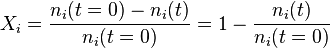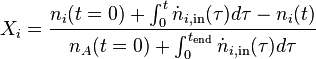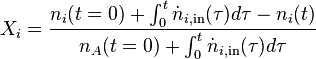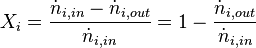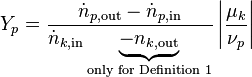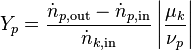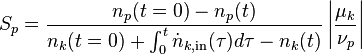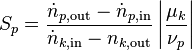Conversion (chemistry)
Conversion and its related terms yield and selectivity are important terms in chemical reaction engineering. They are described as ratios of how much of a reactant has reacted (X — conversion, normally between zero and one), how much of a desired product was formed (Y — yield, normally also between zero and one) and how much desired product was formed in ratio to the undesired product(s) (S — selectivity).
There are conflicting definitions in the literature for selectivity and yield, so each author's intended definition should be verified.
Conversion can be defined for (semi-)batch and continuous reactors and as instantaneous and overall conversion.
Assumptions
The following assumptions are made:
- The following chemical reaction takes place:
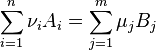 ,
,
where 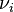 and
and 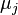 are the stoichiometric coefficients. For multiple parallel reactions, the definitions can also be applied, either per reaction or using the limiting reaction.
are the stoichiometric coefficients. For multiple parallel reactions, the definitions can also be applied, either per reaction or using the limiting reaction.
- Batch reaction assumes all reactants are added at the beginning.
- Semi-Batch reaction assumes some reactants are added at the beginning, the rest is fed during the batch.
- Continuous reaction assumes reactants are fed and products leave the reactor continuously and in steady state.
Conversion
Conversion can be separated into instantaneous conversion and overall conversion. For continuous processes the two are the same, for batch and semi-batch there are important differences. Furthermore, for multiple reactants, conversion can be defined overall or per reactant.
Instantaneous Conversion
Semi-Batch
In this setting there are different definitions. One definition regards the instantaneous conversion as the ratio of the instantaneously converted amount to the amount fed at any point in time:
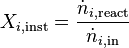 .
.
with 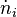 as the change of moles with time of species i.
as the change of moles with time of species i.
This ratio can become larger than 1. It can be used to indicate whether reservoirs are built up and it is ideally close to 1. When the feed stops, its value is not defined.
In semi-batch polymerisation, the instantaneous conversion is defined as the total mass of polymer divided by the total mass of monomer fed:[1][2]
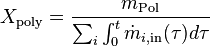 .
.
Overall Conversion
Batch (This is the generally stated form)
Semi-Batch
Total conversion of the formulation:
Total conversion of the fed reactants:
Continuous (This is the generally stated form)
Yield
Yield in general refers to the amount of a specific product (p in 1..m) formed per mole of reactant consumed (Definition 1[3]). However, it is also defined as the amount of product produced per amount of product that could be produced (Definition 2). If not all of the limiting reactant has reacted, the two definitions contradict each other. Combining those two also means that stoichiometry needs to be taken into account and that yield has to be based on the limiting reactant (k in 1..n):
Continuous
The version normally found in the literature:
Selectivity
Instantaneous selectivity is the production rate of one component per production rate of another component.
For overall selectivity the same problem of the conflicting definitions exists. Generally, it is defined as the number of moles of desired product per the number of moles of undesired product (Definition 1[4]). However, the definitions of the total amount of reactant to form a product per total amount of reactant consumed is used (Definition 2) as well as the total amount of desired product formed per total amount of limiting reactant consumed (Definition 3). This last definition is the same as definition 1 for yield.
Batch or Semi-Batch
The version normally found in the literature:
Continuous
The version normally found in the literature:
Combination
For batch and continuous reactors (semi-batch needs to be checked more carefully) and the definitions marked as the ones generally found in the literature, the three concepts can be combined:
For a process with the only reaction
this mean that S=1 and Y=X.
Abstract Example

For the following abstract example and the amounts depicted on the right, the following calculation can be performed with the above definitions, either in batch or a continuous reactor.
B is the desired product.
There are 100 mol of A at the beginning or at the entry to the continuous reactor and 10 mol A, 72 mol B and 18 mol C at the end of the reaction or the exit of the continuous reactor. The three properties are found to be:
The property
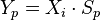 holds. In this reaction, 90% of substance A is converted (consumed), but only 80% of the 90% is converted to the desired substance B and 20% to undesired by-products C. So, conversion of A is 90%, selectivity for B 80% and yield of substance B 72%.
holds. In this reaction, 90% of substance A is converted (consumed), but only 80% of the 90% is converted to the desired substance B and 20% to undesired by-products C. So, conversion of A is 90%, selectivity for B 80% and yield of substance B 72%.
Literature
- Werner Kullbach: Mengenberechnungen in der Chemie. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1980, ISBN 3-527-25869-8.
- Eberhard Aust, Burkhard Bittner: Stöchiometrie - Chemisches Rechnen, CICERO-Verlag, Pegnitz, 4. Auflage, 2011, ISBN 978-3-926292-47-6.
- Uwe Hillebrand: Stöchiometrie, Eine Einführung in die Grundlagen mit Beispielen und Übungsaufgaben, 2. Aufl., Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg 2009, ISBN 978-3-642-00459-9.
References
- ↑ Lazaridis et al.: "Semi-Batch Emulsion Copolymerization of Vinyl Acetate andButyl Acrylate Using Oligomeric Nonionic Surfactants", Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 2614-2622
- ↑ Wayne F. Reed, Alina M. Alb: "Monitoring Polymerization Reactions: From Fundamentals to Applications", Wiley, 2014
- ↑ Fogler, H.: "Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering", 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 1992
- ↑ Fogler, H.: "Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering", 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 1992