Demographics of the Democratic Republic of the Congo

This article is about the demographic features of the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
As many as 250 ethnic groups have been distinguished and named. The most numerous people are the Luba, Mongo, and Bakongo.
Although 700 local languages and dialects are spoken, the linguistic variety is bridged both by the use of French and the intermediary languages Kongo, Luba-Kasai, Swahili, and Lingala.
Population
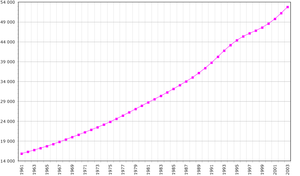
According to the 2010 revision of the World Population Prospects the total population was 65 966 000 in 2010, compared to only 12 184 000 in 1950. The proportion of children below the age of 15 in 2010 was 46.3%, 51.1% was between 15 and 65 years of age, while 2.7% was 65 years or older .[1]
| Total population (x 1000) | Population aged 0–14 (%) | Population aged 15–64 (%) | Population aged 65+ (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 12 184 | 43.7 | 52.5 | 3.8 |
| 1955 | 13 580 | 43.8 | 53.1 | 3.1 |
| 1960 | 15 368 | 43.8 | 53.3 | 2.9 |
| 1965 | 17 543 | 43.9 | 53.2 | 2.8 |
| 1970 | 20 267 | 44.4 | 52.8 | 2.8 |
| 1975 | 23 317 | 44.9 | 52.3 | 2.8 |
| 1980 | 27 019 | 45.4 | 51.8 | 2.8 |
| 1985 | 31 044 | 46.1 | 51.1 | 2.8 |
| 1990 | 36 406 | 47.0 | 50.2 | 2.8 |
| 1995 | 44 067 | 47.9 | 49.4 | 2.7 |
| 2000 | 49 626 | 48.0 | 49.4 | 2.7 |
| 2005 | 57 421 | 47.5 | 49.9 | 2.7 |
| 2010 | 65 966 | 46.3 | 51.1 | 2.7 |
Structure of the population (DHS 2013-2014) (Males 45 548, Females 49 134 = 94 682) :
| Age Group | Male (%) | Female (%) | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-4 | 20,6 | 19,4 | 19,9 |
| 5-9 | 17,5 | 16,7 | 17,1 |
| 10-14 | 15,1 | 13,9 | 14,5 |
| 15-19 | 9,3 | 8,7 | 9,0 |
| 20-24 | 6,8 | 7,9 | 7,3 |
| 25-29 | 6,0 | 7,5 | 6,8 |
| 30-34 | 4,8 | 5,6 | 5,2 |
| 35-39 | 4,2 | 4,7 | 4,4 |
| 40-44 | 4,0 | 3,3 | 3,6 |
| 45-49 | 3,1 | 2,6 | 2,8 |
| 50-54 | 2,4 | 3,5 | 2,9 |
| 55-59 | 1,9 | 2,2 | 2,1 |
| 60-64 | 2,0 | 1,5 | 1,8 |
| 65-69 | 1,1 | 1,2 | 1,1 |
| 70-74 | 0,6 | 0,8 | 0,7 |
| 75-79 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 |
| 80+ | 0,3 | 0,4 | 0,3 |
| Age group | Male (%) | Female (%) | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-14 | 53,2 | 50,0 | 51,5 |
| 15-64 | 44,4 | 47,2 | 46,0 |
| 65+ | 2,4 | 2,8 | 2,5 |
Vital statistics
Registration of vital events in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is incomplete. The Population Departement of the United Nations prepared the following estimates. [1]
| Period | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR* | CDR* | NC* | TFR* | IMR* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950-1955 | 608 000 | 329 000 | 279 000 | 47.2 | 25.5 | 21.7 | 5.98 | 167 |
| 1955-1960 | 683 000 | 341 000 | 342 000 | 47.2 | 23.6 | 23.7 | 5.98 | 158 |
| 1960-1965 | 780 000 | 369 000 | 411 000 | 47.4 | 22.4 | 25.0 | 6.04 | 151 |
| 1965-1970 | 898 000 | 402 000 | 496 000 | 47.5 | 21.3 | 26.3 | 6.15 | 143 |
| 1970-1975 | 1 037 000 | 433 000 | 604 000 | 47.6 | 19.9 | 27.7 | 6.29 | 134 |
| 1975-1980 | 1 208 000 | 488 000 | 720 000 | 48.0 | 19.4 | 28.6 | 6.46 | 129 |
| 1980-1985 | 1 425 000 | 550 000 | 874 000 | 49.1 | 19.0 | 30.1 | 6.72 | 125 |
| 1985-1990 | 1 689 000 | 632 000 | 1 057 000 | 50.1 | 18.7 | 31.4 | 6.98 | 121 |
| 1990-1995 | 2 035 000 | 743 000 | 1 292 000 | 50.6 | 18.5 | 32.1 | 7.14 | 119 |
| 1995-2000 | 2 335 000 | 923 000 | 1 412 000 | 49.8 | 19.7 | 30.1 | 7.04 | 128 |
| 2000-2005 | 2 580 000 | 973 000 | 1 607 000 | 48.2 | 18.2 | 30.0 | 6.70 | 120 |
| 2005-2010 | 2 772 000 | 1 058 000 | 1 714 000 | 44.9 | 17.2 | 27.8 | 6.07 | 116 |
| * CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births; TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman) | ||||||||
Fertility and Births
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[2]
| Year | CBR (Total) | TFR (Total) | CBR (Urban) | TFR (Urban) | CBR (Rural) | TFR (Rural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 44,1 | 6,3 (5,6) | 40,4 | 5,4 (4,8) | 46,8 | 7,0 (6,2) |
| 2013-14 | 44,1 | 6,6 (5,7) | 40,5 | 5,4 (4,6) | 45,9 | 7,3 (6,5) |
Ethnic groups
More than 250 ethnic groups have been identified and named of which the majority are Bantu. The four largest groups - Mongo, Luba, Kongo (all Bantu), and the Mangbetu-Azande make up about 45% of the population. The country has also 60,000 White Congolese most of Belgian ancestry who remained after independence.

Bantu peoples (80%):
- Luba (18%), Mongo (17%), Kongo (12%)
- Others: Ambala, Ambuun, Angba, Babindi, Baboma, Baholo, Balunda, Bangala, Bango, Batsamba, Bazombe, Bemba, Bembe, Bira, Bowa, Dikidiki, Dzing, Fuliru, Havu, Hema, Hima, Hunde, Hutu, Iboko, Kanioka, Kaonde, Kuba, Kumu, Kwango, Lengola, Lokele, Lupu, Lwalwa, Mbala, Mbole, Mbuza (Budja), Nande, Ngoli, Bangoli, Ngombe, Nkumu, Nyanga, Pende, Popoi, Poto, Sango, Shi, Songo, Sukus, Tabwa, Tchokwé, Téké, Tembo, Tetela, Topoke, Tutsi, Ungana, Vira, Wakuti, Yaka, Yakoma, Yanzi, Yeke, Yela etc.
More than 600,000 pygmies (around 1% of the total population) are believed to live in the DR Congo's huge forests, where they survive by hunting wild animals and gathering fruits.[3]
Languages
The four major languages in the DRC are French (official), Lingala (a lingua franca trade language), Kingwana (a dialect of Swahili), Kikongo, and Tshiluba. There are over 200 ethnic languages.
French is generally the medium of instruction in schools. English is taught as a compulsory foreign language in Secondary and High School around the country. It is a required subject in the Faculty of Economics at major universities around the country and there are numerous language schools in the country that teach it. In the town of Beni, for instance, there is a Bilingual University that offer courses in both French and English. President Kabila himself is fluent in both English and French, as was his father.
Religions
Roman Catholic 50%, Protestant 20%, Kimbanguist 10%, Islam 10%, Other (includes Syncretic Sects and Indigenous beliefs) 10% (CIA The World Factbook)[4]
Roman Catholic 43.9%, Protestant 24.8%, Other Christian 23.7%, Muslim 1.6%, Non-religious 0.6%, Hindu 0.1% other syncretic sects and indigenous beliefs 5.3% (Joshua project)[5]
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Population
- 77,433,744
- Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and gender than would otherwise be expected (July 2014 est.)
Median age
- Total: 17.4 years
- Male: 17.2 years
- Female: 17.6 years (2011 est.)
Population growth rate
- 2.614% (2011)
Net migration rate
-0.54 migrant(s)/1,000 population note: fighting between the Congolese Government and Uganda- and Rwanda-backed Congolese rebels spawned a regional war in DRC in August 1998, which left 2.33 million Congolese internally displaced and caused 412,000 Congolese refugees to flee to surrounding countries (2011 est.)
Given the situation in the country and the condition of state structures, it is extremely difficult to obtain reliable data however evidence suggests that DRC continues to be a destination country for immigrants in spite of recent declines. Immigration is seen to be very diverse in nature, with refugees and asylum-seekers - products of the numerous and violent conflicts in the Great Lakes Region - constituting an important subset of the population in the country.[6]
Additionally, the country’s large mine operations attract migrant workers from Africa and beyond and there is considerable migration for commercial activities from other African countries and the rest of the world, but these movements are not well studied. Transit migration towards South Africa and Europe also plays a role. Immigration in the DRC has decreased steadily over the past two decades, most likely as a result of the armed violence that the country has experienced.[6]
According to the International Organization for Migration, the number of immigrants in the DRC has declined from just over 1 million in 1960, to 754,000 in 1990, to 480,000 in 2005, to an estimated 445,000 in 2010. Valid figures are not available on migrant workers in particular, partly due to the predominance of the informal economy in the DRC. Data are also lacking on irregular immigrants, however given neighbouring country ethnic links to nationals of the DRC, irregular migration is assumed to be a significant phenomenon in the country.[6]
Figures on the number of Congolese nationals abroad vary greatly depending on the source, from 3 to 6 million. This discrepancy is due to a lack of official, reliable data. Emigrants from the DRC are above all long-term emigrants, the majority of which live within Africa and to a lesser extent in Europe; 79.7% and 15.3% respectively, according to estimates on 2000 data. Most Congolese emigrants however, remain in Africa, with new destination countries including South Africa and various points en route to Europe.[6]
In addition to being a host country, the DRC has also produced a considerable number of refugees and asylum-seekers located in the region and beyond. These numbers peaked in 2004 when, according to UNHCR, there were more than 460,000 refugees from the DRC; in 2008, Congolese refugees numbered 367,995 in total, 68% of which were living in other African countries.[6]
Gender ratio
- At birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
- Under 15 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
- 15–64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.69 male(s)/female
- Total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 56.93 years
- male: 55.39 years
- female: 58.51 years (2015 est.)[7]
HIV/AIDS
- Adult prevalence rate: 4.2% (2003 est.)
- People living with HIV/AIDS: 1.3 million (2003 est.)
- Deaths: 100,000 (2003 est.)
Major infectious diseases
- Degree of risk: very high
- Food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
- Vectorborne diseases: malaria, plague, and African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) are high risks in some locations
- Water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2005)
Nationality
- Noun: Congolese (singular and plural)
- Adjective: Congolese or Congo
Literacy
- Definition: age 15 and over can read and write French, Lingala, Kingwana, or Tshiluba
- Total population: 65.5%
- Male: 76.2%
- Female: 55.1% (2003 est.)
Congolese diaspora
The table below shows DRC born people who have emigrated abroad (although it excludes their descendants).[8]
| Rank | Country | Region | DRC born population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |
Europe | 19,080 |
| 2 | |
North America | 14,125 |
| 3 | |
Europe | 9,911 |
| 4 | |
Europe | 8,569 |
| 5 | |
North America | 3,455 |
| 6 | |
Europe | 2,570 |
| 7 | |
Europe | 1,759 |
| 8 | |
Europe | 1,453 |
| 9 | |
Europe | 1,314 |
| 10 | |
Europe | 1,302 |
These are only estimates and do not account for Congolese migrants residing illegally in these and other countries. Among African countries, Congo's diaspora is second only to Nigeria in size.
See also
See also
References
- 1 2 Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision
- ↑ http://microdata.worldbank.org/index.php/catalog/1354
- ↑ DR Congo pygmies 'exterminated'
- ↑ "Africa :: CONGO, DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE". CIA The World Factbook.
- ↑ Joshua Project - Congo, Democratic Republic of - Religions
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Migration en République Démocratique du Congo: Profil national 2009". International Organization for Migration. 2009. Retrieved 2010-08-17.
- ↑ CIA "The World Factbook": DR Congo 2015. Retrieved January 13, 2016.
- ↑ "Country-of-birth database". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Retrieved 2008-09-21.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "2007 edition".
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "2007 edition".
External links
- "Mortality in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: An Ongoing Crisis" (PDF). (1.07 MB), International Rescue Committee, January 2008 (estimates 5.4 million excess deaths above sub-Saharan average from 1998 to 2007)