled to South America after WWII". London: Mail Online. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ↑ Penteado, Carlos Joes A. "Hyper War: The Brazilian Participation in World War II". Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ↑ "Health in Latin America and the Caribbean" (PDF). Center for Strategic and International Studies. Retrieved 22 May 2012.
- ↑ Stavans, IIan. "The Impact Of The Holocaust In Latin America".
- ↑ "WWII Bombs Destroyed in the Galapagos Islands". BBC News. 2012-01-18. Retrieved 2012-05-24.
- ↑ "Brazil Amazon deforestation soars". BBC News. 24 January 2008.
- 1 2 "History of Latin America". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- 1 2 Kaufman, Robert. "The Political Effects of Inequality: Some Inconvenient Facts". Rutgers University.
- ↑ Chasteen, John (2011). Born Into Blood and Fire, A Concise History of Latin America. W.W. Norton & Company Inc. p. 253.
- 1 2 Dominguez, Jorge. "US-Latin American Relations During the Cold War and its Aftermath". Institute of Latin American Studies.
- ↑ Schneider, Ronald M. Latin American Political History: Patterns and Personalities. pg 274–275
- ↑ Schneider, Ronald M. Latin American Political History: Patterns and Personalities. pg 376–377
- ↑ "Bay of Pigs Invasion". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ↑ Bakewell, Peter. A history of Latin America. pg541-542
- 1 2 3 Hershberg, Eric, and Fred Rosen, eds. Latin America after Neoliberalism. New York: North American Congress on Latin America, 2006. Print.
- ↑ Escobar, Arturo, and Sonia E. Alvarez, eds. The Making of Social Movements in Latin America. Boulder: Westview, 1992. Print.
- 1 2 3 4 Johnston, Hank, and Paul Almeida, eds. Latin American Social Movements. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield, 2006. Print.
- ↑ Jordi Zamora. "China's double-edged trade with Latin America." Sep 3, 2011. AFP. https://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5ggNqQ5G8UFErmAEw71Y-u51P8_Eg?docId=CNG.e829052752a5436e909ab280ad561af6.671
- ↑ "Geographic Patterns of Genome Admixture in Latin American Mestizos". Plos genetics. 2008-03-21. Retrieved 2013-09-09.
- ↑ "CIA – The World Factbook – Field Listing – Ethnic groups". Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ Lizcano Fernández, Francisco (May–August 2005). "Composición Étnica de las Tres Áreas Culturales del Continente Americano al Comienzo del Siglo XXI" (PDF). Convergencia (in Spanish). Mexico: Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México, Centro de Investigación en Ciencias Sociales y Humanidades. 38: 185–232; table on p. 218. ISSN 1405-1435.
- ↑ "Reference for Welsh language in southern Argentina, Welsh immigration to Patagonia". Bbc.co.uk. 2008-07-22. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ "The Welsh Immigration to Argentina". 1stclassargentina.com.
- ↑ Jeremy Howat. "Reference for Welsh language in southern Argentina, Welsh immigration to Patagonia". Argbrit.org. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ "Reference for Welsh language in southern Argentina, Welsh immigration to Patagonia". Patagonline.com. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ "Reference for Welsh language in southern Argentina, Welsh immigration to Patagonia". Andesceltig.com. 2009-09-29. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ "Reference for Welsh language in southern Argentina, Welsh immigration to Patagonia". Glaniad.com. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ "Brazil – Modern-Day Community". www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/. 2013. Retrieved 2013-12-22.
- ↑ "Christians". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 18 December 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ↑ "CIA – The World Factbook – Field Listing – Religions". Retrieved 2009-03-17.
- ↑ Fraser, Barbara J., In Latin America, Catholics down, church's credibility up, poll says Catholic News Service June 23, 2005
- ↑ Watching Over Greater Mexico: Mexican Migration Policy and Governance of Mexicanos Abroad Archived December 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ United States Census Bureau. "American Factfinder: Hispanic or Latino by Type: 2010 Census Summary File 1 (QT-P3)". American Factfinder. Retrieved 2016-01-17.
- ↑ Archived January 31, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Brasileiros no Exterior – Portal da Câmara dos Deputados Archived July 21, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Country Overview: El Salvador, United States Agency for International Development Archived January 1, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Chavistas in Quito, Forbes.com, January 7, 2008 Archived December 7, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Dominican Republic: Remittances for Development". Ipsnews.net. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ Business With Cuba: The Complete Guide, Jan 12, 2015, Patricia Maroday
- ↑ Chile: Moving Towards a Migration Policy, Migration Information Source
- ↑ "Migration News". Migration.ucdavis.edu. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ "WorldBank Migration and Remittances Factbook 2008". Econ.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- ↑ http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTPROSPECTS/Resources/334934-1199807908806/ElSalvador.pdf
- ↑ http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTPROSPECTS/Resources/334934-1199807908806/Guatemala.pdf
- ↑ http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTPROSPECTS/Resources/334934-1199807908806/Nicaragua.pdf
- ↑ http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTPROSPECTS/Resources/334934-1199807908806/Honduras.pdf
- ↑ http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTPROSPECTS/Resources/334934-1199807908806/Panama.pdf
- ↑ http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTPROSPECTS/Resources/334934-1199807908806/CostaRica.pdf
- ↑ "International Migration Report 2006: A Global Assessment; VII. Profiles by Country or Area". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs/Population Division.
- 1 2 Welti, Carlos (2002). "Adolescents in Latin America: Facing the Future with Skepticism". In Brown, B. The World's Youth: Adolescence in Eight Regions of the Globe ([Online-Ausg.]. ed.). Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521006058.
- 1 2 [BID/EDU Stakeholder Survey 1993/2003, February 8, 2011]
- ↑ Latin America the Most Dangerous Region in terms of Violence, retrieved 28 August 2013
- ↑ Latin America Is the Most Dangerous Region in the World (By Far), retrieved 28 August 2013
- ↑ "Latin America: Crisis behind bars". BBC News. 2005-11-16. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Latin America Is World's Most Violent Region". The Wall Street Journal. April 11, 2014. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ , UNODC Homicide Chart by Country
- ↑ http://www.guncite.com/colombian_crime_rpt_2005
- ↑ "Amnesty International: Latin America 'dangerous' for journalists", CNN, 2011-05-13, retrieved 30 August 2013
- ↑ Crime Hinders Development, Democracy in Latin America, U.S. Says – US Department of State
- ↑ "Understanding the uneven distribution of the incidence of homicide in Latin America" International Journal of Epidemiology
- ↑ "The N-11: More Than an Acronym" (PDF). Appendix II: Projections in Detail. Goldman Sachs Economic Research.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects, the 2010 Revision". Table 1: Selected Demographic Indicators: Population, 2010. United Nations Population Division (UNPD).
- 1 2 "World GDP Ranking 2015 - Data and Charts". Knoema. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ↑ Baten, Jörg (2016). A History of the Global Economy. From 1500 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. p. 123. ISBN 9781107507180.
- ↑ Baten, Jörg (2016). A History of the Global Economy. From 1500 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. p. 138. ISBN 9781107507180.
- ↑ Baten, Jörg (2016). A History of the Global Economy. From 1500 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. p. 148f. ISBN 9781107507180.
- ↑ "GDP per Capita Ranking 2015 - Data and Charts". Knoema. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ↑ "Human Development Report 2011" (PDF). Table 3: Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index. United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- ↑ "Human Development Report 2011" (PDF). Table 5: Multidimensional Poverty Index. United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- ↑ http://www.uis.unesco.org/Education/Documents/literacy-statistics-trends-1985-2015.pdf
- ↑ "Geoba.se: Gazetteer - The World - Life Expectancy - Top 100+ By Country (2016)". Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ↑ "Homicide Statistics 2012". Murder rate per 100,000 inhabitants. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC).
- ↑ "Global Peace Index 2014". Global Peace Index rankings. Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP).
- ↑ "Cifras de pobreza y desigualdad en Colombia en 2012 | Economía". Portafolio.co. Retrieved 2013-12-09.
- ↑ "Colombia registra en 2012 la cifra más baja de homicidios en últimos 27 años". América Economía.
- ↑ "macaw". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ "Environmental Performance Index 2012". Environmental Performance Index 2012 rankings. Yale University.
- ↑ "CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion 2011" (PDF). CO2 emissions / population. International Energy Agency (IEA).
- ↑ "Protección social inclusiva en América Latina. Una mirada integral, un enfoque de derechos" [Inclusive social protection in Latin America. An integral look, a focus on rights]. Resumen. United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (UNECLAC).
- ↑ Francisco H. Ferreira, David de Ferranti et al. An example of the policies introduced to combat the poverty and inequality was the import substitution industrialization economic policy. This policy sought to grow national industry and offer protection from foreign competition as a means to reduce external dependencies and improve local economies. "Inequality in Latin America:Breaking with History?", The World Bank, Washington, D.C., 2004
- ↑ Scanlon, TJ (1998). "Street children in Latin America". BMJ.
- ↑ Tacon, P. (1982). "Carlinhos: the hard gloss of city polish". UNICEF news.
- ↑ Schaefer, Richard T. (ed.) (2008). Encyclopedia of Race, Ethnicity and Society. Sage. p. 1096. ISBN 978-1-4129-2694-2.
For example, in many parts of Latin America, racial groupings are based less on the biological physical features and more on an intersection between physical features and social features such as economic class, dress, education, and context. Thus, a more fluid treatment allows for the construction of race as an achieved status rather than an ascribed status as is the case in the United States.
- ↑ Nutini, Hugo; Barry Isaac (2009). Social Stratification in central Mexico 1500–2000. University of Texas Press. p. 55.
There are basically four operational categories that may be termed ethnic or even racial in Mexico today: (1) güero or blanco (white), denoting European and Near East extraction; (2) criollo (creole), meaning light mestizo in this context but actually of varying complexion; (3) mestizo, an imprecise category that includes many phenotypic variations; and (4) indio, also an imprecise category. These are nominal categories, and neither güero/blanco nor criollo is a widely used term (see Nutini 1997: 230). Nevertheless, there is a popular consensus in Mexico today that these four categories represent major sectors of the nation and that they can be arranged into a rough hierarchy: whites and creoles at the top, a vast population of mestizos in the middle, and Indians (perceived as both a racial and an ethnic component) at the bottom. This popular hierarchy does not constitute a stratificational system or even a set of social classes, however, because its categories are neither exhaustive nor mutually exclusive. While very light skin is indeed characteristic of the country's elite, there is no "white" (güero) class. Rather, the superordinate stratum is divided into four real classes—aristocracy, plutocracy, political class, and the crème of the upper-middle class—or, for some purposes, into ruling, political, and prestige classes (see Chap. 4). Nor is there a mestizo class, as phenotypical mestizos are found in all classes, though only rarely among the aristocracy and very frequently in the middle and lower classes. Finally, the bottom rungs are not constituted mainly of Indians, except in some localized areas, such as the Sierra Norte de Puebla
- ↑ Acuña, Rodolfo F. (2011), Occupied America: A History of Chicanos (7th ed.), Boston: Longman, pp. 23–24, ISBN 0-205-78618-9
- ↑ MacLachlan, Colin; Jaime E. Rodríguez O. (1990). The Forging of the Cosmic Race: A Reinterprretation of Colonial Mexico (Expanded ed.). Berkeley: University of California. pp. 199, 208. ISBN 0-520-04280-8.
[I]n the New World all Spaniards, no matter how poor, claimed hidalgo status. This unprecedented expansion of the privileged segment of society could be tolerated by the Crown because in Mexico the indigenous population assumed the burden of personal tribute.
- ↑ Gibson, Charles (1964). The Aztecs Under Spanish Rule. Stanford: Stanford University. pp. 154–165. ISBN 0-8047-0912-2.
- ↑ See Passing (racial identity) for a discussion of a related phenomenon, although in a later and very different cultural and legal context.
- ↑ Seed, Patricia (1988). To Love, Honor, and Obey in Colonial Mexico: conflicts over Marriage Choice, 1574–1821. Stanford: Stanford University. pp. 21–23. ISBN 0-8047-2159-9.
- ↑ David Cahill (1994). "Colour by Numbers: Racial and Ethnic Categories in the Viceroyalty of Peru" (PDF). Journal of Latin American Studies. 26: 325–346. doi:10.1017/s0022216x00016242.
- ↑ Maria Martinez (2002). "The Spanish concept of Limpieza de Sangre and the emergence of the race/caste system in the viceroyalty of New Spain, PhD dissertation". University of Chicago.
- ↑ Bakewell, Peter (1997). A History of Latin America. Malden, Mass.: Blackwell. pp. 160–163. ISBN 0-631-16791-9.
The Spaniards generally regarded [local Indian lords/caciques] as hidalgos, and used the honorific 'don' with the more eminent of the them. […] Broadly speaking, Spaniards in the Indies in the sixteenth century arranged themselves socially less and less by Iberian criteria or frank, and increasingly by new American standards. […] simple wealth gained from using America's human and natural resources soon became a strong influence on social standing.
- ↑ Fracisco H. Ferreira et al. Inequality in Latin America: Breaking with History?, The World Bank, Washington, D.C., 2004
- ↑ Nicola Jones; Hayley Baker. "Untangling links between trade, poverty and gender". ODI Briefing Papers 38, March 2008. Overseas Development Institute (ODI).
- ↑ Isabel Ortiz; Matthew Cummins (April 2011). "Global Inequality: Beyond the Bottom Billion" (PDF). UNICEF. p. 26.
- ↑ Francisco H. Ferreira et al. Inequality in Latin America: Breaking with History?, The World Bank, Washington, D.C., 2004
- ↑ "- Human Development Reports" (PDF). undp.org.
- ↑ "World Development Indicators database, 1 July 2011". Gross national income per capita 2010, Atlas method and PPP. World Bank Organization (WBO).
- ↑ Barrientos, A. and Claudio Santibanez. (2009). "New Forms of Social Assistance and the Evolution of Social Protection in Latin America". Journal of Latin American Studies. Cambridge University Press 41, 1–26.
- ↑ Benedicte de la Brière and Laura B. Rawlings, "Examining Conditional Cash Transfer Programs: A Role for Increased Social Inclusion?", Social Safety Net Primary Papers, The World Bank, 2006, p.4
- ↑ "Regional Human Development Report for Latin America and the Caribbean 2010" (PDF). Inequality in Latin America and the Caribbean. Inequality in Latin America and the Caribbean.
- ↑ "Societies on the move". The Economist. 2010-09-11.
- ↑ Monika Huber; Wolfgang Kaiser (February 2013). "Mixed Feelings". dandc.eu.
- ↑ Carmen Altés. "El turismo en América Latina y el Caribe y la experiencia del BID" [Tourism in Latin America and the Caribbean and the experience of the IDB]. Ingresos directos por turismo internacional. Inter-American Development Bank (IDB).
- 1 2 "UNWTO Tourism Highlights, 2015 edition". World Tourism Organization. p. 10. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- ↑ "UNWTO Tourism Highlights, 2012 Edition" (PDF). International Tourism Receipts. World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
- ↑ Carmen Altés. "El turismo en América Latina y el Caribe y la experiencia del BID" [Tourism in Latin America and the Caribbean and the experience of the IDB]. Figura 1: Ingresos por turismo internacional (% de exportaciones). Inter-American Development Bank (IDB).
- ↑ Carmen Altés. "El turismo en América Latina y el Caribe y la experiencia del BID" [Tourism in Latin America and the Caribbean and the experience of the IDB]. Figura 2: Ingresos por turismo internacional (% del PIB). Inter-American Development Bank (IDB).
- ↑ Carmen Altés. "El turismo en América Latina y el Caribe y la experiencia del BID" [Tourism in Latin America and the Caribbean and the experience of the IDB]. Figura 3: Empleo en turismo (% del empleo total). Inter-American Development Bank (IDB).
- ↑ "The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011" (PDF). Table 1: Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index 2011 and 2009 comparison. World Economic Forum (WEF).
- ↑ "Traditional Nicaraguan Costumes: Mestizaje Costume". ViaNica.com. Retrieved 2007-11-21.
- ↑ Stepan, Nancy Leys (1991). "The Hour of Eugenics": Race, Gender, and Nation in Latin America. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. in passim. ISBN 978-0-8014-9795-7.
- ↑ "Frida Kahlo "Roots" Sets $5.6 Million Record at Sotheby's". Art Knowledge News. Archived from the original on June 20, 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-23.
- ↑ Notimex / El Siglo De Torreón (2012-04-01). "Fernando Botero, el gran artista de Latinoamérica". Elsiglodetorreon.com.mx. Retrieved 2013-12-09.
- ↑ "Fernando Botero, el aprendiz eterno". Revistaenie.clarin.com. 2013-10-06. Retrieved 2013-12-09.
- ↑ Forero, Juan (2005-05-08). "'Great Crime' at Abu Ghraib Enrages and Inspires an Artist". The New York Times.
- ↑ Paul A. Schroeder Rodriguez. Latin American Cinema: A Comparative History (University of California Press; 2016) studies 50 films since the silent era.
- ↑ Christopher Washburne. "Clave: The African Roots of Salsa". University of Salsa. Retrieved 2006-05-23.
- ↑ "Guide to Latin Music". Caravan Music. Retrieved 2006-05-23.
- ↑ "Heitor Villa-Lobos". Leadership Medica. Retrieved 2006-05-23.
- ↑ The Baltimore Sun. "Latin music returns to America with wave of new pop starlets". The Michigan Daily. Archived from the original on August 30, 2005. Retrieved 2006-05-23.
- ↑ "Daddy Yankee leads the reggaeton charge". Associated Press. Retrieved 2006-05-23.
Further reading
- Azevedo, Aroldo. O Brasil e suas regiões. São Paulo: Companhia Editora Nacional, 1971. (Portuguese)
- Enciclopédia Barsa. Volume 4: Batráquio – Camarão, Filipe. Rio de Janeiro: Encyclopædia Britannica do Brasil, 1987. (Portuguese)
- Coelho, Marcos Amorim. Geografia do Brasil. 4th ed. São Paulo: Moderna, 1996. (Portuguese)
- Galeano, Eduardo. Open Veins of Latin America: Five Centuries of the Pillage of a Continent. 1973
- Gobat, Michel, "The Invention of Latin America: A Transnational History of Anti-Imperialism, Democracy, and Race," American Historical Review Vol. 118, no. 3 (December 2013), pp. 1345-1375.
- Edwards, Sebastián. Left Behind: Latin America and the False Promise of Populism. University of Chicago Press, 2010.
- Sebastian Edwards; Gerardo Esquivel; Graciela Márquez (15 February 2009). The Decline of Latin American Economies: Growth, Institutions, and Crises. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-18503-3.
- Maurer Queipo, Isabel (ed.): "Directory of World Cinema: Latin America", intellectbooks, Bristol 2013, ISBN 9781841506180
- Mignolo, Walter, The Idea of Latin America. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell 2005.
- Moreira, Igor A. G. O Espaço Geográfico, geografia geral e do Brasil. 18. Ed. São Paulo: Ática, 1981. (Portuguese)
- Phelan, John Leddy. (1968). Pan-latinisms, French Intervention in Mexico (1861–1867) and the Genesis of the Idea of Latin America. Mexico City: Universidad Nacional Autonónoma de México 1968.
- Vesentini, José William. Brasil, sociedade e espaço – Geografia do Brasil. 7th Ed. São Paulo: Ática, 1988. (Portuguese)
- Miranda Vidal, José: (2007) Ciencia y tecnología en América Latina Edición electrónica gratuita. Texto completo en http://www.eumed.net/libros/2007a/237/
- Halperin Donghi, Tulio. (1970). Historia contemporánea de América Latina (2. ed.). Madrid: Alianza Editorial.
- Engerman, Stanley L., and Kenneth L. Sokoloff. "History Lessons: Institutions, Factors Endowments, and Paths of Development in the New World." The Journal of Economic Perspectives Vol. 14(3) pp. 217–232 (2000): pp. 217–232. Print.
- Latin American History from 1800 to 1914. Woodville. Colegio Woodville, n.d. Web. 24 Oct. 2013. <http://www.woodville.org/documentos/130506latinamericanhistory-summary.pdf>.
- Leonard, Thomas et al. (2010). Encyclopedia of Latin America. Facts on File. ISBN 9780816073597
- Racine, K. (Aug2010). "This England and This Now": British Cultural and Intellectual Influence in the Spanish American Independence Era. Hispanic American Historical Review, Vol. 90(Issue 3), p423–454.
- Pozas, Mario A. "EL LIBERALISMO HISPANOAMERICANO EN EL SIGLO XIX" University of Central Arkansas.
- Bakewell, Peter. "A History of Latin America": A Blackwell History of the World.
- Schneider, Ronald M. "Latin American Political History: Patterns and Personalities"
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Latin America. |
- IDB Education Initiative
- Latin American Network Information Center
- Latin America Data Base
- Washington Office on Latin America
- Council on Hemispheric Affairs
- Codigos De Barra
- Infolatam. Information and analysis of Latin America
- Map of Land Cover: Latin America and Caribbean (FAO)
- Lessons From Latin America by Benjamin Dangl, The Nation, March 4, 2009
- Keeping Latin America on the World News Agenda – Interview with Michael Reid of The Economist
- Cold War in Latin America, CSU Pomona University
- Latin America Cold War Resources, Yale University
- Latin America Cold War, Harvard University
- http://larc.ucalgary.ca/ Latin American Research Centre, University of Calgary
- The war on Democracy, by John Pilger







