Clavipectoral triangle
| Clavipectoral triangle | |
|---|---|
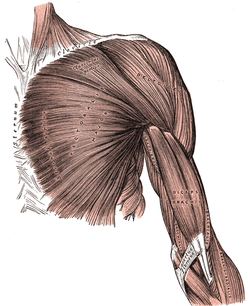 Superficial muscles of the chest and front of the arm. | |
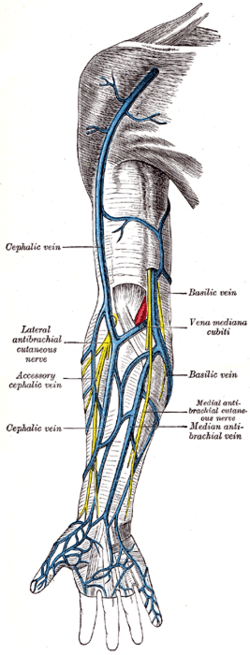 Superficial veins of the upper limb. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum clavipectorale |
| TA | A01.2.03.004 |
| FMA | 61541 |
The clavipectoral triangle (also known as the deltopectoral triangle) is an anatomical region found in humans and other animals. It is bordered by the following structures:
- Superior border of Pectoralis major muscle
- Anterior border of Deltoid muscle
- Clavicle
It contains the cephalic vein,[1] and deltopectoral fascia, which is a layer of deep fascia that invests the three structures that make up the border of the triangle, and also the cephalic vein in the triangle. The deltoid branch of the thoracoacromial artery also passes through this triangle, giving branches to both the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles.
The subclavian vein and the subclavian artery may be accessed via this triangle, as they are deep to it.
See also
References
- ↑ shoulder/surface/surface1 at the Dartmouth Medical School's Department of Anatomy
External links
- Anatomy photo:04:03-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Pectoral Region: Deltopectoral Triangle"
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.