Coronary sinus
| Coronary sinus | |
|---|---|
 Back (posterior) side of the heart, with coronary sinus (blue) labeled | |
 Interior of heart, viewed from the front (opening of coronary sinus is labeled) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Sinus venosus |
Source | Great cardiac vein |
| Drains to | Right atrium |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Sinus coronarius |
| TA | A12.3.01.002 |
| FMA | 4706 |
The coronary sinus is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle (myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior vena cavae. It is present in all mammals, including humans.
The name comes from the Latin "corona' , meaning crown, since this vessel forms a partial circle around the heart. The coronary sinus drains into the right atrium, at the coronary sinus orifice, an opening between the inferior vena cava and the right atrioventricular orifice or tricuspid valve. It returns blood from the heart muscle, and is protected by a semicircular fold of the lining membrane of the auricle, the valve of coronary sinus (or valve of Thebesius). The sinus, before entering the atrium, is considerably dilated - nearly to the size of the end of the little finger. Its wall is partly muscular, and at its junction with the great cardiac vein is somewhat constricted and furnished with a valve, known as the valve of Vieussens consisting of two unequal segments.
Structure
The coronary sinus runs transversely in the left atrioventricular groove on the posterior side of the heart. It is the distal portion of the great cardiac vein feeding into the right atrium.
The valve of the coronary sinus is on the posterior, inferior surface of the heart, medial to the inferior vena cava opening, just superior to the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve. The coronary sinus valve is also known as the Thebesian valve.
Function
The coronary sinus receives blood mainly from the small, middle, great and oblique cardiac veins. It also receives blood from the left marginal vein and the left posterior ventricular vein. It drains into the right atrium.
The anterior cardiac veins do not drain into the coronary sinus but drain directly into the right atrium. Some small veins known as smallest cardiac veins drain directly into any of the four chambers of the heart.
Additional images
-
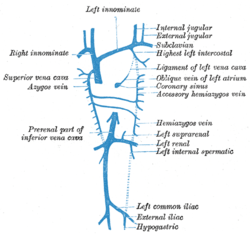
Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins.
-
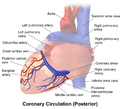
Posterior view of coronary circulation
See also
- Coronary arteries
- Percutaneous coronary intervention
- Pressure-controlled intermittent coronary sinus occlusion
External links
- -200933319 at GPnotebook
- Anatomy figure: 20:04-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior view of the heart."
- MedEd at Loyola Radio/curriculum/Vascular/Coronary_sinus.jpg